参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/dennyzhangdd/p/9602673.html
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44366439/article/details/89030080
spring事务详解(三)源码详解
一、引子
在Spring中,事务有两种实现方式:
- 编程式事务管理: 编程式事务管理使用TransactionTemplate可实现更细粒度的事务控制。
- 申明式事务管理: 基于Spring AOP实现。其本质是对方法前后进行拦截,然后在目标方法开始之前创建或者加入一个事务,在执行完目标方法之后根据执行情况提交或者回滚事务。
申明式事务管理不需要入侵代码,通过@Transactional就可以进行事务操作,更快捷而且简单(尤其是配合spring boot自动配置,可以说是精简至极!),且大部分业务都可以满足,推荐使用。
其实不管是编程式事务还是申明式事务,最终调用的底层核心代码是一致的。本章分别从编程式、申明式入手,再进入核心源码贯穿式讲解。
二、事务源码
2.1 编程式事务TransactionTemplate
编程式事务,Spring已经给我们提供好了模板类TransactionTemplate,可以很方便的使用,如下图:

TransactionTemplate全路径名是:org.springframework.transaction.support.TransactionTemplate。看包名也知道了这是spring对事务的模板类。(spring动不动就是各种Template...),看下类图先:

一看,哟西,实现了TransactionOperations、InitializingBean这2个接口(熟悉spring源码的知道这个InitializingBean又是老套路),我们来看下接口源码如下:
1 public interface TransactionOperations {
2
3 /**
4 * Execute the action specified by the given callback object within a transaction.
5 * <p>Allows for returning a result object created within the transaction, that is,
6 * a domain object or a collection of domain objects. A RuntimeException thrown
7 * by the callback is treated as a fatal exception that enforces a rollback.
8 * Such an exception gets propagated to the caller of the template.
9 * @param action the callback object that specifies the transactional action
10 * @return a result object returned by the callback, or {@code null} if none
11 * @throws TransactionException in case of initialization, rollback, or system errors
12 * @throws RuntimeException if thrown by the TransactionCallback
13 */
14 <T> T execute(TransactionCallback<T> action) throws TransactionException;
15
16 }
17
18 public interface InitializingBean {
19
20 /**
21 * Invoked by a BeanFactory after it has set all bean properties supplied
22 * (and satisfied BeanFactoryAware and ApplicationContextAware).
23 * <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform initialization only
24 * possible when all bean properties have been set and to throw an
25 * exception in the event of misconfiguration.
26 * @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such
27 * as failure to set an essential property) or if initialization fails.
28 */
29 void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
30
31 }
如上图,TransactionOperations这个接口用来执行事务的回调方法,InitializingBean这个是典型的spring bean初始化流程中(飞机票:Spring IOC(四)总结升华篇)的预留接口,专用用来在bean属性加载完毕时执行的方法。
回到正题,TransactionTemplate的2个接口的impl方法做了什么?
1 @Override
2 public void afterPropertiesSet() {
3 if (this.transactionManager == null) {
4 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'transactionManager' is required");
5 }
6 }
7
8
9 @Override
10 public <T> T execute(TransactionCallback<T> action) throws TransactionException {
// 内部封装好的事务管理器
11 if (this.transactionManager instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) {
12 return ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) this.transactionManager).execute(this, action);
13 }// 需要手动获取事务,执行方法,提交事务的管理器
14 else {// 1.获取事务状态
15 TransactionStatus status = this.transactionManager.getTransaction(this);
16 T result;
17 try {// 2.执行业务逻辑
18 result = action.doInTransaction(status);
19 }
20 catch (RuntimeException ex) {
21 // 应用运行时异常 -> 回滚
22 rollbackOnException(status, ex);
23 throw ex;
24 }
25 catch (Error err) {
26 // Error异常 -> 回滚
27 rollbackOnException(status, err);
28 throw err;
29 }
30 catch (Throwable ex) {
31 // 未知异常 -> 回滚
32 rollbackOnException(status, ex);
33 throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex, "TransactionCallback threw undeclared checked exception");
34 }// 3.事务提交
35 this.transactionManager.commit(status);
36 return result;
37 }
38 }
如上图所示,实际上afterPropertiesSet只是校验了事务管理器不为空,execute()才是核心方法,execute主要步骤:
1.getTransaction()获取事务,源码见3.3.1
2.doInTransaction()执行业务逻辑,这里就是用户自定义的业务代码。如果是没有返回值的,就是doInTransactionWithoutResult()。
3.commit()事务提交:调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的commit,rollbackOnException()异常回滚:调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的rollback(),事务提交回滚,源码见3.3.3
2.2 申明式事务@Transactional
1.AOP相关概念
申明式事务使用的是spring AOP,即面向切面编程。(什么❓你不知道什么是AOP...一句话概括就是:把业务代码中重复代码做成一个切面,提取出来,并定义哪些方法需要执行这个切面。其它的自行百度吧...)AOP核心概念如下:
- 通知(Advice):定义了切面(各处业务代码中都需要的逻辑提炼成的一个切面)做什么what+when何时使用。例如:前置通知Before、后置通知After、返回通知After-returning、异常通知After-throwing、环绕通知Around.
- 连接点(Joint point):程序执行过程中能够插入切面的点,一般有多个。比如调用方式时、抛出异常时。
- 切点(Pointcut):切点定义了连接点,切点包含多个连接点,即where哪里使用通知.通常指定类+方法 或者 正则表达式来匹配 类和方法名称。
- 切面(Aspect):切面=通知+切点,即when+where+what何时何地做什么。
- 引入(Introduction):允许我们向现有的类添加新方法或属性。
- 织入(Weaving):织入是把切面应用到目标对象并创建新的代理对象的过程。
2.申明式事务
申明式事务整体调用过程,可以抽出2条线:
1.使用代理模式,生成代理增强类。
2.根据代理事务管理配置类,配置事务的织入,在业务方法前后进行环绕增强,增加一些事务的相关操作。例如获取事务属性、提交事务、回滚事务。
过程如下图:

申明式事务使用@Transactional这种注解的方式,那么我们就从springboot 容器启动时的自动配置载入(spring boot容器启动详解)开始看。在/META-INF/spring.factories中配置文件中查找,如下图:

载入2个关于事务的自动配置类:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration,
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration,
jta咱们就不看了,看一下TransactionAutoConfiguration这个自动配置类:
1 @Configuration
2 @ConditionalOnClass(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
3 @AutoConfigureAfter({ JtaAutoConfiguration.class, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class,
4 DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class,
5 Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration.class })
6 @EnableConfigurationProperties(TransactionProperties.class)
7 public class TransactionAutoConfiguration {
8
9 @Bean
10 @ConditionalOnMissingBean
11 public TransactionManagerCustomizers platformTransactionManagerCustomizers(
12 ObjectProvider<List<PlatformTransactionManagerCustomizer<?>>> customizers) {
13 return new TransactionManagerCustomizers(customizers.getIfAvailable());
14 }
15
16 @Configuration
17 @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
18 public static class TransactionTemplateConfiguration {
19
20 private final PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
21
22 public TransactionTemplateConfiguration(
23 PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager) {
24 this.transactionManager = transactionManager;
25 }
26
27 @Bean
28 @ConditionalOnMissingBean
29 public TransactionTemplate transactionTemplate() {
30 return new TransactionTemplate(this.transactionManager);
31 }
32 }
33
34 @Configuration
35 @ConditionalOnBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
36 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)
37 public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {
38
39 @Configuration
40 @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false)
41 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false", matchIfMissing = false)
42 public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
43
44 }
45
46 @Configuration
47 @EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
48 @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
49 public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
50
51 }
52
53 }
54
55 }
TransactionAutoConfiguration这个类主要看:
1.2个类注解
