Process analysis
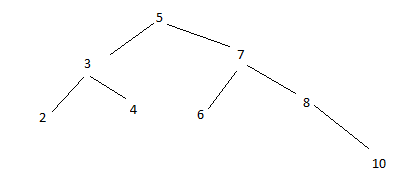
- Stack = 5,
- Push 3, Stack = 5, 3. Pre = 5
- Current = 3, Pre = 5, Push 2 to the stack, stack = 5, 3, 2, Pre = 3
- Current = 2, Pre = 3, pop 2, PRINT 2, Stack = 5, 3. Pre = 2
- Current = 3, push 4, Stack = 5, 3 , 4. Pre = 3
- Current = 4, 4 is leaf node, pop 4. PRINT 4, Pre = 4, Stack = 5, 3
- Current = 3, Pre = 4, 4 is right child of 3, it means it goes up from right side, all visited. Pop one more element from stack, PRINT 3. Pre = 3. Stack = 5
- Current = 5, Pre = 3, 5 has right child, push 7, Stack = 5, 7, Pre = 5
- Current 7, which is right child of 5, meaning it's first time to visit 7, 7 has left child, push 6 to the stack. Stack = 5, 7, 6 Pre = 7
- Current = 6, 6 is 7's left child, but 6 is leaf node, pop 6. Print 6, Pre = 6. Stack = 5, 7
- Current = 7, 7 has right child? yes, 8. Push 8 to the stack, Stack = 5,7,8. Pre = 7
- Current = 8, 8 has no left child, has right child 10, push 10 to the stack. Stack = 5, 7, 8, 10. Pre = 8
- Current = 10, 10 is leaf node, pop 10, Print 10, Stack = 5,7,8, Pre = 10
- Current = 8, pop 8, Print 8, Stack = 5, 7, Pre = 8
- Current = 7, pop 7, Print 7, Stack = 5, Pre = 7
- Current = 5, pop 5, Print 5, stack = empty
public void PostOrderNonRecursion1StackV1() { Stack<TreeNode<T>> stack = new Stack<TreeNode<T>>(); if (root == null) { return; } TreeNode<T> current = this.root; TreeNode<T> pre = null; stack.Push(this.root); while (stack.Count != 0) { current = stack.Peek(); // top down if (pre == null || pre.leftChild == current || pre.rightChild == current) { if (current.leftChild != null) { stack.Push(current.leftChild); } else if (current.rightChild != null) { stack.Push(current.rightChild); } else { // leaf node, have to pop Console.WriteLine("visit node {0}", stack.Pop().data); } } // move up case from left node else if (current.leftChild == pre) { if (current.rightChild != null) { stack.Push(current.rightChild); } else { Console.WriteLine("visit node {0}", stack.Pop().data); } } // move up from right , which means all done, need pop up next one to figure out next action else if (current.rightChild == pre) { Console.WriteLine("visit node {0}", stack.Pop().data); } // remember the previous node, not parent node pre = current; } }
The solution above uses one stack. If you use two stacks, there are the following two ways.
Solution 1 - do pre-order non-recursive firstly, but the sequence is root, right, left, not root, left and right.
Then store the result in stack 2, print stack 2, you will get the final result. Put code as below.
public void PostOrderNonRecursion2StacksV1() { Stack<TreeNode<T>> stack1 = new Stack<TreeNode<T>>(); Stack<TreeNode<T>> stack2 = new Stack<TreeNode<T>>(); TreeNode<T> current = root; if (current == null) { return; } while (current != null) { stack2.Push(current); Console.WriteLine(current.data); stack1.Push(current); current = current.rightChild; } while (stack1.Count != 0) { current = stack1.Pop(); if (current.leftChild != null) { current = current.leftChild; while (current != null) { stack2.Push(current); stack1.Push(current); current = current.rightChild; } } } while (stack2.Count != 0) { Console.WriteLine("value = {0}", stack2.Pop().data); } }
Solution 2:
这个方法对于初学者很难想到,根节点先入栈,然后根节点出栈,存入栈2. 根节点的左孩子入栈,根节点的右孩子入栈。
然后右孩子出栈,入栈2. 右孩子的左右节点入栈1。这样栈2的元素实际从底往上是主根,右孩子,递归右左。 反过来就是先左后右, 再根节点。 下面是代码
public void PostOrderNonRecursion2StackV2() { Stack<TreeNode<T>> stack1 = new Stack<TreeNode<T>>(); Stack<TreeNode<T>> stack2 = new Stack<TreeNode<T>>(); TreeNode<T> current = root; if (current == null) { return; } stack1.Push(current); while (stack1.Count != 0) { current = stack1.Pop(); if (current.leftChild != null) { stack1.Push(current.leftChild); } if (current.rightChild != null) { stack1.Push(current.rightChild); } stack2.Push(current); } while (stack2.Count != 0) { Console.WriteLine("value = {0}", stack2.Pop().data); } }