常用类之Random
Random类位于 java.util 包中,主要用于生成伪随机数
Random类将种子数作为随机算法的起源数字,计算生成伪随机数,其与生成的随机数字的区间无关
创建Random实例时,若没有指定种子数,则会以当前时间作为种子数,来计算生成伪随机数
拥有相同种子的Random实例,在相同次数下,生成的伪随机数完全相同
构造器
// 创建一个新的随机数生成器。
Random()
// 使用单个 long 种子创建一个新的随机数生成器。
Random(long seed)
// 相同种子生成的随机数是一样的
常用方法
// 返回下一个伪随机数,它是此随机数生成器的序列中均匀分布的 int 值
int nextInt()
// 返回一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的、在 [0,n) 之间均匀分布的 int 值。
int nextInt(int n)
// 返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的、在 0.0 和 1.0 之间均匀分布的 double 值
double nextDouble()
// 返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的、在 0.0 和 1.0 之间均匀分布的 float 值
float nextFloat()
// 返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的均匀分布的 boolean 值
boolean nextBoolean()
// 生成随机字节并将其置于用户提供的 byte 数组中
void nextBytes(byte[] bytes)
// 返回下一个伪随机数,它是取自此随机数生成器序列的均匀分布的 long 值
long nextLong()
// 使用单个 long 种子设置此随机数生成器的种子
void setSeed(long seed)
例子1:
Random r = new Random();
System.out.println(r.nextDouble());
System.out.println(r.nextBoolean());
System.out.println("-> " + r.nextInt());
System.out.println("---------------");
// 相同的种子,生成的随机数是一样
Random r2 = new Random(10);
Random r3 = new Random(10);
System.out.println("-> " + r2.nextInt()); // -1157793070
System.out.println("-> " + r3.nextInt()); // -1157793070
// 生成34到179之间的随机数 : 34 + [0 145)
System.out.println(r.nextInt(145) + 34);
例子2:UUID
// UUID:通用唯一识别符
// 在一台机器 上生成 的数字
// 当前的时间,跟当前电脑网卡 生成一段字符
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println(uuid);
例子3:验证码
// 生成验证码
// 5位的随机数 UUID生成的是16进制
String res = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println(res);
res = res.substring(0, 5);
System.out.println(res);
System.out.println("--------------------");
String str = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
str = str + str.toLowerCase();
str += "0123456789";
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(str.length());
// 从所有的字符当中随机生成5个出来
// 随机取5个出来
// 每取出一个结果,在原来的基础 上面进行拼接
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// 角标要随机的值 (0 62:字符串的长度)
int index = new Random().nextInt(str.length());
char ch = str.charAt(index);
sb.append(ch);
}
System.out.println(sb);
常用类之Date
之前,我们定义员工年龄和入职日期是用 int 和 String 来定义的。
class Employee {
int age;
String hireDate;
}
这样每过一年,都要修改年龄;或者要计算员工的工龄不方便。java当中专门提供了日期类型。
构造器
// 使用当前日期和时间来初始化对象(精确到毫秒)。
Date()
// 第二个构造函数接收一个参数,该参数是从1970年1月1日 00:00:00 起的毫秒数。
Date(long date)
e.g. 获取当前日期时间
// 创建 一个日期对象
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
// 获取当前时间的毫秒数
long curTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 把一个毫秒值 转成日期类型
Date date2 = new Date(curTime);
System.out.println(date2);
以上两个两段代码其实是一样的,看下Data()的源码,本质就是用系统当前时间的毫秒数来创建Date对象
public Date() {
this(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
e.g. Java 休眠(sleep)
try {
System.out.println(new Date() + "
");
Thread.sleep(1000 * 3); // 休眠3秒
System.out.println(new Date() + "
");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常!");
}
日期比较
// 测试此日期是否在指定日期之后
boolean after(Date when)
// 测试此日期是否在指定日期之前
boolean before(Date when)
// 比较两个日期的顺序
int compareTo(Date anotherDate)
// 比较两个日期的相等性
boolean equals(Object obj)
e.g.
// 创建 一个日期对象
Date date = new Date(1564387266239L); // 毫秒数大 时间迟
Date date2 = new Date(1564211606445L); // 毫秒数小 时间早
System.out.println(date); // Mon Jul 29 16:01:06 GMT+08:00 2019
System.out.println(date2); // Sat Jul 27 15:13:26 GMT+08:00 2019
System.out.println(date.before(date2)); // false
System.out.println(date.after(date2)); // true
System.out.println(date.compareTo(date2)); // 1
System.out.println(date.equals(date2)); // false
获取和设置时间毫秒值:Date和毫秒值转化
long getTime()
void setTime(long time)
e.g.
// 创建 一个日期对象
Date date = new Date();
Date date2 = new Date();
long time = date.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
date2.setTime(1564387266239L);
// 输出的字符串不符合中文习惯
System.out.println(date2);
// toLocaleString 已经过时了,不建议使用,这里暂时使用
System.out.println(date2.toLocaleString());
日期格式化 DateFormat
创建日期格式化对象:
// 获取日期和时间使用 SHORT 风格的默认日期/时间格式器
static DateFormat getInstance()
// 获取日期和时间使用 默认(DEFAULT) 风格的日期/时间格式器
static DateFormat getDateTimeInstance()
// 获取日期和时间使用 给定日期和时间格式化风格的日期/时间格式器
static DateFormat getDateTimeInstance(int dateStyle, int timeStyle)
// 获取使用 默认(DEFAULT) 风格的日期格式器
static DateFormat getDateInstance()
// 获取使用 给定格式化风格的日期格式器
static DateFormat getDateInstance(int style)
// 获取使用 默认(DEFAULT) 风格的时间格式器
static DateFormat getTimeInstance()
// 获取使用 给定格式化风格的时间格式器
static DateFormat getTimeInstance(int style)
e.g.
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(date.toLocaleString());
System.out.println("------------日期格式化------------");
// 获取为日期和时间使用 SHORT 风格的默认日期/时间格式器
DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getInstance();
// 相当于 : DateFormat df1 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance
// (DateFormat.SHORT, DateFormat.SHORT);
// 对指定的日期进行格式化: Date -> String
String time = df1.format(date);
System.out.println("SHORT 风格: " + time);
// 获取为日期和时间使用 默认(DEFAULT) 风格的日期/时间格式器
DateFormat df2 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance();
// 相当于 : DateFormat df2 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance
// (DateFormat.DEFAULT, DateFormat.DEFAULT);
System.out.println("DEFAULT 风格: " + df2.format(date));
DateFormat df3 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, DateFormat.MEDIUM);
System.out.println("MEDIUM 风格: " + df3.format(date));
DateFormat df4 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG, DateFormat.LONG);
System.out.println("LONG 风格: " + df4.format(date));
DateFormat df5 = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FULL, DateFormat.FULL);
System.out.println("FULL 风格: " + df5.format(date));
输出结果:
Mon Jul 29 17:16:05 GMT+08:00 2019
2019-7-29 17:16:05
------------日期格式化------------
SHORT 风格: 19-7-29 下午5:16
DEFAULT 风格: 2019-7-29 17:16:05
MEDIUM 风格: 2019-7-29 17:16:05
LONG 风格: 2019年7月29日 下午05时16分05秒
FULL 风格: 2019年7月29日 星期一 下午05时16分05秒 GMT+08:00
日期和String的转换
(1)Date -> String : format 格式化
Date date = new Date();
DateFormat df = DateFormat.getInstance();
String format = df.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
(2)String -> Date : parse 解析
DateFormat df = DateFormat.getInstance();
String source = "19-7-29 下午5:23";
try {
Date parse = df.parse(source);
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("日期字符串格式错误!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
自定义日期格式化 SimpleDateFormat
模式字母:
| 字母 | 日期或时间元素 | 表示 |
|---|---|---|
| y | 年 | Year |
| M | 年中的月份 | Month |
| w | 年中的周数 | Number |
| W | 月份中的周数 | Number |
| D | 年中的天数 | Number |
| d | 月份中的天数 | Number |
| F | 月份中的星期 | Number |
| E | 星期中的天数 | Text |
| a | Am/pm 标记 | Text |
| H | 一天中的小时数(0-23) | Number |
| k | 一天中的小时数(1-24) | Number |
| K | am/pm 中的小时数(0-11) | Number |
| h | am/pm 中的小时数(1-12) | Number |
| m | 小时中的分钟数 | Number |
| s | 分钟中的秒数 | Number |
| S | 毫秒数 | Number |
| z | 时区 | General time zone |
| Z | 时区 | RFC 822 time zone |
构造器
常用的两个:
// 用默认的模式和默认语言环境的日期格式符号构造
SimpleDateFormat()
// 用给定的模式和默认语言环境的日期格式符号构造
SimpleDateFormat(String pattern)
常用方法
// 将给定模式字符串应用于此日期格式
void applyPattern(String pattern)
// 返回描述此日期格式的模式字符串
String toPattern()
e.g.
Date date = new Date();
// 自定义日期格式化
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
// 获得默认的模式
System.out.println(sdf.toPattern()); // yy-M-d ah:mm
// 用默认的模式格式化
System.out.println(sdf.format(date)); // 19-7-29 下午8:19
// 定义自己想要什么 样的模式
String pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss E";
sdf.applyPattern(pattern);
// 以指定的模式格式化哪个日期
String res = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(res); // 2019-07-29 20:19:37 星期一
// 自定义日期格式化
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss E");
System.out.println(sdf2.toPattern()); // yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss E
System.out.println(sdf2.format(date)); // 2019-07-29 20:19:37 星期一
日期格式化 格式化字符串输出
标准的
| 转 换 符 | 说 明 | 示 例 |
|---|---|---|
| c | 包括全部日期和时间信息 | 星期一 七月 29 21:54:44 GMT+08:00 2019 |
| F | "年-月-日"格式 | 2019-07-29 |
| D | "月/日/年"格式 | 07/29/19 |
| r | "HH:MM:SS PM"格式(12时制) | 09:54:44 下午 |
| T | "HH:MM:SS"格式(24时制) | 21:54:44 |
| R | "HH:MM"格式(24时制) | 21:54 |
e.g.
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("%tc", date)); // 星期一 七月 29 21:57:57 GMT+08:00 2019
System.out.println(String.format("%tF", date)); // 2019-07-29
System.out.println(String.format("%tD", date)); // 07/29/19
System.out.println(String.format("%tr", date)); // 09:57:57 下午
System.out.println(String.format("%tT", date)); // 21:57:57
System.out.println(String.format("%tR", date)); // 21:57
/*
* 组合:
* (1)可以利用一个格式化字符串指出要被格式化的参数的索引。
* 索引必须紧跟在%后面,而且必须以$结束。
* 或者
* (2)你可以使用 < 标志。它表明先前被格式化的参数要被再次使用
*/
System.out.println(String.format("%1$s %2$tF %2$tT", "Due date:", date)); // Due date: 2019-07-29 21:57:57
System.out.println(String.format("%tF %<tT", date)); // 2019-07-29 21:57:57
自定义
日期:
| 转 换 符 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| y | 日期的二位数的年份(如99) |
| m | 日期的月份 |
| d | 日期的日号 |
| Y | 日期的四位数的年份(如1999) |
| B | 日期的月份的完整名 |
| b | 日期的月份的简称 |
e.g.
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("%ty", date)); // 19
System.out.println(String.format("%tm", date)); // 07
System.out.println(String.format("%td", date)); // 29
System.out.println(String.format("%tY", date)); // 2019
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.US, "%tB", date)); // July
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.US, "%tb", date)); // Jul
System.out.println(String.format("%tB %<tb", date)); // 七月 七月
时间:
| 转 换 符 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| H | 时间的时(24进制) |
| I | 时间的时(12进制) |
| M | 时间的分 |
| S | 时间的秒 |
| L | 时间的秒中的毫秒数 |
| p | 时间是上午还是下午 |
e.g.
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("%tH:%<tM:%<tS; %<tI:%<tM:%<tS", date)); // 22:27:47; 10:27:47
System.out.println(String.format("%tH:%<tM:%<tS.%<tL %<tp", date)); // 22:27:47.274 下午
星期:
| 转 换 符 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| A | 日期的星期全称 |
| a | 日期的星期简称 |
e.g.
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("%tH:%<tM:%<tS %<tA", date)); // 22:31:41 星期一
System.out.println(String.format("%tH:%<tM:%<tS %<ta", date)); // 22:31:41 星期一
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.US, "%tH:%<tM:%<tS %<tA", date)); // 22:31:41 Monday
System.out.println(String.format(Locale.US, "%tH:%<tM:%<tS %<ta", date)); // 22:31:41 Mon
日历类
使用Calendar类 可以设置和获取日期数据的特定部分,比如说小时,日,或者分钟。
我们也可以在日期的这些部分加上或者减去值(日期的加减)
创建日历类对象:
// 使用默认时区和语言环境获得一个日历
static Calendar getInstance()
常用方法
// 返回给定日历字段的值
int get(int field)
// 将给定的日历字段设置为给定值
void set(int field, int value)
// 返回一个表示此 Calendar 时间值的 Date 对象
Date getTime()
// 使用给定的 Date 设置此 Calendar 的时间
void setTime(Date date)
// 返回此 Calendar 的时间值,以毫秒为单位
long getTimeInMillis()
// 用给定的 long 值设置此 Calendar 的当前时间值
void setTimeInMillis(long millis)
// 设置日历字段 YEAR、MONTH 和 DAY_OF_MONTH 的值
void set(int year, int month, int date)
// 设置日历字段 YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR_OF_DAY 和 MINUTE 的值
void set(int year, int month, int date, int hourOfDay, int minute)
// 设置字段 YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR、MINUTE 和 SECOND 的值
void set(int year, int month, int date, int hourOfDay, int minute, int second)
// 根据日历的规则,为给定的日历字段添加或减去指定的时间量
abstract void add(int field, int amount)
// 比较两个 Calendar 对象表示的时间值
int compareTo(Calendar anotherCalendar)
e.g.
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(String.format("%tF %<tT %<ta",c.getTime()));
System.out.println("-----------");
System.out.println("年= " + c.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println("月= " + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1)); // 获取是从0开始,所以加1
System.out.println("日= " + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println("时= " + c.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println("分= " + c.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println("秒= " + c.get(Calendar.SECOND));
System.out.println("星期= " + (c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK) - 1));
System.out.println("-----------");
// 加上3天 (正:3天之后;负:3天之前)
c.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 3);
System.out.println(String.format("%tF %<tT %<ta",c.getTime()));
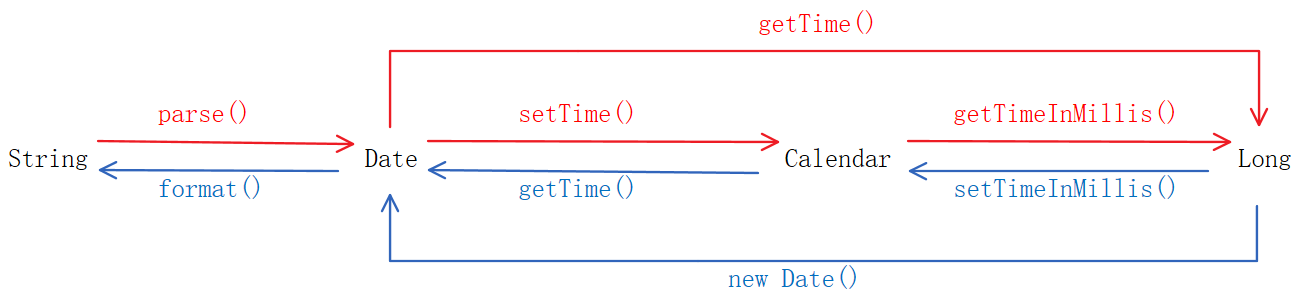
日期类型转换小结
String Long Date Calendar
(1)String <——> Date
// String -> Date 解析parse
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
String source = "2019-7-29";
try {
Date parse = sdf1.parse(source);
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("日期字符串格式错误!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Date -> String 格式化format
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss E");
String format = sdf2.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
// Date -> String 格式化String
Date date2 = new Date();
System.out.println(String.format("%tF %<tT %<tA", date2));
(2)String <——> Calendar
// String -> Calendar (String -> Date -> Calendar)
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
String source = "2019-7-29";
try {
Date parse = sdf1.parse(source);
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
c1.setTime(parse);
System.out.print(c1.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + (c1.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "-" + c1.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
System.out.println(" " + c1.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY) + ":" + c1.get(Calendar.MINUTE) + ":" + c1.get(Calendar.SECOND));
} catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("日期字符串格式错误!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Calendar -> String (Calendar -> Date -> String)
Calendar c2 = Calendar.getInstance();
Date date = c2.getTime();
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss E");
String format = sdf2.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
(3)Long <——> Date
// Date -> Long
Date date1 = new Date();
long time1 = date1.getTime();
System.out.println(time1);
// Long -> Date
long time2 = 1564414169841L;
Date date2 = new Date(time2);
System.out.println(date2);
(4)Long <——> Calendar
// Long -> Calendar
long time1 = 1564414169841L;
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
c1.setTimeInMillis(time1);
System.out.println(String.format("%tF %<tT %<ta", c1.getTime()));
// Calendar -> Long
Calendar c2 = Calendar.getInstance();
long time2 = c2.getTimeInMillis();
System.out.println(time2);
(5)Date <——> Calendar
// Date <——> Calendar
// Date -> Calendar
Date date1 = new Date();
Calendar c1 = Calendar.getInstance();
c1.setTime(date1);
System.out.println(String.format("%tF %<tT %<ta", c1.getTime()));
// Calendar -> Date
Calendar c2 = Calendar.getInstance();
Date date2 = c2.getTime();
System.out.println(date2);
LocalDate 日期时间(Java 8)
在旧版的 Java 中,日期时间 API 存在诸多问题,其中有:
(1)非线程安全
java.util.Date 是非线程安全的,所有的日期类都是可变的,这是Java日期类最大的问题之一。
(2)设计很差
Java的日期/时间类的定义并不一致,在java.util和java.sql的包中都有日期类,此外用于格式化和解析的类在java.text包中定义。java.util.Date同时包含日期和时间,而java.sql.Date仅包含日期,将其纳入java.sql包并不合理。另外这两个类都有相同的名字,这本身就是一个非常糟糕的设计。
(3)时区处理麻烦
日期类并不提供国际化,没有时区支持,因此Java引入了java.util.Calendar和java.util.TimeZone类,但他们同样存在上述所有的问题。
Java 8 在 java.time 包下提供了很多新的 API。以下为两个比较重要的 API:
Local(本地) : 简化了日期时间的处理,没有时区的问题。
Zoned(时区) : 通过制定的时区处理日期时间。
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(2019, 5, 20);
System.out.println(String.format("%tF",c.getTime())); // 2019-06-20
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2019, 5, 20);
System.out.println(date); // 2019-05-20

可以看到旧版计算结果面向机器,对人不够友好。
创建 LocalDateTime/LocalDate/LocalTime 对象
// of : 根据指定的日期和时间创建对象
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2019, 7, 30, 9, 30, 0);
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2019, 7, 30);
LocalTime time = LocalTime.of(9, 30, 0);
// now : 根据当前的日期和时间创建对象
LocalDateTime dateTime2 = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime time2 = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime类包含了LocalDate类和LocalTime类。
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDate localDate = localDateTime.toLocalDate();
LocalTime localTime = localDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localTime);
运行结果
2019-07-31T12:40:00.134
2019-07-31
12:40:00.134
获取日期的年月日周时分秒
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
int dayOfYear = dateTime.getDayOfYear();
int dayOfMonth = dateTime.getDayOfMonth();
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = dateTime.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println("今天是" + dateTime);
System.out.println("本年当中第" + dayOfYear + "天");
System.out.println("本月当中第" + dayOfMonth + "天");
System.out.println("本周中星期" + dayOfWeek.getValue() + "--即" + dayOfWeek);
// 获取当天时间的年月日时分秒
int year = dateTime.getYear();
Month month = dateTime.getMonth();
int day = dateTime.getDayOfMonth();
int hour = dateTime.getHour();
int minute = dateTime.getMinute();
int second = dateTime.getSecond();
System.out.println("今天是" + dateTime);
System.out.println("年 : " + year);
System.out.println("月 : " + month.getValue() + "--即 " + month);
System.out.println("日 : " + day);
System.out.println("时 : " + hour);
System.out.println("分 : " + minute);
System.out.println("秒 : " + second);
运行结果
今天是2019-07-30T18:00:36.022
本年当中第211天
本月当中第30天
本周中星期2--即TUESDAY
今天是2019-07-30T18:00:36.022
年 : 2019
月 : 7--即 JULY
日 : 30
时 : 18
分 : 0
秒 : 36
将年、月、日等修改为指定的值,并返回新的日期(时间)对象
如今天是2019-07-13,要想变为2019-07-20有两种方式
a. 相加指定的天数
b. 直接指定到哪一天
e.g.
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate withDayOfMonthResult = localDate.withDayOfMonth(20);
LocalDate plusDays = localDate.plusDays(-10L);
System.out.println("当前时间是 : " + localDate);
System.out.println("相加指定的天数:" + plusDays);
System.out.println("直接指定到哪一天: " + withDayOfMonthResult);
运行结果
当前时间是 : 2019-07-30
相加指定的天数:2019-07-20
直接指定到哪一天: 2019-07-20
e.g.
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
// 当前时间基础上,指定本年当中的第几天,取值范围为1-365,366
LocalDate withDayOfYearResult = localDate.withDayOfYear(200);
// 当前时间基础上,指定本月当中的第几天,取值范围为1-29,30,31
LocalDate withDayOfMonthResult = localDate.withDayOfMonth(5);
// 当前时间基础上,直接指定年份
LocalDate withYearResult = localDate.withYear(2017);
// 当前时间基础上,直接指定月份
LocalDate withMonthResult = localDate.withMonth(5);
System.out.println("当前时间是 : " + localDate);
System.out.println("指定本年当中的第200天 : " + withDayOfYearResult);
System.out.println("指定本月当中的第5天 : " + withDayOfMonthResult);
System.out.println("直接指定年份为2017 : " + withYearResult);
System.out.println("直接指定月份为5月 : " + withMonthResult);
运行结果
当前时间是 : 2019-07-30
指定本年当中的第200天 : 2019-07-19
指定本月当中的第5天 : 2019-07-05
直接指定年份为2017 : 2017-07-30
直接指定月份为5月 : 2019-05-30
日期时间的加减
对于LocalDate,只有精度大于或等于日的加减,如年、月、日;
对于LocalTime,只有精度小于或等于时的加减,如时、分、秒、纳秒;
对于LocalDateTime,则可以进行任意精度的时间相加减;
相加:
(1) plus(正数);
(2) minus(负数);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
// 以下方法的参数都是long型,返回值都是LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime plusYearsResult = localDateTime.plusYears(2L);
LocalDateTime plusMonthsResult = localDateTime.plusMonths(3L);
LocalDateTime plusDaysResult = localDateTime.plusDays(7L);
LocalDateTime plusHoursResult = localDateTime.plusHours(2L);
LocalDateTime plusMinutesResult = localDateTime.plusMinutes(10L);
LocalDateTime plusSecondsResult = localDateTime.plusSeconds(10L);
System.out.println("当前时间是 : " + localDateTime);
System.out.println("当前时间加2年后为 : " + plusYearsResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加3个月后为 : " + plusMonthsResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加7日后为 : " + plusDaysResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加2小时后为 : " + plusHoursResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加10分钟后为 : " + plusMinutesResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加10秒后为 : " + plusSecondsResult);
// 也可以以另一种方式来相加减日期,即plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
// 参数1 : 相加的数量, 参数2 : 相加的单位
LocalDateTime nextMonth = localDateTime.plus(1, ChronoUnit.MONTHS);
LocalDateTime nextYear = localDateTime.plus(1, ChronoUnit.YEARS);
LocalDateTime nextWeek = localDateTime.plus(1, ChronoUnit.WEEKS);
System.out.println("now : " + localDateTime);
System.out.println("nextYear : " + nextYear);
System.out.println("nextMonth : " + nextMonth);
System.out.println("nextWeek :" + nextWeek);
运行结果
当前时间是 : 2019-07-31T11:23:57.546
当前时间加2年后为 : 2021-07-31T11:23:57.546
当前时间加3个月后为 : 2019-10-31T11:23:57.546
当前时间加7日后为 : 2019-08-07T11:23:57.546
当前时间加2小时后为 : 2019-07-31T13:23:57.546
当前时间加10分钟后为 : 2019-07-31T11:33:57.546
当前时间加10秒后为 : 2019-07-31T11:24:07.546
now : 2019-07-31T11:23:57.546
nextYear : 2020-07-31T11:23:57.546
nextMonth : 2019-08-31T11:23:57.546
nextWeek :2019-08-07T11:23:57.546
相减:
(1) minus(正数);
(2) plus(负数);
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
// 以下方法的参数都是long型,返回值都是LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime minusYearsResult = localDateTime.minusYears(2L);
LocalDateTime minusMonthsResult = localDateTime.minusMonths(3L);
LocalDateTime minusDaysResult = localDateTime.minusDays(7L);
LocalDateTime minusHoursResult = localDateTime.minusHours(2L);
LocalDateTime minusMinutesResult = localDateTime.minusMinutes(10L);
LocalDateTime minusSecondsResult = localDateTime.minusSeconds(10L);
System.out.println("当前时间是 : " + localDateTime);
System.out.println("当前时间加2年前为 : " + minusYearsResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加3个月前为 : " + minusMonthsResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加7日前为 : " + minusDaysResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加2小时前为 : " + minusHoursResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加10分钟前为 : " + minusMinutesResult);
System.out.println("当前时间加10秒前为 : " + minusSecondsResult);
// 也可以以另一种方式来相加减日期,即minus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
// 参数1 : 相减的数量, 参数2 : 相减的单位
LocalDateTime lastMonth = localDateTime.minus(1, ChronoUnit.MONTHS);
LocalDateTime lastYear = localDateTime.minus(1, ChronoUnit.YEARS);
LocalDateTime lastWeek = localDateTime.minus(1, ChronoUnit.WEEKS);
System.out.println("now : " + localDateTime);
System.out.println("lastYear : " + lastYear);
System.out.println("lastMonth : " + lastMonth);
System.out.println("lastWeek :" + lastWeek);
运行结果
当前时间是 : 2019-07-31T12:33:36.843
当前时间加2年前为 : 2017-07-31T12:33:36.843
当前时间加3个月前为 : 2019-04-30T12:33:36.843
当前时间加7日前为 : 2019-07-24T12:33:36.843
当前时间加2小时前为 : 2019-07-31T10:33:36.843
当前时间加10分钟前为 : 2019-07-31T12:23:36.843
当前时间加10秒前为 : 2019-07-31T12:33:26.843
now : 2019-07-31T12:33:36.843
lastYear : 2018-07-31T12:33:36.843
lastMonth : 2019-06-30T12:33:36.843
lastWeek :2019-07-24T12:33:36.843
时间日期的格式化
(1)使用jdk自身配置好的日期格式
// 使用jdk自身配置好的日期格式
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME;
LocalDateTime date = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(date);
String format1 = dtf.format(date);
// 反过来调用也可以
String format2 = date.format(dtf);
System.out.println(format1);
System.out.println(format2);
运行结果
2019-07-31T11:34:01.899
2019-07-31T11:34:01.899
2019-07-31T11:34:01.899
(2)使用自定义格式
LocalDateTime date = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
String format = dtf.format(date);
System.out.println(date);
System.out.println(format);
运行结果
2019-07-31T11:37:12.673
2019年07月31日 11:37:12
注:自定义转化的格式一定要与日期类型对应
-
LocalDate只能设置仅含年月日的格式
-
LocalTime只能设置仅含时分秒的格式
-
LocalDateTime可以设置含年月日时分秒的格式
将时间字符串形式转化为日期对象
String datetime = "2018-01-13 21:27:30";
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime ldt = LocalDateTime.parse(datetime, dtf);
System.out.println(ldt);
运行结果
2018-01-13T21:27:30
注:格式的写法必须与字符串的形式一样,否则会报运行时异常!
-
2018-01-13 21:27:30 对应 yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
-
20180113213328 对应 yyyyMMddHHmmss
时间日期前后的比较与判断
// 判断两个时间点的前后
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2017, 8, 8);
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.of(2018, 8, 8);
boolean before = date1.isBefore(date2);
boolean after = date1.isAfter(date2);
System.out.println(before); // true
System.out.println(after); // false
判断是否为闰年,该年/该月有多少天
LocalDate date = LocalDate.of(2000, 2, 21);
System.out.println("date : " + date);
System.out.println("is leap year ? " + date.isLeapYear());
System.out.println("There are " + date.lengthOfYear() + " days in the current year");
System.out.println("There are " + date.lengthOfMonth() + " days in the current month.");
运行结果
date : 2000-02-21
is leap year ? true
There are 366 days in the current year
There are 29 days in the current month.
时间戳
事实上Instant就是java8以前的Date,可以使用以下两个类中的方法在这两个类型之间进行转换。
比如Date.from(Instant)就是用来把Instant转换成java.util.date的,而new Date().toInstant()就是将Date转换成Instant的
Instant instant = Instant.now();
System.out.println(instant);
Date date = Date.from(instant);
System.out.println(date);
Instant instant2 = date.toInstant();
System.out.println(instant2);
运行结果
2019-07-31T04:02:09.942Z
Wed Jul 31 12:02:09 GMT+08:00 2019
2019-07-31T04:02:09.942Z
LocalDateTime和Date的转换
// Date转换为LocalDateTime
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
System.out.println(instant);
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(instant, ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println(dateTime);
// 链式
System.out.println(LocalDateTime.ofInstant(date.toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault()));
System.out.println("--------------------");
// LocalDateTime转换为Date
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
ZonedDateTime atZone = now.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault());
System.out.println(atZone);
Instant instant2 = atZone.toInstant();
System.out.println(instant2);
Date date2 = Date.from(instant2);
System.out.println(date2);
// 链式
System.out.println(Date.from(now.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant()));
运行结果
Wed Jul 31 12:15:57 GMT+08:00 2019
2019-07-31T04:15:57.060Z
2019-07-31T12:15:57.060
2019-07-31T12:15:57.060
--------------------
2019-07-31T12:15:57.140
2019-07-31T12:15:57.140+08:00[GMT+08:00]
2019-07-31T04:15:57.140Z
Wed Jul 31 12:15:57 GMT+08:00 2019
Wed Jul 31 12:15:57 GMT+08:00 2019
计算时间、日期间隔
Duration:用于计算两个“时间”间隔
Period:用于计算两个“日期”间隔
// 计算两个日期的日期间隔-年月日
LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2018, 2, 13);
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.of(2017, 3, 12);
// 内部是用date2-date1,所以得到的结果是负数
Period period = Period.between(date1, date2);
System.out.println("相差年数 : " + period.getYears());
System.out.println("相差月数 : " + period.getMonths());
System.out.println("相差日数 : " + period.getDays());
// 还可以这样获取相差的年月日
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
long years = period.get(ChronoUnit.YEARS);
long months = period.get(ChronoUnit.MONTHS);
long days = period.get(ChronoUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("相差的年月日分别为 : " + years + ", " + months + ", " + days);
// 注意,当获取两个日期的间隔时,并不是单纯的年月日对应的数字相加减,而是会先算出具体差多少天,在折算成相差几年几月几日的
// 计算两个时间的间隔
System.out.println("-------------------------------");
LocalDateTime date3 = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime date4 = LocalDateTime.of(2018, 1, 13, 22, 30, 10);
Duration duration = Duration.between(date3, date4);
System.out.println(date3 + " 与 " + date4 + " 间隔 " + "
" + " 天 :" + duration.toDays() + "
" + " 时 :"
+ duration.toHours() + "
" + " 分 :" + duration.toMinutes() + "
" + " 毫秒 :" + duration.toMillis()
+ "
" + " 纳秒 :" + duration.toNanos() + "
");
// 注意,并没有获得秒差的,但既然可以获得毫秒,秒就可以自行获取了
运行结果
相差年数 : 0
相差月数 : -11
相差日数 : -1
-------------------------------
相差的年月日分别为 : 0, -11, -1
-------------------------------
2019-07-31T12:20:56.624 与 2018-01-13T22:30:10 间隔
天 :-563
时 :-13525
分 :-811550
毫秒 :-48693046624
纳秒 :-48693046624000000
当计算程序的运行时间时,应当使用时间戳Instant
Instant ins1 = Instant.now();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) {
// 循环一百万次
}
Instant ins2 = Instant.now();
Duration duration = Duration.between(ins1, ins2);
System.out.println("程序运行耗时为 : " + duration.toMillis() + "毫秒");
long毫秒值转换为日期
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
long timeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(timeMillis);
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(instant, ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
String format = dtf.format(dateTime);
System.out.println(format);