PyTorch : torch.nn.xxx 和 torch.nn.functional.xxx
在写 PyTorch 代码时,我们会发现在
torch.nn.xxx和torch.nn.functional.xxx中有一些功能重复的操作,比如卷积、激活、池化。这些操作有什么不同?各有什么用处?
首先可以观察源码:
eg:torch.nn.Conv2d
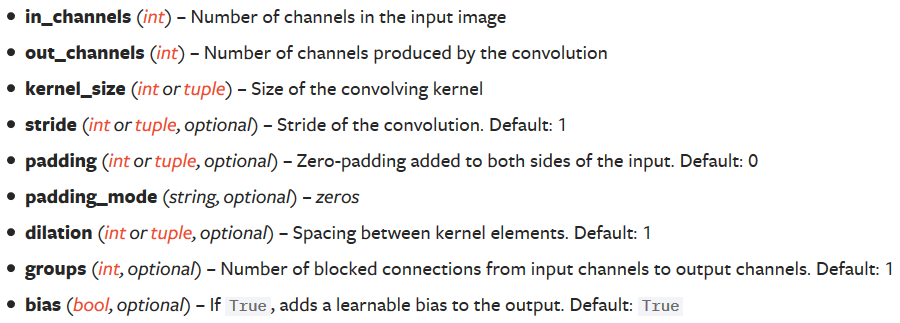
CLASS torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
eg:torch.nn.functional
torch.nn.functional.conv2d(input, weight, bias=None, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1) → Tensor
从中,我们可以发现,nn.Conv2d 是一个类,而 nn.functional.conv2d是一个函数。
换言之:
- nn.Module 实现的 layer 是由 class Layer(nn.Module) 定义的特殊类
- nn.functional 中的函数更像是纯函数,由 def function(input) 定义
此外:
-
两者的调用方式不同:调用 nn.xxx 时要先在里面传入超参数,然后再将数据以函数调用的方式传入 nn.xxx
# torch.nn inputs = torch.randn(64, 3, 244, 244) self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, padding=1) outputs = self.conv(inputs) # torch.nn.functional 需要同时传入数据和 weight,bias等参数 inputs = torch.randn(64, 3, 244, 244) weight = torch.randn(64, 3, 3, 3) bias = torch.randn(64) outputs = nn.functinoal.conv2d(inputs, weight, bias, padding=1) -
nn.xxx 能够放在 nn.Sequential里,而 nn.functional.xxx 就不行
-
nn.functional.xxx 需要自己定义 weight,每次调用时都需要手动传入 weight,而 nn.xxx 则不用
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F # torch.nn 定义的CNN class CNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(CNN, self).__init__() self.conv_1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 16, krenel_size=5, padding=0) self.relu_1 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.maxpool_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2) self.conv_2 = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, krenel_size=5, padding=0) self.relu_2 = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.maxpool_2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2) self.linear = nn.Linear(4*4*32, 10) def forward(self, x): x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) out = self.maxpool_1(self.relu_1(self.conv_1(x))) out = self.maxpool_2(self.relu_2(self.conv_2(out))) out = self.linear(out.view(x.size(0), -1)) return out # torch.nn.functional 定义一个相同的CNN class CNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(CNN, self).__init__() self.conv_1_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(16, 1, 5, 5)) self.bias_1_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(16)) self.conv_2_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(32, 16, 5, 5)) self.bias_2_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(32)) self.linear_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(4 * 4 * 32, 10)) self.bias_weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(10)) def forward(self, x): x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) out = F.conv2d(x, self.conv_1_weight, self.bias_1_weight) out = F.conv2d(out, self.conv_2_weight, self.bias_2_weight) out = F.linear(out.view(x.size(0), -1), self.linear_weight, self.bias_weight) -
在使用Dropout时,推荐使用 nn.xxx。因为一般只有训练时才使用 Dropout,在验证或测试时不需要使用 Dropout。使用 nn.Dropout时,如果调用 model.eval() ,模型的 Dropout 层都会关闭;但如果使用 nn.functional.dropout,在调用 model.eval() 时,不会关闭 Dropout。
-
当我们想要自定义卷积核时,是不能使用
torch.nn.ConvNd的,因为它里面的权重都是需要学习的参数,没有办法自行定义。但是,我们可以使用torch.nn.functional.conv2d()。
References: