Lee tried so hard to make a good div.2 D problem to balance his recent contest, but it still doesn't feel good at all. Lee invented it so tediously slow that he managed to develop a phobia about div.2 D problem setting instead. And now he is hiding behind the bushes...
Let's define a Rooted Dead Bush (RDB) of level nn as a rooted tree constructed as described below.
A rooted dead bush of level 11 is a single vertex. To construct an RDB of level ii we, at first, construct an RDB of level i−1i−1, then for each vertex uu:
- if uu has no children then we will add a single child to it;
- if uu has one child then we will add two children to it;
- if uu has more than one child, then we will skip it.
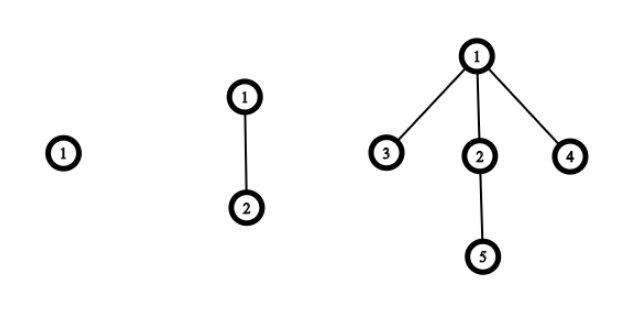 Rooted Dead Bushes of level 11, 22 and 33.
Rooted Dead Bushes of level 11, 22 and 33.Let's define a claw as a rooted tree with four vertices: one root vertex (called also as center) with three children. It looks like a claw:
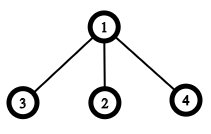 The center of the claw is the vertex with label 11.
The center of the claw is the vertex with label 11.Lee has a Rooted Dead Bush of level nn. Initially, all vertices of his RDB are green.
In one move, he can choose a claw in his RDB, if all vertices in the claw are green and all vertices of the claw are children of its center, then he colors the claw's vertices in yellow.
He'd like to know the maximum number of yellow vertices he can achieve. Since the answer might be very large, print it modulo 109+7109+7.
Input
The first line contains one integer tt (1≤t≤1041≤t≤104) — the number of test cases.
Next tt lines contain test cases — one per line.
The first line of each test case contains one integer nn (1≤n≤2⋅1061≤n≤2⋅106) — the level of Lee's RDB.
Output
For each test case, print a single integer — the maximum number of yellow vertices Lee can make modulo 109+7109+7.
Example
7 1 2 3 4 5 100 2000000
0 0 4 4 12 990998587 804665184
Note
It's easy to see that the answer for RDB of level 11 or 22 is 00.
The answer for RDB of level 33 is 44 since there is only one claw we can choose: {1,2,3,4}{1,2,3,4}.
The answer for RDB of level 44 is 44 since we can choose either single claw {1,3,2,4}{1,3,2,4} or single claw {2,7,5,6}{2,7,5,6}. There are no other claws in the RDB of level 44 (for example, we can't choose {2,1,7,6}{2,1,7,6}, since 11 is not a child of center vertex 22).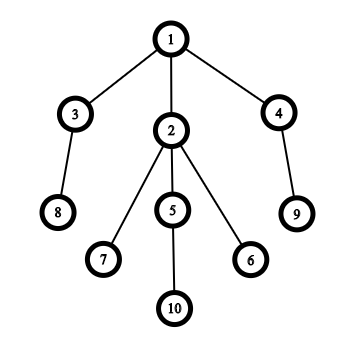

#include <bits/stdc++.h> int dp[2000007]; int main() { dp[0] = dp[1] = 0;dp[2] = 4; for (int i = 3; i < 2000007; i++) { long long a = dp[i - 1]; a += 2 * dp[i - 2] + (i % 3 == 2) * 4; a %= 1000000007; dp[i] = a; } int t,n; scanf("%d",&t); while (t--) { scanf("%d", &n); n--; printf("%d ", dp[n] % 1000000007); } }