@ConditionalOnClass(PlatformTransactionManager.class)即类路径下包含PlatformTransactionManager这个类时这个自动配置生效,这个类是spring事务的核心包,肯定引入了。
@AutoConfigureAfter({ JtaAutoConfiguration.class, HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration.class, Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration.class }),这个配置在括号中的4个配置类后才生效。
2. 2个内部类
TransactionTemplateConfiguration事务模板配置类:
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(PlatformTransactionManager.class)当能够唯一确定一个PlatformTransactionManager bean时才生效。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean如果没有定义TransactionTemplate bean生成一个。
EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration开启事务管理器配置类:
@ConditionalOnBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class)当存在PlatformTransactionManager bean时生效。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)当没有自定义抽象事务管理器配置类时才生效。(即用户自定义抽象事务管理器配置类会优先,如果没有,就用这个默认事务管理器配置类)
EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration支持2种代理方式:
- 1.JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration:
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false),即proxyTargetClass = false表示是JDK动态代理支持的是:面向接口代理。
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false", matchIfMissing = false),即spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false时生效,且没有这个配置不生效。
- 2.CglibAutoProxyConfiguration:
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true),即proxyTargetClass = true标识Cglib代理支持的是子类继承代理。
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true),即spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true时生效,且没有这个配置默认生效。
注意了,默认没有配置,走的Cglib代理。说明@Transactional注解支持直接加在类上。
好吧,看了这么多配置类,终于到了@EnableTransactionManagement这个注解了。
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE)
2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
3 @Documented
4 @Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
5 public @interface EnableTransactionManagement {
6
7 //proxyTargetClass = false表示是JDK动态代理支持接口代理。true表示是Cglib代理支持子类继承代理。
8 boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
9
10 //事务通知模式(切面织入方式),默认代理模式(同一个类中方法互相调用拦截器不会生效),可以选择增强型AspectJ
11 AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
12
13 //连接点上有多个通知时,排序,默认最低。值越大优先级越低。
14 int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
15
16 }
重点看类注解@Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class)
TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector类图如下:
如上图所示,TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector继承自AdviceModeImportSelector实现了ImportSelector接口。
1 public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> {
2
3 /**
4 * {@inheritDoc}
5 * @return {@link ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration} or
6 * {@code AspectJTransactionManagementConfiguration} for {@code PROXY} and
7 * {@code ASPECTJ} values of {@link EnableTransactionManagement#mode()}, respectively
8 */
9 @Override
10 protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
11 switch (adviceMode) {
12 case PROXY:
13 return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(), ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()};
14 case ASPECTJ:
15 return new String[] {TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME};
16 default:
17 return null;
18 }
19 }
20
21 }
如上图,最终会执行selectImports方法导入需要加载的类,我们只看proxy模式下,载入了AutoProxyRegistrar、ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration2个类。
- AutoProxyRegistrar:
给容器中注册一个 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 组件;利用后置处理器机制在对象创建以后,包装对象,返回一个代理对象(增强器),代理对象执行方法利用拦截器链进行调用; - ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration:就是一个配置类,定义了事务增强器。
AutoProxyRegistrar
先看AutoProxyRegistrar实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,复写registerBeanDefinitions方法,源码如下:
1 public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
2 boolean candidateFound = false;
3 Set<String> annoTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes();
4 for (String annoType : annoTypes) {
5 AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annoType);
6 if (candidate == null) {
7 continue;
8 }
9 Object mode = candidate.get("mode");
10 Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass");
11 if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() &&
12 Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) {
13 candidateFound = true;
14 if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) {//代理模式
15 AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
16 if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) {//如果是CGLOB子类代理模式
17 AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
18 return;
19 }
20 }
21 }
22 }
23 if (!candidateFound) {
24 String name = getClass().getSimpleName();
25 logger.warn(String.format("%s was imported but no annotations were found " +
26 "having both 'mode' and 'proxyTargetClass' attributes of type " +
27 "AdviceMode and boolean respectively. This means that auto proxy " +
28 "creator registration and configuration may not have occurred as " +
29 "intended, and components may not be proxied as expected. Check to " +
30 "ensure that %s has been @Import'ed on the same class where these " +
31 "annotations are declared; otherwise remove the import of %s " +
32 "altogether.", name, name, name));
33 }
34 }
代理模式:AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
最终调用的是:registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);基础构建增强自动代理构造器
1 private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
2 Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//如果当前注册器包含internalAutoProxyCreator
3 if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {//org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator内部自动代理构造器
4 BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
5 if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {//如果当前类不是internalAutoProxyCreator
6 int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
7 int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
8 if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {//如果下标大于已存在的内部自动代理构造器,index越小,优先级越高,InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator index=0,requiredPriority最小,不进入
9 apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
10 }
11 }
12 return null;//直接返回
13 }//如果当前注册器不包含internalAutoProxyCreator,则把当前类作为根定义
14 RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
15 beanDefinition.setSource(source);
16 beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);//优先级最高
17 beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
18 registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
19 return beanDefinition;
20 }
如上图,APC_PRIORITY_LIST列表如下图:
1 /**
2 * Stores the auto proxy creator classes in escalation order.
3 */
4 private static final List<Class<?>> APC_PRIORITY_LIST = new ArrayList<Class<?>>();
5
6 /**
7 * 优先级上升list
8 */
9 static {
10 APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class);
11 APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class);
12 APC_PRIORITY_LIST.add(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
13 }
如上图,由于InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator这个类在list中第一个index=0,requiredPriority最小,不进入,所以没有重置beanClassName,啥都没做,返回null.
那么增强代理类何时生成呢?
InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类图如下:

如上图所示,看2个核心方法:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInstantiation实例化前+BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessAfterInitialization初始化后。关于spring bean生命周期飞机票:Spring IOC(四)总结升华篇
1 @Override
2 public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
3 Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
4
5 if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
6 if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {//如果已经存在直接返回
7 return null;
8 }//是否基础构件(基础构建不需要代理):Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean这四类都算基础构建
9 if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
10 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);//添加进advisedBeans ConcurrentHashMap<k=Object,v=Boolean>标记是否需要增强实现,这里基础构建bean不需要代理,都置为false,供后面postProcessAfterInitialization实例化后使用。
11 return null;
12 }
13 }
14
15 // TargetSource是spring aop预留给我们用户自定义实例化的接口,如果存在TargetSource就不会默认实例化,而是按照用户自定义的方式实例化,咱们没有定义,不进入
18 if (beanName != null) {
19 TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
20 if (targetSource != null) {
21 this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
22 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
23 Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
24 this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
25 return proxy;
26 }
27 }
28
29 return null;
30 }
通过追踪,由于InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator是基础构建类,
advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE)
添加进advisedBeans ConcurrentHashMap<k=Object,v=Boolean>标记是否需要增强实现,这里基础构建bean不需要代理,都置为false,供后面postProcessAfterInitialization实例化后使用。
我们再看postProcessAfterInitialization源码如下:
1 @Override
2 public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
3 if (bean != null) {
4 Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
5 if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
6 return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
7 }
8 }
9 return bean;
10 }
11
12 protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 如果是用户自定义获取实例,不需要增强处理,直接返回
13 if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
14 return bean;
15 }// 查询map缓存,标记过false,不需要增强直接返回
16 if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
17 return bean;
18 }// 判断一遍springAOP基础构建类,标记过false,不需要增强直接返回
19 if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
20 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
21 return bean;
22 }
23
24 // 获取增强List<Advisor> advisors
25 Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 如果存在增强
26 if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
27 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);// 标记增强为TRUE,表示需要增强实现
// 生成增强代理类
28 Object proxy = createProxy(
29 bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
30 this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
31 return proxy;
32 }
33 // 如果不存在增强,标记false,作为缓存,再次进入提高效率,第16行利用缓存先校验
34 this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
35 return bean;
36 }
下面看核心方法createProxy如下:
1 protected Object createProxy(
2 Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
3 // 如果是ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口(咱们DefaultListableBeanFactory就是该接口的实现类)则,暴露目标类
4 if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
//给beanFactory->beanDefinition定义一个属性:k=AutoProxyUtils.originalTargetClass,v=需要被代理的bean class
5 AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
6 }
7
8 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
9 proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
10 //如果不是代理目标类
11 if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {//如果beanFactory定义了代理目标类(CGLIB)
12 if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
13 proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);//代理工厂设置代理目标类
14 }
15 else {//否则设置代理接口(JDK)
16 evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
17 }
18 }
19 //把拦截器包装成增强(通知)
20 Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
21 proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);//设置进代理工厂
22 proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
23 customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);//空方法,留给子类拓展用,典型的spring的风格,喜欢处处留后路
24 //用于控制代理工厂是否还允许再次添加通知,默认为false(表示不允许)
25 proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
26 if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {//默认false,上面已经前置过滤了匹配的增强Advisor
27 proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
28 }
29 //代理工厂获取代理对象的核心方法
30 return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
31 }
最终我们生成的是CGLIB代理类.到此为止我们分析完了代理类的构造过程。
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration
下面来看ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration:
1 @Configuration
2 public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration {
3
4 @Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
5 @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)//定义事务增强器
6 public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() {
7 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor j = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor();
8 advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
9 advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor());
10 advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
11 return advisor;
12 }
13
14 @Bean
15 @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)//定义基于注解的事务属性资源
16 public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() {
17 return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource();
18 }
19
20 @Bean
21 @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)//定义事务拦截器
22 public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() {
23 TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor();
24 interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource());
25 if (this.txManager != null) {
26 interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager);
27 }
28 return interceptor;
29 }
30
31 }
核心方法:transactionAdvisor()事务织入
定义了一个advisor,设置事务属性、设置事务拦截器TransactionInterceptor、设置顺序。核心就是事务拦截器TransactionInterceptor。
TransactionInterceptor使用通用的spring事务基础架构实现“声明式事务”,继承自TransactionAspectSupport类(该类包含与Spring的底层事务API的集成),实现了MethodInterceptor接口。spring类图如下:

事务拦截器的拦截功能就是依靠实现了MethodInterceptor接口,熟悉spring的同学肯定很熟悉MethodInterceptor了,这个是spring的方法拦截器,主要看invoke方法:
1 @Override
2 public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
3 // Work out the target class: may be {@code null}.
4 // The TransactionAttributeSource should be passed the target class
5 // as well as the method, which may be from an interface.
6 Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null);
7
8 // 调用TransactionAspectSupport的 invokeWithinTransaction方法
9 return invokeWithinTransaction(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass, new InvocationCallback() {
10 @Override
11 public Object proceedWithInvocation() throws Throwable {
12 return invocation.proceed();
13 }
14 });
15 }
如上图TransactionInterceptor复写MethodInterceptor接口的invoke方法,并在invoke方法中调用了父类TransactionAspectSupport的invokeWithinTransaction()方法,源码如下:
1 protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, Class<?> targetClass, final InvocationCallback invocation)
2 throws Throwable {
3
4 // 如果transaction attribute为空,该方法就是非事务(非编程式事务)
5 final TransactionAttribute txAttr = getTransactionAttributeSource().getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
6 final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
7 final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
8 // 标准声明式事务:如果事务属性为空 或者 非回调偏向的事务管理器
9 if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
10 // Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
11 TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
12 Object retVal = null;
13 try {
14 // 这里就是一个环绕增强,在这个proceed前后可以自己定义增强实现
15 // 方法执行
16 retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
17 }
18 catch (Throwable ex) {
19 // 根据事务定义的,该异常需要回滚就回滚,否则提交事务
20 completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
21 throw ex;
22 }
23 finally {//清空当前事务信息,重置为老的
24 cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
25 }//返回结果之前提交事务
26 commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
27 return retVal;
28 }
29 // 编程式事务:(回调偏向)
30 else {
31 final ThrowableHolder throwableHolder = new ThrowableHolder();
32
33 // It's a CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager: pass a TransactionCallback in.
34 try {
35 Object result = ((CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager) tm).execute(txAttr,
36 new TransactionCallback<Object>() {
37 @Override
38 public Object doInTransaction(TransactionStatus status) {
39 TransactionInfo txInfo = prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
40 try {
41 return invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
42 }
43 catch (Throwable ex) {// 如果该异常需要回滚
44 if (txAttr.rollbackOn(ex)) {
45 // 如果是运行时异常返回
46 if (ex instanceof RuntimeException) {
47 throw (RuntimeException) ex;
48 }// 如果是其它异常都抛ThrowableHolderException
49 else {
50 throw new ThrowableHolderException(ex);
51 }
52 }// 如果不需要回滚
53 else {
54 // 定义异常,最终就直接提交事务了
55 throwableHolder.throwable = ex;
56 return null;
57 }
58 }
59 finally {//清空当前事务信息,重置为老的
60 cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
61 }
62 }
63 });
64
65 // 上抛异常
66 if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
67 throw throwableHolder.throwable;
68 }
69 return result;
70 }
71 catch (ThrowableHolderException ex) {
72 throw ex.getCause();
73 }
74 catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
75 if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
76 logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
77 ex2.initApplicationException(throwableHolder.throwable);
78 }
79 throw ex2;
80 }
81 catch (Throwable ex2) {
82 if (throwableHolder.throwable != null) {
83 logger.error("Application exception overridden by commit exception", throwableHolder.throwable);
84 }
85 throw ex2;
86 }
87 }
88 }
如上图,我们主要看第一个分支,申明式事务,核心流程如下:
1.createTransactionIfNecessary():如果有必要,创建事务
2.InvocationCallback的proceedWithInvocation():InvocationCallback是父类的内部回调接口,子类中实现该接口供父类调用,子类TransactionInterceptor中invocation.proceed()。回调方法执行
3.异常回滚completeTransactionAfterThrowing()
1.createTransactionIfNecessary():
1 protected TransactionInfo createTransactionIfNecessary(
2 PlatformTransactionManager tm, TransactionAttribute txAttr, final String joinpointIdentification) {
3
4 // 如果还没有定义名字,把连接点的ID定义成事务的名称
5 if (txAttr != null && txAttr.getName() == null) {
6 txAttr = new DelegatingTransactionAttribute(txAttr) {
7 @Override
8 public String getName() {
9 return joinpointIdentification;
10 }
11 };
12 }
13
14 TransactionStatus status = null;
15 if (txAttr != null) {
16 if (tm != null) {
17 status = tm.getTransaction(txAttr);
18 }
19 else {
20 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
21 logger.debug("Skipping transactional joinpoint [" + joinpointIdentification +
22 "] because no transaction manager has been configured");
23 }
24 }
25 }
26 return prepareTransactionInfo(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification, status);
27 }
核心就是:
1)getTransaction(),根据事务属性获取事务TransactionStatus,大道归一,都是调用PlatformTransactionManager.getTransaction(),源码见3.3.1。
2)prepareTransactionInfo(),构造一个TransactionInfo事务信息对象,绑定当前线程:ThreadLocal<TransactionInfo>。
2.invocation.proceed()回调业务方法:
最终实现类是ReflectiveMethodInvocation,类图如下:

如上图,ReflectiveMethodInvocation类实现了ProxyMethodInvocation接口,但是ProxyMethodInvocation继承了3层接口...ProxyMethodInvocation->MethodInvocation->Invocation->Joinpoint
Joinpoint:连接点接口,定义了执行接口:Object proceed() throws Throwable; 执行当前连接点,并跳到拦截器链上的下一个拦截器。
Invocation:调用接口,继承自Joinpoint,定义了获取参数接口: Object[] getArguments();是一个带参数的、可被拦截器拦截的连接点。
MethodInvocation:方法调用接口,继承自Invocation,定义了获取方法接口:Method getMethod(); 是一个带参数的可被拦截的连接点方法。
ProxyMethodInvocation:代理方法调用接口,继承自MethodInvocation,定义了获取代理对象接口:Object getProxy();是一个由代理类执行的方法调用连接点方法。
ReflectiveMethodInvocation:实现了ProxyMethodInvocation接口,自然就实现了父类接口的的所有接口。获取代理类,获取方法,获取参数,用代理类执行这个方法并且自动跳到下一个连接点。
下面看一下proceed方法源码:
1 @Override
2 public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
3 // 启动时索引为-1,唤醒连接点,后续递增
4 if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
5 return invokeJoinpoint();
6 }
7
8 Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
9 this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
10 if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
11 // 这里进行动态方法匹配校验,静态的方法匹配早已经校验过了(MethodMatcher接口有两种典型:动态/静态校验)
13 InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
14 (InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
15 if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
16 return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
17 }
18 else {
19 // 动态匹配失败,跳过当前拦截,进入下一个(拦截器链)
21 return proceed();
22 }
23 }
24 else {
25 // 它是一个拦截器,所以我们只调用它:在构造这个对象之前,切入点将被静态地计算。
27 return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
28 }
29 }
咱们这里最终调用的是((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);就是TransactionInterceptor事务拦截器回调 目标业务方法(addUserBalanceAndUser)。
3.completeTransactionAfterThrowing()
最终调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的rollback(),提交事务commitTransactionAfterReturning()最终调用AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的commit(),源码见3.3.3
总结:
可见不管是编程式事务,还是声明式事务,最终源码都是调用事务管理器的PlatformTransactionManager接口的3个方法:
- getTransaction
- commit
- rollback
下一节我们就来看看这个事务管理如何实现这3个方法。
三、事务核心源码
咱们看一下核心类图:

如上提所示,PlatformTransactionManager顶级接口定义了最核心的事务管理方法,下面一层是AbstractPlatformTransactionManager抽象类,实现了PlatformTransactionManager接口的方法并定义了一些抽象方法,供子类拓展。最后下面一层是2个经典事务管理器:
1.DataSourceTransactionmanager,即JDBC单数据库事务管理器,基于Connection实现,
2.JtaTransactionManager,即多数据库事务管理器(又叫做分布式事务管理器),其实现了JTA规范,使用XA协议进行两阶段提交。
我们这里只看基于JDBC connection的DataSourceTransactionmanager源码。
PlatformTransactionManager接口:
1 public interface PlatformTransactionManager {
2 // 获取事务状态
3 TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException;
4 // 事务提交
5 void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
6 // 事务回滚
7 void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException;
8 }
1. getTransaction获取事务

AbstractPlatformTransactionManager实现了getTransaction()方法如下:
1 @Override
2 public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
3 Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
4
5 // Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
6 boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
7
8 if (definition == null) {
9 // Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
10 definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
11 }
12 // 如果当前已经存在事务
13 if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
14 // 根据不同传播机制不同处理
15 return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
16 }
17
18 // 超时不能小于默认值
19 if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
20 throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
21 }
22
23 // 当前不存在事务,传播机制=MANDATORY(支持当前事务,没事务报错),报错
24 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
25 throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
26 "No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
27 }// 当前不存在事务,传播机制=REQUIRED/REQUIRED_NEW/NESTED,这三种情况,需要新开启事务,且加上事务同步
28 else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
29 definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
30 definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
31 SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
32 if (debugEnabled) {
33 logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
34 }
35 try {// 是否需要新开启同步// 开启// 开启
36 boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
37 DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
38 definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
39 doBegin(transaction, definition);// 开启新事务
40 prepareSynchronization(status, definition);//预备同步
41 return status;
42 }
43 catch (RuntimeException ex) {
44 resume(null, suspendedResources);
45 throw ex;
46 }
47 catch (Error err) {
48 resume(null, suspendedResources);
49 throw err;
50 }
51 }
52 else {
53 // 当前不存在事务当前不存在事务,且传播机制=PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS/PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED/PROPAGATION_NEVER,这三种情况,创建“空”事务:没有实际事务,但可能是同步。警告:定义了隔离级别,但并没有真实的事务初始化,隔离级别被忽略有隔离级别但是并没有定义实际的事务初始化,有隔离级别但是并没有定义实际的事务初始化,
54 if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
55 logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
56 "isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition);
57 }
58 boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
59 return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, null, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
60 }
61 }
如上图,源码分成了2条处理线,
1.当前已存在事务:isExistingTransaction()判断是否存在事务,存在事务handleExistingTransaction()根据不同传播机制不同处理
2.当前不存在事务: 不同传播机制不同处理
handleExistingTransaction()源码如下:
1 private TransactionStatus handleExistingTransaction(
2 TransactionDefinition definition, Object transaction, boolean debugEnabled)
3 throws TransactionException {
4 // 1.NERVER(不支持当前事务;如果当前事务存在,抛出异常)报错
5 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER) {
6 throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
7 "Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'");
8 }
9 // 2.NOT_SUPPORTED(不支持当前事务,现有同步将被挂起)挂起当前事务
10 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED) {
11 if (debugEnabled) {
12 logger.debug("Suspending current transaction");
13 }
14 Object suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
15 boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
16 return prepareTransactionStatus(
17 definition, null, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
18 }
19 // 3.REQUIRES_NEW挂起当前事务,创建新事务
20 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW) {
21 if (debugEnabled) {
22 logger.debug("Suspending current transaction, creating new transaction with name [" +
23 definition.getName() + "]");
24 }// 挂起当前事务
25 SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(transaction);
26 try {// 创建新事务
27 boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
28 DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
29 definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
30 doBegin(transaction, definition);
31 prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
32 return status;
33 }
34 catch (RuntimeException beginEx) {
35 resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginEx);
36 throw beginEx;
37 }
38 catch (Error beginErr) {
39 resumeAfterBeginException(transaction, suspendedResources, beginErr);
40 throw beginErr;
41 }
42 }
43 // 4.NESTED嵌套事务
44 if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
45 if (!isNestedTransactionAllowed()) {
46 throw new NestedTransactionNotSupportedException(
47 "Transaction manager does not allow nested transactions by default - " +
48 "specify 'nestedTransactionAllowed' property with value 'true'");
49 }
50 if (debugEnabled) {
51 logger.debug("Creating nested transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]");
52 }// 是否支持保存点:非JTA事务走这个分支。AbstractPlatformTransactionManager默认是true,JtaTransactionManager复写了该方法false,DataSourceTransactionmanager没有复写,还是true,
53 if (useSavepointForNestedTransaction()) {
54 // Usually uses JDBC 3.0 savepoints. Never activates Spring synchronization.
55 DefaultTransactionStatus status =
56 prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, false, debugEnabled, null);
57 status.createAndHoldSavepoint();// 创建保存点
58 return status;
59 }
60 else {
61 // JTA事务走这个分支,创建新事务
62 boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
63 DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
64 definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
65 doBegin(transaction, definition);
66 prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
67 return status;
68 }
69 }
70
71
72 if (debugEnabled) {
73 logger.debug("Participating in existing transaction");
74 }
75 if (isValidateExistingTransaction()) {
76 if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT) {
77 Integer currentIsolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
78 if (currentIsolationLevel == null || currentIsolationLevel != definition.getIsolationLevel()) {
79 Constants isoConstants = DefaultTransactionDefinition.constants;
80 throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
81 definition + "] specifies isolation level which is incompatible with existing transaction: " +
82 (currentIsolationLevel != null ?
