Spring Cloud Config提供了一种在分布式系统中外部化配置服务器和客户端的支持。配置服务器有一个中心位置,管理所有环境下的应用的外部属性。客户端和服务器映射到相同Spring Eventment 和 PropertySrouce抽象的概念,所以非常适合Spring应用,但也可以在任何语言开发的任何应用中使用。在一个应用从开发、测试到生产的过程中,你可以分别地管理开发、测试、生产环境的配置,并且在迁移的时候获取相应的配置来运行。
准备工作
准备几个配置文件,命名规范为 项目名称-环境名称.yml。本文在git仓库:https://github.com/xuwenjin中,新建目录config-repo-xwj,创建以下几个文件:
每个文件内容如下:
application.yml
profile: profile-default
config-client.yml
profile: config-client
config-client-dev.yml
profile: dev
config-client-test.yml
profile: test
代码示例
创建一个Maven项目,在pom.xml文件中添加如下内容:
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Edgware.SR4</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<!-- 解决启动报Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.eclipse.jgit.api.TransportConfigCallback -->
<groupId>org.eclipse.jgit</groupId>
<artifactId>org.eclipse.jgit</artifactId>
<version>4.9.0.201710071750-r</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
启动类:
@SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigServer // 通过@EnableConfigServer注解激活配置服务 public class ConfigServerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ConfigServerApplication.class, args); } }
配置文件:application.yml
server: port: 18083 spring: application: name: config-server #应用程序名称 cloud: config: server: git: uri: https://github.com/xuwenjin/config-repo-xwj #git上,配置文件地址
这样,一个Config Server就完成了。
测试工作

规则中的参数含义如下:
{application}映射到客户端的“spring.application.name”(项目名称){profile}映射到客户端上的“spring.profiles.active”(环境名称){label}这是一个服务器端功能,标记“版本”的配置文件集(在git中,相当于分支名)
启动服务,也可以看到匹配规则:
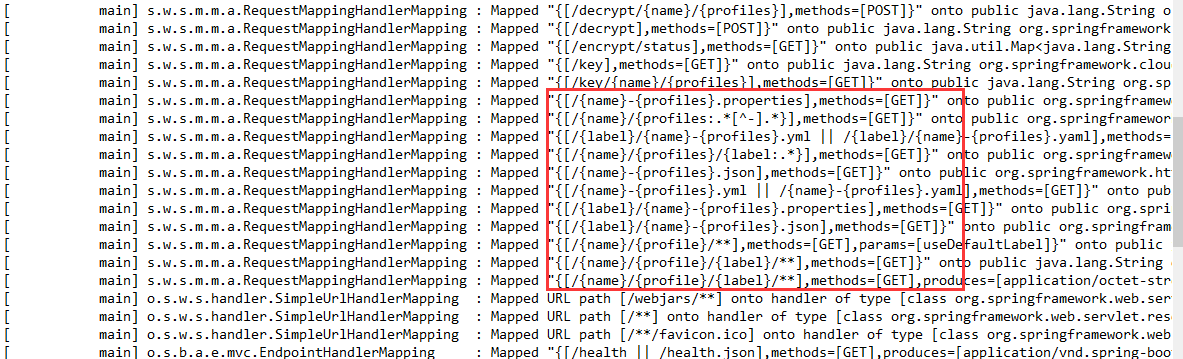
先试下 {application}/{profile}[/{label}] 这个规则,请求路径是 http://localhost:18083/config-client/dev/master,返回了所有配置文件信息:

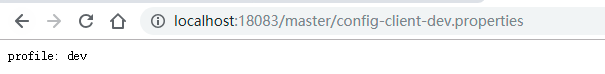
另外四种规则差不多,可使用以下路径来访问config-client-dev.yml文件,并直接返回其中的内容:
http://localhost:18083/config-client-dev.yml
http://localhost:18083/master/config-client-dev.yml
http://localhost:18083/config-client-dev.properties
http://localhost:18083/master/config-client-dev.properties
如果想要访问config-client-test.yml文件,只需要将上面的 dev 换成 test 就行。
但是如果匹配不上呢?结果如下:
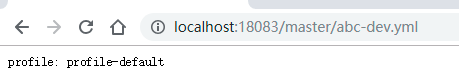
可以看到,当匹配不上时,会默认读取application.yml文件。
Config Server服务端是支持热加载的,即不重启服务的情况下更改配置文件信息,是可以直接读取的
源码分析
当发送请求时(如:http://localhost:18083/master/config-client-dev.yml ),会在 EnvironmentController 中进行匹配。如下:
@RestController @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "${spring.cloud.config.server.prefix:}") public class EnvironmentController { private EnvironmentRepository repository; // ... @RequestMapping({ "/{label}/{name}-{profiles}.yml", "/{label}/{name}-{profiles}.yaml" }) public ResponseEntity<String> labelledYaml(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String profiles, @PathVariable String label, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "true") boolean resolvePlaceholders) throws Exception { // 校验profiles是否含义"-",如果有则抛出异常 validateProfiles(profiles); // 获取环境信息,即远程配置文件数据 Environment environment = labelled(name, profiles, label); // 将environment对象转为Map Map<String, Object> result = convertToMap(environment); if (this.stripDocument && result.size() == 1 && result.keySet().iterator().next().equals("document")) { Object value = result.get("document"); if (value instanceof Collection) { return getSuccess(new Yaml().dumpAs(value, Tag.SEQ, FlowStyle.BLOCK)); } else { return getSuccess(new Yaml().dumpAs(value, Tag.STR, FlowStyle.BLOCK)); } } String yaml = new Yaml().dumpAsMap(result); if (resolvePlaceholders) { yaml = resolvePlaceholders(prepareEnvironment(environment), yaml); } return getSuccess(yaml); } // ... }
核心方法 labelled 中,会调用最核心的类 NativeEnvironmentRepositor 的 findOne 方法:
@RequestMapping("/{name}/{profiles}/{label:.*}") public Environment labelled(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String profiles, @PathVariable String label) { if (name != null && name.contains("(_)")) { // "(_)" is uncommon in a git repo name, but "/" cannot be matched // by Spring MVC name = name.replace("(_)", "/"); } if (label != null && label.contains("(_)")) { // "(_)" is uncommon in a git branch name, but "/" cannot be matched // by Spring MVC label = label.replace("(_)", "/"); } Environment environment = this.repository.findOne(name, profiles, label); return environment; }
findOne方法会从远程git仓库中获取配置文件数据:
@Override public Environment findOne(String config, String profile, String label) { SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder( PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getEnvironment(profile); builder.environment(environment); builder.web(false).bannerMode(Mode.OFF); if (!logger.isDebugEnabled()) { builder.logStartupInfo(false); } String[] args = getArgs(config, profile, label); // 设置监听器 builder.application() .setListeners(Arrays.asList(new ConfigFileApplicationListener())); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run(args); environment.getPropertySources().remove("profiles"); try { return clean(new PassthruEnvironmentRepository(environment).findOne(config, profile, label)); } finally { context.close(); } }
获取的Environment对象,数据结构如下:
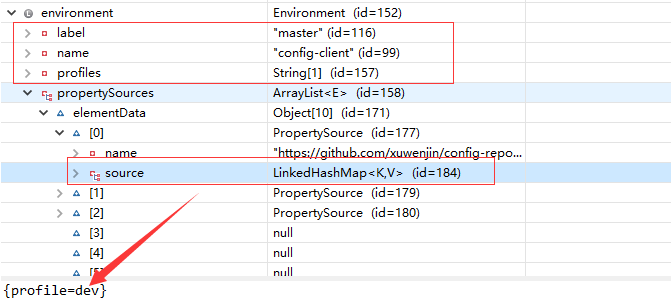
可以看到,配置文件信息,会放在 PropertySources 对象中~