参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/babylorin/article/details/67637454
https://blog.csdn.net/shijinupc/article/details/7827507
https://blog.csdn.net/woxueliuyun/article/details/3902530
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43849277/article/details/107890019
关于Java中的Arrays.copyOfRange()方法
要使用这个方法,首先要import java.util.*;
Arrays.copyOfRange(T[ ] original,int from,int to)
将一个原始的数组original,从下标from开始复制,复制到上标to,生成一个新的数组。
注意这里包括下标from,不包括上标to。
这个方法在一些处理数组的编程题里很好用,效率和clone基本一致,都是native method,比利用循环复制数组效率要高得多。
int a[] = new int[] { 18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9 };
int[] b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, 3);
Arrays.copyof(···)与System.arraycopy(···)区别
首先观察先System.arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)的声明:
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
src - 源数组。
srcPos - 源数组中的起始位置。
dest - 目标数组。
destPos - 目标数据中的起始位置。
length - 要复制的数组元素的数量。
该方法是用了native关键字,调用的为C++编写的底层函数,可见其为JDK中的底层函数。
再来看看Arrays.copyOf();该方法对于不同的数据类型都有相应的方法重载。
//复杂数据类型 public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; } public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); }
由U类型复制为T类型?
original - 要复制的数组
newLength - 要返回的副本的长度
newType - 要返回的副本的类型
//基本数据类型(其他类似byte,short···) public static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) { int[] copy = new int[newLength]; System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; }
观察其源代码发现copyOf(),在其内部创建了一个新的数组,然后调用arrayCopy()向其复制内容,返回出去。
总结:
1.copyOf()的实现是用的是arrayCopy();
2.arrayCopy()需要目标数组,对两个数组的内容进行可能不完全的合并操作。
3.copyOf()在内部新建一个数组,调用arrayCopy()将original内容复制到copy中去,并且长度为newLength。返回copy;
Arrays.copyOf()&Arrays.copyOfRange()
在JDK1.5的类System类中有方法
public static void arraycopy(Object src,
int srcPos,
Object dest,
int destPos,
int length)
标题上的这两上方法是JDK1.6新增的方法,这两个方法并没有用什么其它更奇妙的技巧,还是用的System.arraycopy(),只是在一定程度上减轻了程序员的工作,处理了一些常可能发生的错误。
如:
public static int[] copyOf(int[] original, int newLength) {
int[] copy = new int[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
public static byte[] copyOfRange(byte[] original, int from, int to) {
int newLength = to - from;
if (newLength < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(from + " > " + to);
byte[] copy = new byte[newLength];
System.arraycopy(original, from, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length - from, newLength));
return copy;
}
Arrays.copyOf()、Arrays.copyOfRange()与System.arraycopy()用法
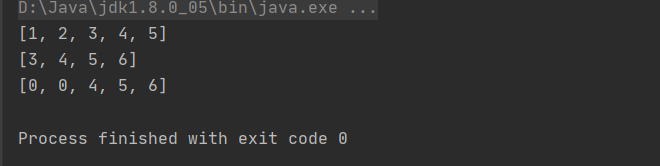
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8}; //数组b复制a的前五个元素, int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a,5); //数组c复制a中以下标2开始到6结束的元素,不包含下标为6的元素, int[] c = Arrays.copyOfRange(a,2,6); //数组d从下标2开始,复制a中以下标3开始的元素,复制长度为3 int[] d = new int[5]; System.arraycopy(a,3,d,2,3); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(c)); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(d)); } }
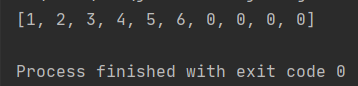
值得注意的是,int[ ] b = Arrays.copyOf(a,5);第二个参数5表示新数组b的长度,当该参数大于a的长度时,多余部分补0。
此外该方法还可以对数组a自身长度扩充,常用于StringBuffer、集合中容量扩充
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,5,6}; a = Arrays.copyOf(a,10);//会改变a数组的引用,相当于重新指向另外一个返回的数组 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));