给定一个二叉树
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
进阶:
你只能使用常量级额外空间。
使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序占用的栈空间不算做额外的空间复杂度。
示例:
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
输出:[1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
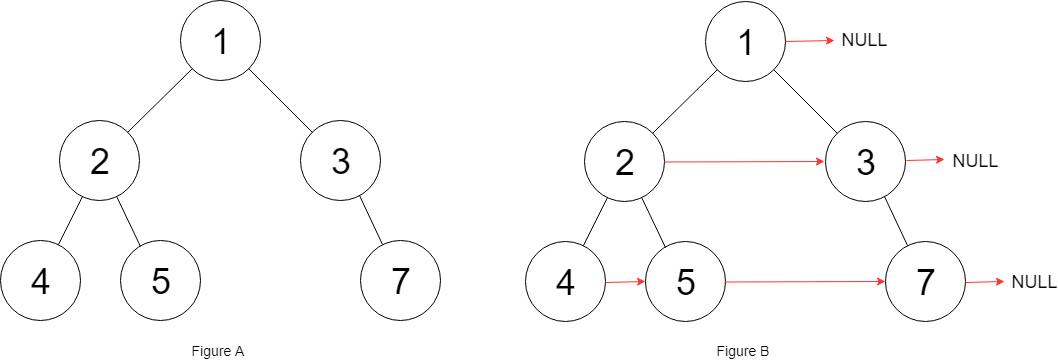
解释:给定二叉树如图 A 所示,你的函数应该填充它的每个 next 指针,以指向其下一个右侧节点,如图 B 所示。
提示:
树中的节点数小于 6000
-100 <= node.val <= 100
自顶向下遍历法
""" # Definition for a Node. class Node: def __init__(self, val: int = 0, left: 'Node' = None, right: 'Node' = None, next: 'Node' = None): self.val = val self.left = left self.right = right self.next = next """ class Solution: def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node': left=root while left: head=tail=Node(0) cur=left while cur: if cur.left: tail.next=cur.left tail=tail.next if cur.right: tail.next=cur.right tail=tail.next cur=cur.next left=head.next return root

列表层次遍历
/* // Definition for a Node. class Node { public: int val; Node* left; Node* right; Node* next; Node() : val(0), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val) : val(_val), left(NULL), right(NULL), next(NULL) {} Node(int _val, Node* _left, Node* _right, Node* _next) : val(_val), left(_left), right(_right), next(_next) {} }; */ class Solution { public: Node* connect(Node* root) { if(!root)return nullptr; queue<Node*>q; q.push(root); while(!q.empty()){ int l=q.size(); Node *last=nullptr; for(int i=1;i<=l;i++){ Node *f=q.front(); q.pop(); if(f->left)q.push(f->left); if(f->right)q.push(f->right); if(i!=1)last->next=f; last=f; } } return root; } };