83 isoConstants.toCode(currentIsolationLevel, DefaultTransactionDefinition.PREFIX_ISOLATION) :
84 "(unknown)"));
85 }
86 }
87 if (!definition.isReadOnly()) {
88 if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly()) {
89 throw new IllegalTransactionStateException("Participating transaction with definition [" +
90 definition + "] is not marked as read-only but existing transaction is");
91 }
92 }
93 }// 到这里PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS 或 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED或PROPAGATION_MANDATORY,存在事务加入事务即可,prepareTransactionStatus第三个参数就是是否需要新事务。false代表不需要新事物
94 boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
95 return prepareTransactionStatus(definition, transaction, false, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, null);
96 }
如上图,当前线程已存在事务情况下,新的不同隔离级别处理情况:
1.NERVER:不支持当前事务;如果当前事务存在,抛出异常:"Existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'never'"
2.NOT_SUPPORTED:不支持当前事务,现有同步将被挂起:suspend()
3.REQUIRES_NEW挂起当前事务,创建新事务:
1)suspend()
2)doBegin()
4.NESTED嵌套事务
1)非JTA事务:createAndHoldSavepoint()创建JDBC3.0保存点,不需要同步
2) JTA事务:开启新事务,doBegin()+prepareSynchronization()需要同步
这里有几个核心方法:挂起当前事务suspend()、开启新事务doBegin()。
suspend()源码如下:
1 protected final SuspendedResourcesHolder suspend(Object transaction) throws TransactionException {
2 if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {// 1.当前存在同步,
3 List<TransactionSynchronization> suspendedSynchronizations = doSuspendSynchronization();
4 try {
5 Object suspendedResources = null;
6 if (transaction != null) {// 事务不为空,挂起事务
7 suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
8 }// 解除绑定当前事务各种属性:名称、只读、隔离级别、是否是真实的事务.
9 String name = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionName();
10 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionName(null);
11 boolean readOnly = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isCurrentTransactionReadOnly();
12 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionReadOnly(false);
13 Integer isolationLevel = TransactionSynchronizationManager.getCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel();
14 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setCurrentTransactionIsolationLevel(null);
15 boolean wasActive = TransactionSynchronizationManager.isActualTransactionActive();
16 TransactionSynchronizationManager.setActualTransactionActive(false);
17 return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(
18 suspendedResources, suspendedSynchronizations, name, readOnly, isolationLevel, wasActive);
19 }
20 catch (RuntimeException ex) {
21 // doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active...
22 doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
23 throw ex;
24 }
25 catch (Error err) {
26 // doSuspend failed - original transaction is still active...
27 doResumeSynchronization(suspendedSynchronizations);
28 throw err;
29 }
30 }// 2.没有同步但,事务不为空,挂起事务
31 else if (transaction != null) {
32 // Transaction active but no synchronization active.
33 Object suspendedResources = doSuspend(transaction);
34 return new SuspendedResourcesHolder(suspendedResources);
35 }// 2.没有同步但,事务为空,什么都不用做
36 else {
37 // Neither transaction nor synchronization active.
38 return null;
39 }
40 }
doSuspend(),挂起事务,AbstractPlatformTransactionManager抽象类doSuspend()会报错:不支持挂起,如果具体事务执行器支持就复写doSuspend(),DataSourceTransactionManager实现如下:
1 @Override
2 protected Object doSuspend(Object transaction) {
3 DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
4 txObject.setConnectionHolder(null);
5 return TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(this.dataSource);
6 }
挂起DataSourceTransactionManager事务的核心操作就是:
1.把当前事务的connectionHolder数据库连接持有者清空。
2.当前线程解绑datasource.其实就是ThreadLocal移除对应变量(TransactionSynchronizationManager类中定义的private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources = new NamedThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>>("Transactional resources");)
TransactionSynchronizationManager事务同步管理器,该类维护了多个线程本地变量ThreadLocal,如下图:
1 public abstract class TransactionSynchronizationManager {
2
3 private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(TransactionSynchronizationManager.class);
4 // 事务资源:map<k,v> 两种数据对。1.会话工厂和会话k=SqlsessionFactory v=SqlSessionHolder 2.数据源和连接k=DataSource v=ConnectionHolder
5 private static final ThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>> resources =
6 new NamedThreadLocal<Map<Object, Object>>("Transactional resources");
7 // 事务同步
8 private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations =
9 new NamedThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>>("Transaction synchronizations");
10 // 当前事务名称
11 private static final ThreadLocal<String> currentTransactionName =
12 new NamedThreadLocal<String>("Current transaction name");
13 // 当前事务的只读属性
14 private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> currentTransactionReadOnly =
15 new NamedThreadLocal<Boolean>("Current transaction read-only status");
16 // 当前事务的隔离级别
17 private static final ThreadLocal<Integer> currentTransactionIsolationLevel =
18 new NamedThreadLocal<Integer>("Current transaction isolation level");
19 // 是否存在事务
20 private static final ThreadLocal<Boolean> actualTransactionActive =
21 new NamedThreadLocal<Boolean>("Actual transaction active");
22 。。。
23 }
doBegin()源码如下:
1 @Override
2 protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
3 DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
4 Connection con = null;
5
6 try {// 如果事务还没有connection或者connection在事务同步状态,重置新的connectionHolder
7 if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
8 txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
9 Connection newCon = this.dataSource.getConnection();
10 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
11 logger.debug("Acquired Connection [" + newCon + "] for JDBC transaction");
12 }// 重置新的connectionHolder
13 txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
14 }
15 //设置新的连接为事务同步中
16 txObject.getConnectionHolder().setSynchronizedWithTransaction(true);
17 con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
18 //conn设置事务隔离级别,只读
19 Integer previousIsolationLevel = DataSourceUtils.prepareConnectionForTransaction(con, definition);
20 txObject.setPreviousIsolationLevel(previousIsolationLevel);//DataSourceTransactionObject设置事务隔离级别
21
22 // 如果是自动提交切换到手动提交
23 // so we don't want to do it unnecessarily (for example if we've explicitly
24 // configured the connection pool to set it already).
