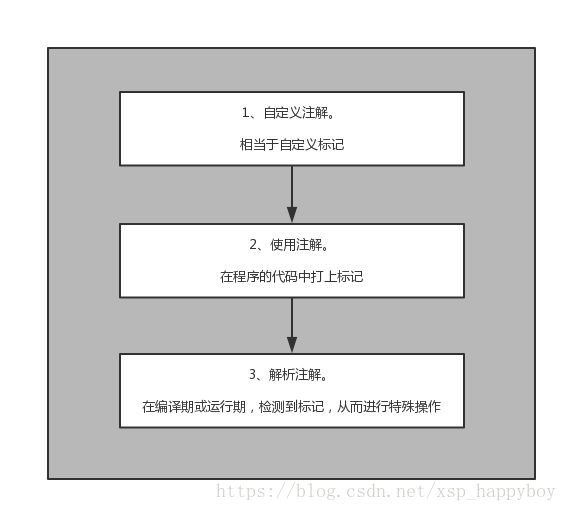
本文思路参考于用大白话聊聊JavaSE -- 自定义注解入门、自定义注解详解
0.背景
在写代码时,我们通常会加上一些注释,告诉开发人员这段代码的含义.eg:
/**
* @Description: 输入的Integer必须大于0
* @Author: Yiang37
* @Date: 2021/04/22 23:58:27
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public int checkIn(Integer integer) {
return integer > 0 ? integer : -1;
}
//...
写下的注释,让阅读代码的人了解到了这段代码所做的事情.
当然,注解是写给人看的,那么有没有一种方式,可以让程序知道这段代码想干什么事情呢?
注解,就是写给程序看的一种注释.
注解不会直接的代码产生影响,只是给程序中打上了标记,在编译或者运行期间进行处理.
1.注解的创建
// 没错.就是@interface
public @interface Annotation01 {
//...
}
1.1.1 元注解
元注解理解为描述注解的注解,元数据理解为描述数据的数据,元类理解为描述类的类…
在JDK中提供了4个标准的用来对注解类型进行注解的注解类(元注解),他们分别是:
所以,在Java中,除了有限的几个固定的"描述注解的注解"以外,所有的注解都是自定义注解。
@Target
@Retention
@Documented
@Inherited
2.注解要解决的问题
- 注解要用在哪里
- 注解在什么时候起作用
- 注解里包含哪些东西
2.1 注解要用在哪里 @Target()
eg: @Target(ElementType.METHOD) : 注解要用在方法上.
2.1.1 按住ctrl+p,可以看到期望输出一个ElementType类型的数组
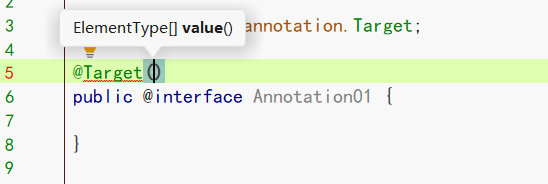
2.2.2 点击@Target进入后,可以看到@Target本身就是一个注解
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
public @interface Target {
/**
* Returns an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to.
* @return an array of the kinds of elements an annotation type
* can be applied to
*/
ElementType[] value();
}
2.2.3 点击去ElementType,可以看到具体的枚举值.
public enum ElementType {
/** 类,接口(包括注解类型)或枚举的声明 */
TYPE,
/** 属性的声明 */
FIELD,
/** 方法的声明 */
METHOD,
/** 方法形式参数声明 */
PARAMETER,
/** 构造方法的声明 */
CONSTRUCTOR,
/** 局部变量声明 */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,
/** 注解类型声明 */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,
/** 包的声明 */
PACKAGE
}
2.2.4 枚举示例
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) // 接口、类、枚举、注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD) // 字段、枚举的常量
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) // 方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) // 方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) // 构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE) // 局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) // 注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) // 包
2.2 注解在什么时候起作用 @Retention
eg: @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) : 我们希望在程序运行的时候,注解发挥作用.就是说,当你的程序跑起来了,电脑才开始阅读这些注解.
2.2.1 对应的类型
注解的生命周期有三个阶段
-
Java源文件阶段
如果一个注解被定义为RetentionPolicy.SOURCE,则它将被限定在Java源文件中,那么这个注解即不会参与编译也不会在运行期起任何作用,这个注解就和一个注释是一样的效果,只能被阅读Java文件的人看到;
-
编译到class文件阶段
在默认的情况下,自定义注解是使用的RetentionPolicy.CLASS.
如果一个注解被定义为RetentionPolicy.CLASS,则它将被编译到Class文件中,那么编译器可以在编译时根据注解做一些处理动作,但是运行时JVM(Java虚拟机)会忽略它,我们在运行期也不能读取到;
-
运行期阶段
如果一个注解被定义为RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,那么这个注解可以在运行期的加载阶段被加载到Class对象中。那么在程序运行阶段,我们可以通过反射得到这个注解,并通过判断是否有这个注解或这个注解中属性的值,从而执行不同的程序代码段。我们实际开发中的自定义注解几乎都是使用的RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME;
RetentionPolicy枚举类型定义了三个阶段:
public enum RetentionPolicy {
/**
* Annotations are to be discarded by the compiler.
* (注解将被编译器忽略掉)
*/
SOURCE,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler
* but need not be retained by the VM at run time. This is the default
* behavior.
* (注解将被编译器记录在class文件中,但在运行时不会被虚拟机保留,这是一个默认的行为)
*/
CLASS,
/**
* Annotations are to be recorded in the class file by the compiler and
* retained by the VM at run time, so they may be read reflectively.
* (注解将被编译器记录在class文件中,而且在运行时会被虚拟机保留,因此它们能通过反射被读取到)
* @see java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement
*/
RUNTIME
}
2.2.1 枚举示例
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) // 注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) // 默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
2.3 注解里包含哪些东西
- 访问修饰符必须为public,不写默认为public;
- 元素的类型只能是基本数据类型、String、Class、枚举类型、注解类型(体现了注解的嵌套效果)以及一维数组;
- 元素的名称一般定义为名词,如果注解中只有一个元素,请把名字起为value(后面使用会带来便利操作);
- ()不是定义方法参数的地方,也不能在括号中定义任何参数,仅仅只是一个特殊的语法;
- default代表默认值,值必须和第2点定义的类型一致;
- 如果没有默认值,代表后续使用注解时必须给该类型元素赋值。
eg:注解中包含一个String和int
public @interface Annotation01 {
String oneStr() default "this is one str";
int onData();
}
2.4 创建一个完整的注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface Annotation01 {
String oneStr() default "this is one str";
int onData();
}
3.注解的启用
@Annotation01(oneStr = "abc",onData = 1)
public class AnnotationTest01 {
}
4.注解的运用
上文中,用上注解后,我们好像什么也没做.
只是知道AnnotationTest01这个类上对应着一个@Annotation01的注解,里面有着oneStr = "abc",onData = 1两个字段.
注解的应用,是基于Java的反射.
/**
* @Description: Annotation01注解的应用
* @Class: Annotation01Explain
* @Author: Yiang37
* @Date: 2021/4/25 21:20
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class Annotation01Explain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
// 获取测试类AnnotationTest01对象
Class inClass = Class.forName("cn.yang37.annotation.p20214022.AnnotationTest01");
// 获取AnnotationTest01对象上的注解
Annotation declaredAnnotation = inClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(Annotation01.class);
if (declaredAnnotation instanceof Annotation01){
//转换为Annotation01对象
Annotation01 annotation01 = (Annotation01) declaredAnnotation;
System.out.println(annotation01.onData());
System.out.println(annotation01.oneStr());
}
}
}
输出
1234
abcd