(一)抽象类的使用
- 设计一个类层次,定义一个抽象类--形状,其中包括有求形状的面积的抽象方法。 继承该抽象类定义三角型、矩形、圆。 分别创建一个三角形、矩形、圆存对象,将各类图形的面积输出。
注:三角形面积s=sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c)) 其中,a,b,c为三条边,p=(a+b+c)/2
2.编程技巧
(1) 抽象类定义的方法在具体类要实现;
(2) 使用抽象类的引用变量可引用子类的对象;
(3) 通过父类引用子类对象,通过该引用访问对象方法时实际用的是子类的方法。可将所有对象存入到父类定义的数组中。
实验代码:
```
package 实验报告5;
abstract class shape{
public abstract double print(); //定义抽象方法
}
class Triangle extends shape{
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
public Triangle(double a,double b,double c){
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
this.c=c;
}
public double print(){
double p=(a+b+c)/2;
return Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
}
}
class Rectangle extends shape{
private double height;
private double width;
public Rectangle(double height,double width){
this.height=height;
this.width=width;
}
public double print(){
return height*width;
}
}
class yuan extends shape{
private double radius;
public yuan(double radius){
this.radius=radius;
}
public double print(){
return Math.PI*Math.pow(radius, 2);
}
}
public class 实验报告5{
public static void main(String[] args){
Triangle Tr=new Triangle(8,9,10);
Rectangle Re=new Rectangle(4,5);
yuan yu=new yuan(6);
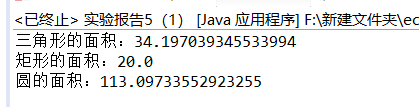
System.out.println("三角形的面积:"+Tr.print());
System.out.println("矩形的面积:"+Re.print());
System.out.println("圆的面积:"+yu.print());
}
}
```
实验截图:
(二)使用接口技术
1定义接口Shape,其中包括一个方法size(),设计“直线”、“圆”、类实现Shape接口。分别创建一个“直线”、“圆”对象,将各类图形的大小输出。
- 编程技巧
(1) 接口中定义的方法在实现接口的具体类中要重写实现;
(2) 利用接口类型的变量可引用实现该接口的类创建的对象。
接口
```
public interface Shape {
public double size();
public void print();
}
```
直线
```
public class Line implements Shape {
private double a;
private double b;
private double c;
private double d;
public double getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(double a) {
this.a = a;
}
public double getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(double b) {
this.b = b;
}
public double getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(double c) {
this.c = c;
}
public double getD() {
return d;
}
public void setD(double d) {
this.d = d;
}
public Line(double a,double b,double c,double d) {
this.a=a;
this.b=b;
this.c=c;
this.d=d;
}
public double size(){
return Math.sqrt((a-b)*(a-b)+(c-d)*(c-d));
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("直线的面积: "+this.size());
}
}
```
圆
```
public class Circle implements Shape{
private double radius;
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double size(){
return Math.PI*Math.pow(radius, 2);
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("圆的面积: "+this.size());
}
}
```
测试
```
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape s=new Line (16,12,20,26);
s.print();
Shape s1=new Circle (36);
s1.print();
}
```
总结:
一、接口
接口的声明语法格式:
```
interface 接口名称 [extends 其他的接口名] {
// 声明变量
// 抽象方法
}
```
二、抽象类:
1.是以abstract关键字声明的一个类
2.抽象类不可以被实例化。因为用抽象方法无意义。
3.抽象类必须由其子类覆盖了所有的抽象方法,该子类才可以被实例化,否则这个子类还是抽象类。
接口与类相似点
1.一个接口可以有多个方法。
2.接口文件保存在 .java 结尾的文件中,文件名使用接口名。
3.接口的字节码文件保存在 .class 结尾的文件中。