1.. Trie通常被称为"字典树"或"前缀树"
-
Trie的形象化描述如下图:
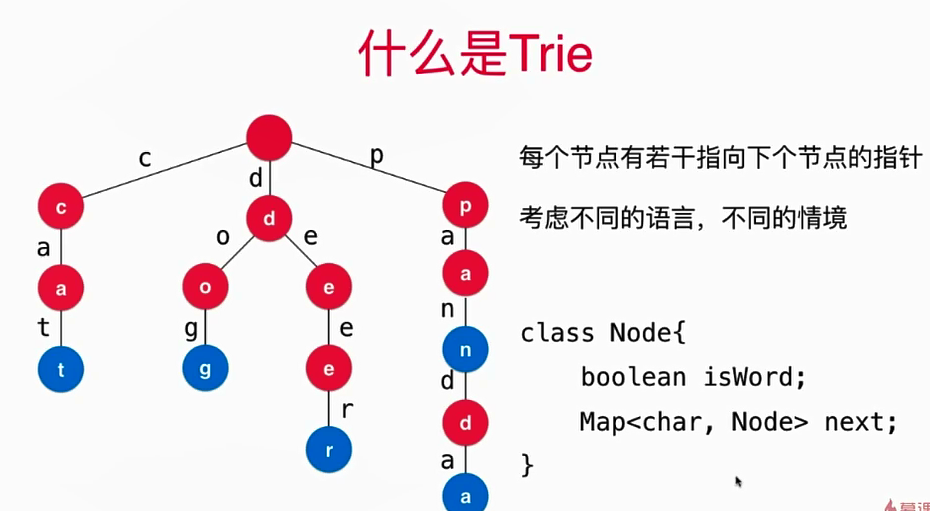
- Trie的优势和适用场景
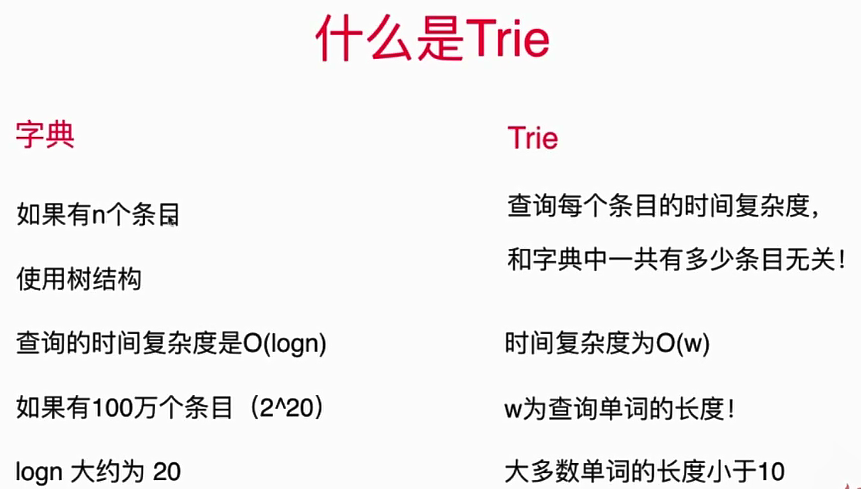
2.. 实现Trie
- 实现Trie的业务无逻辑如下:
-
import java.util.TreeMap; public class Trie { private class Node { public boolean isWord; public TreeMap<Character, Node> next; // 构造函数 public Node(boolean isWord) { this.isWord = isWord; next = new TreeMap<>(); } // 无参数构造函数 public Node() { this(false); } } private Node root; private int size; // 构造函数 public Trie() { root = new Node(); size = 0; } // 实现getSize方法,获得Trie中存储的单词数量 public int getSize() { return size; } // 实现add方法,向Trie中添加新的单词word public void add(String word) { Node cur = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char c = word.charAt(i); if (cur.next.get(c) == null) { cur.next.put(c, new Node()); } cur = cur.next.get(c); } if (!cur.isWord) { cur.isWord = true; size++; } } // 实现contains方法,查询Trie中是否包含单词word public boolean contains(String word) { Node cur = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char c = word.charAt(i); if (cur.next.get(c) == null) { return false; } cur = cur.next.get(c); } return cur.isWord; // 好聪明 } // 实现isPrefix方法,查询Trie中时候保存了以prefix为前缀的单词 public boolean isPrefix(String prefix) { Node cur = root; for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) { char c = prefix.charAt(i); if (cur.next.get(c) == null) { return false; } cur = cur.next.get(c); } return true; } }
3.. Trie和简单的模式匹配
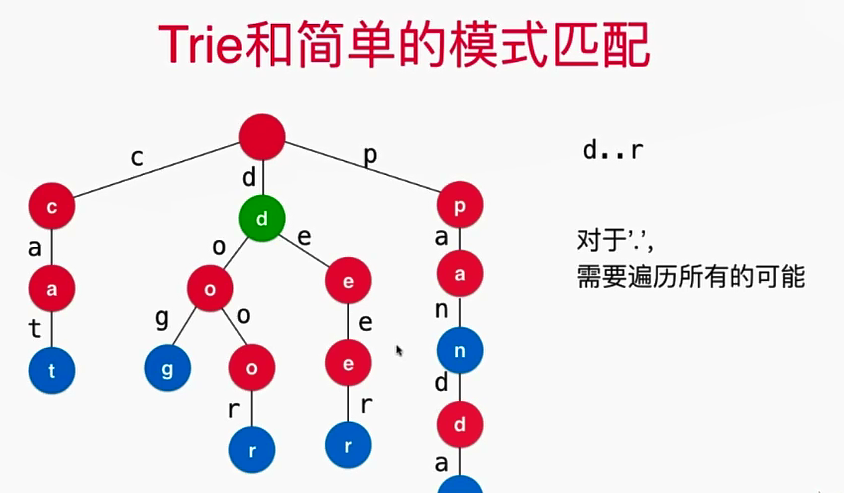
- 实现的业务逻辑如下:
-
import java.util.TreeMap; class WordDictionary { private class Node { public boolean isWord; public TreeMap<Character, Node> next; public Node(boolean isWord) { this.isWord = isWord; next = new TreeMap<>(); } public Node() { this(false); } } /** * Initialize your data structure here. */ private Node root; public WordDictionary() { root = new Node(); } /** * Adds a word into the data structure. */ public void addWord(String word) { Node cur = root; for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) { char c = word.charAt(i); if (cur.next.get(c) == null) { cur.next.put(c, new Node()); } cur = cur.next.get(c); } cur.isWord = true; } /** * Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter. */ public boolean search(String word) { return match(root, word, 0); } private boolean match(Node node, String word, int index) { if (index == word.length()) { return node.isWord; } char c = word.charAt(index); if (c != '.') { if (node.next.get(c) == null) { return false; } return match(node.next.get(c), word, index + 1); } else { for (char nextChar : node.next.keySet()) { if (match(node.next.get(nextChar), word, index + 1)) { return true; } } return false; } } }