一、概述
TreeMap是基于红黑树实现的。由于TreeMap实现了java.util.sortMap接口,集合中的映射关系是具有一定顺序的,该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序或者根据创建映射时提供的Comparator进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。另外TreeMap中不允许键对象是null。
1、什么是红黑树?
红黑树是一种特殊的二叉排序树,主要有以下几条基本性质:
- 每个节点都只能是红色或者黑色
- 根节点是黑色
- 每个叶子节点是黑色的
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点都是黑色的
- 从任意一个节点到每个叶子节点的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点
红黑树的具体原理分析和算法设计可参见博文:红黑树的原理分析和算法设计。
2、key的两种排序方式
自然排序:TreeMap的所有key必须实现Comparable接口,并且所有key应该是同一个类的对象,否则将会抛ClassCastException异常
指定排序:这种排序需要在构造TreeMap时,传入一个Comparator对象,该对象负责对TreeMap中的key进行排序
3、TreeMap类的继承关系
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
其中,NavigableMap接口是扩展的SortMap,具有了针对给定搜索目标返回最接近匹配项的导航方法。其方法 lowerEntry、floorEntry、ceilingEntry 和 higherEntry 分别返回与小于、小于等于、大于等于、大于给定键的键关联的 Map.Entry 对象,如果不存在这样的键,则返回 null。类似地,方法 lowerKey、floorKey、ceilingKey 和 higherKey 只返回关联的键。所有这些方法是为查找条目而不是遍历条目而设计的。
二、TreeMap源码分析
1、存储结构
TreeMap是基于红黑树实现的,树的节点定义如下:
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { //键 K key; //值 V value; //左孩子 Entry<K,V> left; //右孩子 Entry<K,V> right; //父节点 Entry<K,V> parent; //节点颜色 boolean color = BLACK; //构造函数 Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) { this.key = key; this.value = value; this.parent = parent; } ...... }
2、构造函数
TreeMap有四种构造函数,分别对应不同的参数。
//1.使用键的自然顺序构造一个新的、空的树映射 public TreeMap() { comparator = null; } //2.构造一个新的、空的树映射,该映射根据给定比较器进行排序 public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; } /3.构造一个与给定映射具有相同映射关系的新的树映射,该映射根据其键的自然顺序 进行排序 public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = null; putAll(m); } //4.构造一个与指定有序映射具有相同映射关系和相同排序顺序的新的树映射 public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) { comparator = m.comparator(); try { buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null); } catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) { } catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) { } }
3、TreeMap常用方法
V put(K key,V value):将键值对(key,value)添加到TreeMap中
public V put(K key, V value) { Entry<K,V> t = root; //若根节点为空,则以(key,value)为参数新建节点 if (t == null) { compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); size = 1; modCount++; return null; } int cmp; Entry<K,V> parent; // split comparator and comparable paths Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; //指定的排序算法 if (cpr != null) { do { parent = t; cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); if (cmp < 0) //表示新增节点的key小于当前及节点的key,则以当前节点的左子节点作为新的当前节点 t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) //表示新增节点的key大于当前及节点的key,则以当前节点的右子节点作为新的当前节点 t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); //相等则覆盖旧值 } while (t != null); } //如果cpr为空,则采用默认的排序算法进行创建TreeMap集合 else { if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; do { parent = t; cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); if (cmp < 0) t = t.left; else if (cmp > 0) t = t.right; else return t.setValue(value); } while (t != null); } //将新增节点当做parent的子节点 Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); if (cmp < 0) parent.left = e; else parent.right = e; //插入新的节点后,调用fixAfterInsertion调整红黑树 fixAfterInsertion(e); size++; modCount++; return null; }
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():返回此映射中包含的映射关系的Set视图
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() { EntrySet es = entrySet; return (es != null) ? es : (entrySet = new EntrySet()); }
boolean remove(Object o): 如果此 TreeMap 中存在该键的映射关系,则将其删除
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry<K,V> entry = (Map.Entry<K,V>) o; K key = entry.getKey(); if (!inRange(key)) return false; TreeMap.Entry<K,V> node = m.getEntry(key); if (node!=null && valEquals(node.getValue(), entry.getValue())) { m.deleteEntry(node); return true; } return false; } }
三、TreeMap应用示例代码
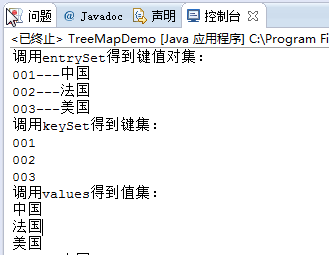
public class TreeMapDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //使用键的自然顺序构造一个新的、空的树映射 TreeMap<String,String> tm=new TreeMap<>(); tm.put("001", "中国"); tm.put("003", "美国"); tm.put("002", "法国"); System.out.println("调用entrySet得到键值对集:"); Set<Entry<String, String>> result=tm.entrySet(); for(Entry<String, String> result2:result) { System.out.println(result2.getKey()+"---"+result2.getValue()); } System.out.println("调用keySet得到键集:"); Set<String> result3=tm.keySet(); for(String str:result3) { System.out.println(str); } System.out.println("调用values得到值集:"); Collection result4=tm.values(); for(Object str:result4) System.out.println(str); //新建一个带比较器的TreeMap TreeMap<String,String> tm2=new TreeMap<>(new ComparatorDemo()); tm2.put("001", "中国"); tm2.put("003", "美国"); tm2.put("002", "法国"); Set<Entry<String, String>> result5=tm2.entrySet(); for(Entry<String, String> result2:result5) { System.out.println(result2.getKey()+"---"+result2.getValue()); } } }
首先按照键的自然顺序构建TreeMap,加入元素并遍历:
然后新建一个比较器类,实现Comparator接口
public class ComparatorDemo implements Comparator<String> { public int compare(String o1, String o2) { return 1; } }
在带比较器的tm2中,按照与tm1相同的顺序添加元素,此时再遍历tm2,结果如下:

这里的顺序是按照比较器的compare方法得来的。由于compare方法总是返回1,即大小均相同,所以tm2中key顺序为初始添加顺序。