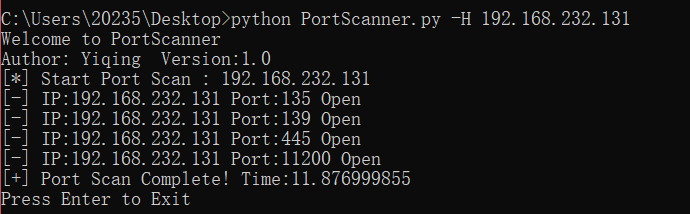
首先是最常用的端口扫描器:
虽说有nmap等强大的工具,不过如果由于条件限制无法安装Nmap呢?
我这个脚本写的比较简单,默认扫描1-65535全部的端口
实际的话,可以根据需要自己修改脚本来实现定制化扫描
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = "Yiqing" import socket import time import thread import optparse import re socket.setdefaulttimeout(3) def port_scan(ip, port): """ 对某一个IP的某一个端口进行扫描 :param ip: 目标 :param port: 端口 :return: None """ try: if port > 65535 or port < 1: print "[!] Port Scan End" s = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) result = s.connect_ex((ip, port)) if int(result) == 0: lock.acquire() print "[-] IP:" + str(ip) + " Port:" + str(port) + " Open" lock.release() s.close() except Exception: pass def ip_scan(ip): """ 对IP的所有端口扫描 :param ip:目标 :return: None """ try: print "[*] Start Port Scan : " + ip start_time = time.time() for port in range(1, 65535): thread.start_new_thread(port_scan, (ip, int(port))) print "[+] Port Scan Complete! Time:" + str(time.time() - start_time) except Exception: pass def main(): """ 输入参数处理 :return: None """ print "Welcome to PortScanner" print "Author: %s Version:1.0" % __author__ parse = optparse.OptionParser( 'python %prog -H <target host>') parse.add_option('-H', dest="target_host", type="string", help='specify the host') (options, args) = parse.parse_args() target_host = options.target_host if target_host is not None and re.match(r'd{1,3}.d{1,3}.d{1,3}.d{1,3}', target_host): ip_scan(target_host) else: exit() if __name__ == '__main__': lock = thread.allocate_lock() main() time.sleep(3) raw_input("Press Enter to Exit")
使用: