一、运算符重载
运算符重载(Operator Overloading):让一个运算符可以有不同的功能。
已经熟知的运算符重载,如‘+’,可以对不同类型的(int,float)的数据进行加法操作;'<<’既是位移运算符,又可以配合 cout 向控制台输出数据。
C++允许程序员自己重载运算符。
以下代码定义了一个复数类,通过运算符重载,可以用+号实现复数的加法运算:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 //多行注释:Ctrl+k+c 5 //取消注释:Ctrl+k+u 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 class complex { 10 public: 11 complex(); 12 complex(double real, double imag); 13 public: 14 //声明运算符重载 15 complex operator + (const complex & A) const; 16 void display() const; 17 private: 18 double m_real; //实部 19 double m_imag; //虚部 20 }; 21 22 complex::complex() :m_real(0.0), m_imag(0.0) {} 23 complex::complex(double real, double imag) :m_real(real), m_imag(imag) {} 24 25 //实现运算符重载 26 complex complex::operator+(const complex& A) const { 27 complex B; 28 B.m_real = this->m_real + A.m_real; 29 B.m_imag = this->m_imag + A.m_imag; 30 return B; 31 } 32 33 void complex::display() const { 34 cout << m_real << "+" << m_imag << "i" << endl; 35 } 36 37 int main() { 38 complex c1(4.5, 5.8); 39 complex c2(2.4, 3.6); 40 complex c3; 41 c3 = c1 + c2; 42 c3.display(); 43 44 return 0; 45 }
以上是以成员函数来实现运算符重载,通过this指针来访问本身的对象的成员。
运行结果:
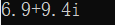
运算符重载其实就是定义一个函数,在函数体内实现想要的功能,当用到该运算符时,编译器会自动调用这个函数。即本质上是函数重载。
运算符重载的格式为:
返回值类型 operator 运算符名称 (形参表列){
//TODO:
}
operator是关键字,专门用于定义重载运算符的函数,可将“operate 运算符名称”这一部分看做函数名。
上面的例子中,我们在 complex 类中重载了运算符 + ,该重载只对 complex 对象有效。当执行 c3 = c1 + c2; 语句时,编译器检测到 + 号左边(+号具有左结合性,所以先检测左边)是一个 complex 对象,就会调用成员函数 operator+(),也就是转换为下面的形式:
c3 = c1.operator+(c2);
c1是要调用函数的对象,c2是函数的实参。
在全局范围内重载运算符
运算符重载函数不仅可以作为类的成员函数,还可以作为全局函数。

1 #include <iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 class complex{ 5 public: 6 complex(); 7 complex(double real, double imag); 8 public: 9 void display() const; 10 //声明为友元函数 11 friend complex operator+(const complex &A, const complex &B); 12 private: 13 double m_real; 14 double m_imag; 15 }; 16 17 complex operator+(const complex &A, const complex &B); 18 19 complex::complex(): m_real(0.0), m_imag(0.0){ } 20 complex::complex(double real, double imag): m_real(real), m_imag(imag){ } 21 void complex::display() const{ 22 cout<<m_real<<" + "<<m_imag<<"i"<<endl; 23 } 24 25 //在全局范围内重载+ 26 complex operator+(const complex &A, const complex &B){ 27 complex C; 28 C.m_real = A.m_real + B.m_real; 29 C.m_imag = A.m_imag + B.m_imag; 30 return C; 31 } 32 33 int main(){ 34 complex c1(4.3, 5.8); 35 complex c2(2.4, 3.7); 36 complex c3; 37 c3 = c1 + c2; 38 c3.display(); 39 40 return 0; 41 }
运算符重载函数不是complex类的成员函数,但是用到了类内的私有成员,所以必须将声明为友元函数。
当执行c3 = c1 + c2;语句时,编译器检测到+号两边都是 complex 对象,就会转换为类似下面的函数调用:
c3 = operator+(c1, c2);
小结:
运算符被重载后,原有的功能仍然保留,没有丧失或改变。通过运算符重载,扩大了C++已有运算符的功能,使之能用于对象。
1)实现一元运算符重载
用全局函数实现,前置++操作符 用成员函数实现 后置++操作符

1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class complex { 6 public: 7 complex(); 8 complex(double real, double imag); 9 friend complex& operator++(complex& c1); 10 11 public: 12 void display() const { cout << m_real << "+" << m_imag << "i" << endl; } 13 14 //用成员函数实现重载后置++ 添加无用参数作为占位符 15 complex operator++(int) { 16 complex temp; 17 this->m_real++; 18 this->m_imag++; 19 return temp; 20 } 21 22 private: 23 double m_real; 24 double m_imag; 25 }; 26 27 complex::complex() : m_real(0.0), m_imag(0.0) {} 28 complex::complex(double real, double imag) : m_real(real), m_imag(imag) {} 29 30 //重载前置++ 31 complex& operator++(complex& c1) { 32 c1.m_real++; 33 c1.m_imag++; 34 return c1; 35 } 36 37 int main() { 38 complex c1; 39 ++c1; 40 c1.display(); 41 42 c1++; 43 c1.display(); 44 }
2)实现<<运算符重载
用全局函数重载实现<<操作符

1 #include <iostream> 2 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class complex { 6 public: 7 complex(); 8 complex(double real, double imag); 9 10 public: 11 void display() const { cout << m_real << "+" << m_imag << "i" << endl; } 12 13 friend void operator<<(ostream& out, complex& c1); 14 15 private: 16 double m_real; 17 double m_imag; 18 }; 19 20 complex::complex() : m_real(0.0), m_imag(0.0) {} 21 complex::complex(double real, double imag) : m_real(real), m_imag(imag) {} 22 23 void operator<<(ostream& out, complex& c1) { 24 out << c1.m_real << "+" << c1.m_imag << "i" << endl; 25 } 26 27 int main() { 28 complex c1; 29 cout << c1; 30 }
cout << c1, 可以正常打印,但是对于cout << c1 <<"aaa"; 就会报错,提示第二个<<的左操作符为void
确实,重载<<后返回的是void,所以应该返回ostream类,以支持链式编程
class complex{ ... friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, complex& c1); ... }; ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, complex& c1) { out << c1.m_real << "+" << c1.m_imag << "i" << endl; return out; }
运算符重载的初衷是给类添加新的功能,方便类的运算,它作为类的成员函数是理所应当的,是首选的。
不过,类的成员函数不能对称地处理数据,程序员必须在(参与运算的)所有类型的内部都重载当前的运算符。
比如,cout << c1;
cout 是 ostream 类的对象,要想达到这个目标,就必须以全局函数(友元函数)的形式重载<<,否则就要修改标准库中的类,这显然不是我们所期望的。
所以友元函数重载运算符常用于运算符左右操作数类型不同的情况。
3)实现 [] , =, ==, != 运算符重载
函数返回值当左值,需要返回一个引用
通过一个数组类来实现

1 #ifndef ARRAY_H 2 #define ARRAY_H 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 class Array { 8 public: 9 Array(int length); 10 Array(const Array& obj); 11 ~Array(); 12 13 public: 14 void setData(int index, int value); 15 int getData(int index); 16 int length(); 17 18 private: 19 int m_length; 20 int* m_space; 21 22 public: 23 int& operator[](int i); 24 Array& operator=(Array& a); 25 bool operator==(Array& a); 26 }; 27 28 #endif

1 #include "array.h" 2 3 Array::Array(int length) { 4 if (length < 0) { 5 length = 0; 6 } 7 m_length = length; 8 m_space = new int[m_length]; 9 } 10 Array::Array(const Array& obj) { 11 this->m_length = obj.m_length; 12 this->m_space = new int[m_length]; 13 for (int i = 0; i < this->m_length; i++) { 14 this->m_space[i] = obj.m_space[i]; 15 } 16 } 17 Array::~Array() { 18 if (m_space != nullptr) { 19 delete[] m_space; 20 m_length = 0; 21 } 22 } 23 void Array::setData(int index, int value) { m_space[index] = value; } 24 int Array::getData(int index) { return m_space[index]; } 25 int Array::length() { return m_length; } 26 27 int& Array::operator[](int i) { return m_space[i]; } 28 Array& Array::operator=(Array& a) { 29 // 1.释放原来的内存 30 if (this->m_space != nullptr) { 31 delete[] m_space; 32 m_length = 0; 33 } 34 // 2.根据a的大小重新分配内存 35 m_length = a.m_length; 36 m_space = new int[m_length]; 37 // 3.拷贝数据 38 for (int i = 0; i < m_length; i++) { 39 m_space[i] = a.m_space[i]; 40 } 41 return *this; 42 } 43 44 bool Array::operator==(Array& a) { 45 if (m_length != a.m_length) { 46 return false; 47 } 48 for (int i = 0; i < m_length; i++) { 49 if (m_space[i] != a.m_space[i]) { 50 return false; 51 } 52 } 53 return true; 54 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 3 #include "array.h" 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int main() { 8 Array a(10); 9 Array a1(6); 10 Array a2(20); 11 a1 = a = a2; 12 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 13 a[i] = i; //函数返回值当左值,需要返回一个引用 14 } 15 16 for (int i = 0; i < a.length(); i++) { 17 cout << a[i] << " "; 18 } 19 20 cout << "a1:length=" << a1.length() << endl; 21 22 if (a1 == a) { 23 cout << "a == a1" << endl; 24 } 25 }
二、运算符重载时要遵循的规则
1、常见可被重载的运算符:
+ - * / % ^ & | ~ ! = < > += -= *= /= %= ^= &= |= << >> <<= >>= == != <= >= && || ++ -- , ->* -> () [] new new[] delete delete[]
[]是下标运算符,()是函数调用运算符。自增自减运算符的前置和后置形式都可以重载。长度运算符sizeof、条件运算符: ?、成员选择符.和域解析运算符::不能被重载。
2、重载不能改变运算符的优先级与结合性
3、重载不会改变运算符的用法
4、运算符重载函数不能有默认的参数,否则就改变了运算符操作数的个数
5、运算符重载函数既可以是类的成员函数,也可以是全局函数
三、是以成员函数还是以全局函数的形式重载运算符
1)只能重载为成员函数:“=”、“()”、“[ ]”、“->”等,与 this(自身)关联太多。
2)只能重载为友元函数:只能重载为友元函数:输出运算符 << ,第一个操作符一定是 ostream 。