25 if (con.getAutoCommit()) {
26 txObject.setMustRestoreAutoCommit(true);
27 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
28 logger.debug("Switching JDBC Connection [" + con + "] to manual commit");
29 }
30 con.setAutoCommit(false);
31 }
32 // 如果只读,执行sql设置事务只读
33 prepareTransactionalConnection(con, definition);
34 txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTransactionActive(true);// 设置connection持有者的事务开启状态
35
36 int timeout = determineTimeout(definition);
37 if (timeout != TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
38 txObject.getConnectionHolder().setTimeoutInSeconds(timeout);// 设置超时秒数
39 }
40
41 // 绑定connection持有者到当前线程
42 if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
43 TransactionSynchronizationManager.bindResource(getDataSource(), txObject.getConnectionHolder());
44 }
45 }
46
47 catch (Throwable ex) {
48 if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
49 DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource);
50 txObject.setConnectionHolder(null, false);
51 }
52 throw new CannotCreateTransactionException("Could not open JDBC Connection for transaction", ex);
53 }
54 }
如上图,开启新事务的准备工作doBegin()的核心操作就是:
1.DataSourceTransactionObject“数据源事务对象”,设置ConnectionHolder,再给ConnectionHolder设置各种属性:自动提交、超时、事务开启、隔离级别。
2.给当前线程绑定一个线程本地变量,key=DataSource数据源 v=ConnectionHolder数据库连接。
2. commit提交事务
一、讲解源码之前先看一下资源管理类:
SqlSessionSynchronization是SqlSessionUtils的一个内部类,继承自TransactionSynchronizationAdapter抽象类,实现了事务同步接口TransactionSynchronization。
类图如下:

TransactionSynchronization接口定义了事务操作时的对应资源的(JDBC事务那么就是SqlSessionSynchronization)管理方法:
1 // 挂起事务
2 void suspend(); 3 // 唤醒事务 4 void resume(); 5 6 void flush(); 7 8 // 提交事务前 9 void beforeCommit(boolean readOnly); 10 11 // 提交事务完成前 12 void beforeCompletion(); 13 14 // 提交事务后 15 void afterCommit(); 16 17 // 提交事务完成后 18 void afterCompletion(int status);
后续很多都是使用这些接口管理事务。
二、 commit提交事务

AbstractPlatformTransactionManager的commit源码如下:
1 @Override
2 public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
3 if (status.isCompleted()) {// 如果事务已完结,报错无法再次提交
4 throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
5 "Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
6 }
7
8 DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
9 if (defStatus.isLocalRollbackOnly()) {// 如果事务明确标记为回滚,
10 if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
11 logger.debug("Transactional code has requested rollback");
12 }
13 processRollback(defStatus);//执行回滚
14 return;
15 }//如果不需要全局回滚时提交 且 全局回滚
16 if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
17 if (defStatus.isDebug()) {
18 logger.debug("Global transaction is marked as rollback-only but transactional code requested commit");
19 }//执行回滚
20 processRollback(defStatus);
21 // 仅在最外层事务边界(新事务)或显式地请求时抛出“未期望的回滚异常”
23 if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
24 throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
25 "Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
26 }
27 return;
28 }
29 // 执行提交事务
30 processCommit(defStatus);
31 }
如上图,各种判断:
- 1.如果事务明确标记为本地回滚,-》执行回滚
- 2.如果不需要全局回滚时提交 且 全局回滚-》执行回滚
- 3.提交事务,核心方法processCommit()
processCommit如下:
1 private void processCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
2 try {
3 boolean beforeCompletionInvoked = false;
4 try {//3个前置操作
5 prepareForCommit(status);
6 triggerBeforeCommit(status);
7 triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
8 beforeCompletionInvoked = true;//3个前置操作已调用
9 boolean globalRollbackOnly = false;//新事务 或 全局回滚失败
10 if (status.isNewTransaction() || isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
11 globalRollbackOnly = status.isGlobalRollbackOnly();
12 }//1.有保存点,即嵌套事务
13 if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
14 if (status.isDebug()) {
15 logger.debug("Releasing transaction savepoint");
16 }//释放保存点
17 status.releaseHeldSavepoint();
18 }//2.新事务
19 else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
20 if (status.isDebug()) {
21 logger.debug("Initiating transaction commit");
22 }//调用事务处理器提交事务
23 doCommit(status);
24 }
25 // 3.非新事务,且全局回滚失败,但是提交时没有得到异常,抛出异常
27 if (globalRollbackOnly) {
28 throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
29 "Transaction silently rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
30 }
31 }
32 catch (UnexpectedRollbackException ex) {
33 // 触发完成后事务同步,状态为回滚
34 triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
35 throw ex;
36 }// 事务异常
37 catch (TransactionException ex) {
38 // 提交失败回滚
39 if (isRollbackOnCommitFailure()) {
40 doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
41 }// 触发完成后回调,事务同步状态为未知
42 else {
43 triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
44 }
45 throw ex;
46 }// 运行时异常
47 catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// 如果3个前置步骤未完成,调用前置的最后一步操作
48 if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
49 triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
50 }// 提交异常回滚
51 doRollbackOnCommitException(status, ex);
52 throw ex;
53 }// 其它异常
54 catch (Error err) {
// 如果3个前置步骤未完成,调用前置的最后一步操作
55 if (!beforeCompletionInvoked) {
56 triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
57 }// 提交异常回滚
58 doRollbackOnCommitException(status, err);
59 throw err;
60 }
61
62 // Trigger afterCommit callbacks, with an exception thrown there
63 // propagated to callers but the transaction still considered as committed.
64 try {
65 triggerAfterCommit(status);
66 }
67 finally {
68 triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
69 }
70
71 }
72 finally {
73 cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
74 }
75 }
如上图,commit事务时,有6个核心操作,分别是3个前置操作,3个后置操作,如下:
1.prepareForCommit(status);源码是空的,没有拓展目前。
2.triggerBeforeCommit(status); 提交前触发操作
1 protected final void triggerBeforeCommit(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
2 if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
3 if (status.isDebug()) {
4 logger.trace("Triggering beforeCommit synchronization");
5 }
6 TransactionSynchronizationUtils.triggerBeforeCommit(status.isReadOnly());
7 }
8 }
triggerBeforeCommit源码如下:
1 public static void triggerBeforeCommit(boolean readOnly) {
2 for (TransactionSynchronization synchronization : TransactionSynchronizationManager.getSynchronizations()) {
3 synchronization.beforeCommit(readOnly);
4 }
5 }
如上图,TransactionSynchronizationManager类定义了多个ThreadLocal(线程本地变量),其中一个用以保存当前线程的事务同步:
private static final ThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>> synchronizations = new NamedThreadLocal<Set<TransactionSynchronization>>("Transaction synchronizations");
遍历事务同步器,把每个事务同步器都执行“提交前”操作,比如咱们用的jdbc事务,那么最终就是SqlSessionUtils.beforeCommit()->this.holder.getSqlSession().commit();提交会话。(源码由于是spring管理实务,最终不会执行事务提交,例如是DefaultSqlSession:执行清除缓存、重置状态操作)
3.triggerBeforeCompletion(status);完成前触发操作,如果是jdbc事务,那么最终就是,
SqlSessionUtils.beforeCompletion->
TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(sessionFactory); 解绑当前线程的会话工厂
this.holder.getSqlSession().close();关闭会话。(源码由于是spring管理实务,最终不会执行事务close操作,例如是DefaultSqlSession,也会执行各种清除收尾操作)
4.triggerAfterCommit(status);提交事务后触发操作。TransactionSynchronizationUtils.triggerAfterCommit();->TransactionSynchronizationUtils.invokeAfterCommit,如下:
1 public static void invokeAfterCommit(List<TransactionSynchronization> synchronizations) {
2 if (synchronizations != null) {
3 for (TransactionSynchronization synchronization : synchronizations) {
4 synchronization.afterCommit();
5 }
6 }
7 }
好吧,一顿找,最后在TransactionSynchronizationAdapter中复写过,并且是空的....SqlSessionSynchronization继承了TransactionSynchronizationAdapter但是没有复写这个方法。
5. triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_COMMITTED);
TransactionSynchronizationUtils.TransactionSynchronizationUtils.invokeAfterCompletion,如下:
1 public static void invokeAfterCompletion(List<TransactionSynchronization> synchronizations, int completionStatus) {
2 if (synchronizations != null) {
3 for (TransactionSynchronization synchronization : synchronizations) {
4 try {
5 synchronization.afterCompletion(completionStatus);
6 }
7 catch (Throwable tsex) {
8 logger.error("TransactionSynchronization.afterCompletion threw exception", tsex);
9 }
10 }
11 }
12 }
afterCompletion:对于JDBC事务来说,最终:
1)如果会话任然活着,关闭会话,
2)重置各种属性:SQL会话同步器(SqlSessionSynchronization)的SQL会话持有者(SqlSessionHolder)的referenceCount引用计数、synchronizedWithTransaction同步事务、rollbackOnly只回滚、deadline超时时间点。
6.cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
1)设置事务状态为已完成。
2) 如果是新的事务同步,解绑当前线程绑定的数据库资源,重置数据库连接
3)如果存在挂起的事务(嵌套事务),唤醒挂起的老事务的各种资源:数据库资源、同步器。
1 private void cleanupAfterCompletion(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
2 status.setCompleted();//设置事务状态完成
//如果是新的同步,清空当前线程绑定的除了资源外的全部线程本地变量:包括事务同步器、事务名称、只读属性、隔离级别、真实的事务激活状态
3 if (status.isNewSynchronization()) {
4 TransactionSynchronizationManager.clear();
5 }//如果是新的事务同步
6 if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
7 doCleanupAfterCompletion(status.getTransaction());
8 }//如果存在挂起的资源
9 if (status.getSuspendedResources() != null) {
10 if (status.isDebug()) {
11 logger.debug("Resuming suspended transaction after completion of inner transaction");
12 }//唤醒挂起的事务和资源(重新绑定之前挂起的数据库资源,唤醒同步器,注册同步器到TransactionSynchronizationManager)
13 resume(status.getTransaction(), (SuspendedResourcesHolder) status.getSuspendedResources());
14 }
15 }
对于DataSourceTransactionManager,doCleanupAfterCompletion源码如下:
1 protected void doCleanupAfterCompletion(Object transaction) {
2 DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
3
4 // 如果是最新的连接持有者,解绑当前线程绑定的<数据库资源,ConnectionHolder>
5 if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
6 TransactionSynchronizationManager.unbindResource(this.dataSource);
7 }
8
9 // 重置数据库连接(隔离级别、只读)
10 Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
11 try {
12 if (txObject.isMustRestoreAutoCommit()) {
13 con.setAutoCommit(true);
14 }
15 DataSourceUtils.resetConnectionAfterTransaction(con, txObject.getPreviousIsolationLevel());
16 }
17 catch (Throwable ex) {
18 logger.debug("Could not reset JDBC Connection after transaction", ex);
19 }
20
21 if (txObject.isNewConnectionHolder()) {
22 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
23 logger.debug("Releasing JDBC Connection [" + con + "] after transaction");
24 }// 资源引用计数-1,关闭数据库连接
25 DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, this.dataSource);
26 }
27 // 重置连接持有者的全部属性
28 txObject.getConnectionHolder().clear();
29 }
3. rollback回滚事务

AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中rollback源码如下:
1 public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
2 if (status.isCompleted()) {
3 throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
4 "Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
5 }
6
7 DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
8 processRollback(defStatus);
9 }
processRollback源码如下:
1 private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
2 try {
3 try {// 解绑当前线程绑定的会话工厂,并关闭会话
4 triggerBeforeCompletion(status);
5 if (status.hasSavepoint()) {// 1.如果有保存点,即嵌套式事务
6 if (status.isDebug()) {
7 logger.debug("Rolling back transaction to savepoint");
8 }//回滚到保存点
9 status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
10 }//2.如果就是一个简单事务
11 else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
12 if (status.isDebug()) {
13 logger.debug("Initiating transaction rollback");
14 }//回滚核心方法
15 doRollback(status);
16 }//3.当前存在事务且没有保存点,即加入当前事务的
17 else if (status.hasTransaction()) {//如果已经标记为回滚 或 当加入事务失败时全局回滚(默认true)
18 if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
19 if (status.isDebug()) {//debug时会打印:加入事务失败-标记已存在事务为回滚
20 logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - marking existing transaction as rollback-only");
21 }//设置当前connectionHolder:当加入一个已存在事务时回滚
22 doSetRollbackOnly(status);
23 }
24 else {
25 if (status.isDebug()) {
26 logger.debug("Participating transaction failed - letting transaction originator decide on rollback");
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 else {
31 logger.debug("Should roll back transaction but cannot - no transaction available");
32 }
33 }
34 catch (RuntimeException ex) {//关闭会话,重置SqlSessionHolder属性
35 triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
36 throw ex;
37 }
38 catch (Error err) {
39 triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_UNKNOWN);
40 throw err;
41 }
42 triggerAfterCompletion(status, TransactionSynchronization.STATUS_ROLLED_BACK);
43 }
44 finally {、、解绑当前线程
45 cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
46 }
47 }
如上图,有几个公共方法和提交事务时一致,就不再重复。
这里主要看doRollback,DataSourceTransactionManager的doRollback()源码如下:
1 protected void doRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
2 DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
3 Connection con = txObject.getConnectionHolder().getConnection();
4 if (status.isDebug()) {
5 logger.debug("Rolling back JDBC transaction on Connection [" + con + "]");
6 }
7 try {
8 con.rollback();
9 }
10 catch (SQLException ex) {
11 throw new TransactionSystemException("Could not roll back JDBC transaction", ex);
12 }
13 }
好吧,一点不复杂,就是Connection的rollback.
四、时序图
特地整理了时序图(简单的新事务,没有画出保存点等情况)如下:

===========参考========
《Spring实战4》第四章 面向切面的Spring
Spring事务实现原理及源码分析
Spring事务实现原理及源码分析
流程介绍
主流程介绍
众所周知,Spring事务采用AOP的方式实现,我们从TransactionAspectSupport这个类开始f分析。
- 获取事务的属性(@Transactional注解中的配置)
- 加载配置中的TransactionManager.
- 获取收集事务信息TransactionInfo
- 执行目标方法
- 出现异常,尝试处理。
- 清理事务相关信息
- 提交事务
//1. 获取@Transactional注解的相关参数
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
// 2. 获取事务管理器
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
// Standard transaction demarcation with getTransaction and commit/rollback calls.
// 3. 获取TransactionInfo,包含了tm和TransactionStatus
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
Object retVal = null;
try {
// This is an around advice: Invoke the next interceptor in the chain.
// This will normally result in a target object being invoked.
// 4.执行目标方法
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
//5.回滚
// target invocation exception
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// 6. 清理当前线程的事务相关信息
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
}
// 提交事务
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
return retVal;
}
doBegin做了什么
在执行createTransactionIfNecessary获取事务状态时,就准备好了开启事务的所有内容,主要是执行了JDBC的con.setAutoCommit(false)方法。同时处理了很多和数据库连接相关的ThreadLocal变量。
关键对象介绍
PlatformTransactionManager
TransactionManager是做什么的?它保存着当前的数据源连接,对外提供对该数据源的事务提交回滚操作接口,同时实现了事务相关操作的方法。一个数据源DataSource需要一个事务管理器。
属性:DataSource
内部核心方法:
public commit 提交事务
public rollback 回滚事务
public getTransaction 获得当前事务状态
protected doSuspend 挂起事务
protected doBegin 开始事务,主要是执行了JDBC的con.setAutoCommit(false)方法。同时处理了很多和数据库连接相关的ThreadLocal变量。
protected doCommit 提交事务
protected doRollback 回滚事务
protected doGetTransaction() 获取事务信息
final getTransaction 获取事务状态
获取对应的TransactionManager
@Nullable
protected PlatformTransactionManager determineTransactionManager(@Nullable TransactionAttribute txAttr) {
// Do not attempt to lookup tx manager if no tx attributes are set
if (txAttr == null || this.beanFactory == null) {
return getTransactionManager();
}
String qualifier = txAttr.getQualifier();
//如果指定了Bean则取指定的PlatformTransactionManager类型的Bean
if (StringUtils.hasText(qualifier)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, qualifier);
}
//如果指定了Bean的名称,则根据bean名称获取对应的bean
else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.transactionManagerBeanName)) {
return determineQualifiedTransactionManager(this.beanFactory, this.transactionManagerBeanName);
}
else {
// 默认取一个PlatformTransactionManager类型的Bean
PlatformTransactionManager defaultTransactionManager = getTransactionManager();
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.transactionManagerCache.get(DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY);
if (defaultTransactionManager == null) {
defaultTransactionManager = this.beanFactory.getBean(PlatformTransactionManager.class);
this.transactionManagerCache.putIfAbsent(
DEFAULT_TRANSACTION_MANAGER_KEY, defaultTransactionManager);
}
}
return defaultTransactionManager;
}
}
可以看到,如果没有指定TransactionManager参数的话,会使用默认的一个实现,所以当程序中有多个数据库时,事务执行最好是指定事务管理器。
事务的信息TransactionInfo
TransactionInfo是对当前事务的描述,其中记录了事务的状态等信息。它记录了和一个事务所有的相关信息。它没有什么方法,只是对事务相关对象的一个组合。最关键的对象是TransactionStatus,它代表当前正在运行的是哪个事务。
1.核心属性:事务状态TransactionStatus
2.事务管理器
3.事务属性
4.上一个事务信息oldTransactionInfo,REQUIRE_NEW传播级别时,事务挂起后前一个事务的事务信息
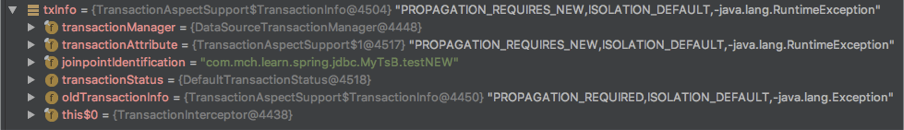
当前事务状态TransactionStatus
通过TransactionManager的getTransaction方法,获取当前事务的状态。
具体是在AbstractPlatformTransactionManager中实现.
TransactionStatus被用来做什么:TransactionManager对事务进行提交或回滚时需要用到该对象
具体方法有: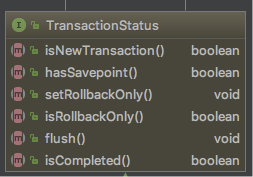
作用:
- 判断当前事务是否是一个新的事务,否则加入到一个已经存在的事务中。事务传播级别REQUIRED和REQUIRE_NEW有用到。
- 当前事务是否携带保存点,嵌套事务用到。
setRollbackOnly,isRollbackOnly,当子事务回滚时,并不真正回滚事务,而是对子事务设置一个标志位。 - 事务是否已经完成,已经提交或者已经回滚。
传播级别
介绍
Spring事务的传播级别描述的是多个使用了@Transactional注解的方法互相调用时,Spring对事务的处理。包涵的传播级别有:
- REQUIRED, 如果当前线程已经在一个事务中,则加入该事务,否则新建一个事务。
- SUPPORT, 如果当前线程已经在一个事务中,则加入该事务,否则不使用事务。
- MANDATORY(强制的),如果当前线程已经在一个事务中,则加入该事务,否则抛出异常。
- REQUIRES_NEW,无论如何都会创建一个新的事务,如果当前线程已经在一个事务中,则挂起当前事务,创建一个新的事务。
- NOT_SUPPORTED,如果当前线程在一个事务中,则挂起事务。
- NEVER,如果当前线程在一个事务中则抛出异常。
- NESTED, 执行一个嵌套事务,有点像REQUIRED,但是有些区别,在Mysql中是采用SAVEPOINT来实现的。
挂起事务,指的是将当前事务的属性如事务名称,隔离级别等属性保存在一个变量中,同时将当前线程中所有和事务相关的ThreadLocal变量设置为从未开启过线程一样。Spring维护着一个当前线程的事务状态,用来判断当前线程是否在一个事务中以及在一个什么样的事务中,挂起事务后,当前线程的事务状态就好像没有事务。
现象描述
@Service
public class MyTsA {
@Resource
private UserServiceImpl userService;
@Resource
private MyTsB myTsB;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void testNewRollback(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("张三");
userService.save(user);
myTsB.save();
}
}
@Service
public class MyTsB {
@Resource
private UserServiceImpl userService;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class, propagation = ???)
public void save(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(2);
user.setName(“李四”)
userService.save(user);
}
如上面所示有两个事务A和事务B,事务A方法中调用了事务B方法,区分两种回滚情况。
A提交,B回滚。
A回滚,B提交。
对于不同的传播级别:
1.当传播级别为为REQUIRED时,第一种情况A和B都会回滚。
2.。当传播级别为RQUIRED_NEW时,第一种情况A可以成功提交,B回滚,第二种情况A回滚,B可以正确提交,二者互不影响。(在A事务捕获B事务异常的情况下,保证A事务提交)
3.当传播级别为NESTED时,第一种情况A可以正常提交,B回滚,第二种情况二者都会回滚。
原理
我们从两个角度看他们的实现原理,一个是刚进入事务时,针对不同的传播级别,它们的行为有什么区别。另一个角度是当事务提交或者回滚时,传播级别对事务行为的影响。
首先在尝试获取事务信息时,如果当前已经存在一个事务,则会根据传播级别做一些处理:
隔离级别对开始事务的影响(获取TransactionStatus)
@Override
public final TransactionStatus getTransaction(@Nullable TransactionDefinition definition) throws TransactionException {
// 从当前的transactionManager获取DataSource对象
// 然后以该DataSource对象为Key,
// 去一个ThreadLocal变量中的map中获取该DataSource的连接
// 然后设置到DataSourceTransactionObject中返回。
Object transaction = doGetTransaction();
// Cache debug flag to avoid repeated checks.
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (definition == null) {
// Use defaults if no transaction definition given.
definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
}
// 如果当前线程已经在一个事务中了,则需要根据事务的传播级别
//来决定如何处理并获取事务状态对象
if (isExistingTransaction(transaction)) {
// Existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to behave.
return handleExistingTransaction(definition, transaction, debugEnabled);
}
// Check definition settings for new transaction.
if (definition.getTimeout() < TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT) {
throw new InvalidTimeoutException("Invalid transaction timeout", definition.getTimeout());
}
// No existing transaction found -> check propagation behavior to find out how to proceed.
if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY) {
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
"No existing transaction found for transaction marked with propagation 'mandatory'");
}
else if (definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW ||
definition.getPropagationBehavior() == TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED) {
SuspendedResourcesHolder suspendedResources = suspend(null);
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Creating new transaction with name [" + definition.getName() + "]: " + definition);
}
try {
//如果当前不在一个事务中,则执行事务的准备操作
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() != SYNCHRONIZATION_NEVER);
// 构造事务状态对象,注意这里第三个参数为true,代表是一个新事务
DefaultTransactionStatus status = newTransactionStatus(
definition, transaction, true, newSynchronization, debugEnabled, suspendedResources);
//执行begin操作,核心操作是设置隔离级别,执行 conn.setAutoCommit(false); 同时将数据连接绑定到当前线程
doBegin(transaction, definition);
// 针对事务相关属性如隔离级别,是否在事务中,设置绑定到当前线程
prepareSynchronization(status, definition);
return status;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
resume(null, suspendedResources);
throw ex;
}
}
else {
// Create "empty" transaction: no actual transaction, but potentially synchronization.
if (definition.getIsolationLevel() != TransactionDefinition.ISOLATION_DEFAULT && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Custom isolation level specified but no actual transaction initiated; " +
"isolation level will effectively be ignored: " + definition);
}
boolean newSynchronization = (getTransactionSynchronization() == SYNCHRONIZATION_ALWAYS);
return prepareTransactionStatus
