- print两种写法
- 打印pytorch权重
- python os.path glob
- np.unique(b) numpy 去重
- 根据标签图和颜色表显示标签图
- pytorch继承的Dataset类的自己定义的OrientClassifyDataset,可以用iter next来迭代访问
- to_tensor || transforms.functional.to_tensor
- pytorch数据处理,继承的Dataset类的函数的单元测试
- pytorch保存模型两种方式
- shape[1,6] + shape[6,1] = shape[6,6]
- numpy 数组,[x1,y1,x2,y2,score,cls] 比如我有形状[100,6]这样的一个numpy数组,需要保留score大于0.8的,其余不要。如何写?
- 图片保持长宽比,缩放到固定尺寸
print两种写法
print('[Epoch: %d, numImages: %5d]' % (epoch, i * self.args.batch_size + image.data.shape[0]))
print("Acc:{}, Acc_class:{}, mIoU:{}, fwIoU: {}".format(Acc, Acc_class, mIoU, FWIoU))
print('Loss: %.3f' % test_loss)
print(f'The corresponding prune ratio is {percent_limit:.3f}.')
打印pytorch权重
model = model.cuda()
print("Model's state_dict:")
for param_tensor in model.state_dict():
print(param_tensor, " ", model.state_dict()[param_tensor].size())
print(model.state_dict()['backbone.layer1.0.conv1.weight'][0])
打印如下:
Model's state_dict:
backbone.conv1.weight torch.Size([64, 3, 7, 7])
backbone.bn1.weight torch.Size([64])
backbone.bn1.bias torch.Size([64])
backbone.bn1.running_mean torch.Size([64])
backbone.bn1.running_var torch.Size([64])
backbone.bn1.num_batches_tracked torch.Size([])
backbone.layer1.0.conv1.weight torch.Size([64, 64, 1, 1])
backbone.layer1.0.bn1.weight torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn1.bias torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn1.running_mean torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn1.running_var torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn1.num_batches_tracked torch.Size([])
backbone.layer1.0.conv2.weight torch.Size([64, 64, 3, 3])
backbone.layer1.0.bn2.weight torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn2.bias torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn2.running_mean torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn2.running_var torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.0.bn2.num_batches_tracked torch.Size([])
backbone.layer1.0.conv3.weight torch.Size([256, 64, 1, 1])
backbone.layer1.0.bn3.weight torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.bn3.bias torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.bn3.running_mean torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.bn3.running_var torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.bn3.num_batches_tracked torch.Size([])
backbone.layer1.0.downsample.0.weight torch.Size([256, 64, 1, 1])
backbone.layer1.0.downsample.1.weight torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.downsample.1.bias torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.downsample.1.running_mean torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.downsample.1.running_var torch.Size([256])
backbone.layer1.0.downsample.1.num_batches_tracked torch.Size([])
backbone.layer1.1.conv1.weight torch.Size([64, 256, 1, 1])
backbone.layer1.1.bn1.weight torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.1.bn1.bias torch.Size([64])
backbone.layer1.1.bn1.running_mean torch.Size([64])
...
tensor([[[-1.8738e-01]],
[[ 2.3853e-02]],
[[-2.1837e-02]],
[[-5.4712e-02]],
[[ 2.1917e-02]],
[[ 1.4151e-09]],
[[ 8.2899e-02]],
[[-1.8761e-08]],
[[-1.2909e-08]],
...
[[ 5.3678e-02]],
[[-1.3887e-08]],
[[-5.2007e-02]]], device='cuda:0')
model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'],strict=False)
strict=False表示名字对不上的就不加载,
默认是true,如果有名字不一致就报错
python os.path glob
directory = os.path.join(path_tmp, 'tmp', 'pascal')
aa = glob.glob(os.path.join(directory, 'experiment_*'))
print(directory)
# /data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal
print(aa)
# ['/data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_7', '/data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_0', '/data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_1']
bb = sorted(glob.glob(os.path.join(directory, 'experiment_*')))
print(bb)
# ['/data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_0', '/data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_1', '/data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_7']
id = 7
experiment_dir = os.path.join(directory, 'experiment_{}'.format(str(id)))
print(experiment_dir)
# /data_2/everyday/0815/tmp/pascal/experiment_7
这里'experiment_{}'.format(str(id) 写法可以代替字符串
2.提取文件名
path = '/data_2/fengjing'
file_name = os.path.basename(path)
np.unique(b) numpy 去重
import numpy as np
b = np.array([(1.5, 2, 3), (3, 5, 6),(1,2,3),(4,5,6)])
print(b)
print(b.shape)
a = np.unique(b)
print(a)
打印如下:
[[1.5 2. 3. ]
[3. 5. 6. ]
[1. 2. 3. ]
[4. 5. 6. ]]
(4, 3)
[1. 1.5 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. ]
这个可以用在:比如训练分割的时候数据检查。
例如:
标签图有16万,分割的标签图看起来都是黑的,里面的像素值代表类别,
说好的只有26个类别,但是训练的时候莫名其妙的报错,报cudnn的错误:
THCudaCheck FAIL file=/opt/conda/conda-bld/pytorch_1532581333611/work/aten/src/THC/THCCachingHostAllocator.cpp line=271 error=59 : device-side assert triggered
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/data_2/tmp_paper/image-segmentation/DeepLab/v3+/pytorch0.41/pytorch-deeplab-xception-master/train.py", line 339, in <module>
main()
File "/data_2/tmp_paper/image-segmentation/DeepLab/v3+/pytorch0.41/pytorch-deeplab-xception-master/train.py", line 298, in main
trainer.training(epoch)
File "/data_2/tmp_paper/image-segmentation/DeepLab/v3+/pytorch0.41/pytorch-deeplab-xception-master/train.py", line 108, in training
loss.backward()
File "/data_1/Yang/software_install/Anaconda1105/envs/pytorch0.4.1/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/tensor.py", line 93, in backward
torch.autograd.backward(self, gradient, retain_graph, create_graph)
File "/data_1/Yang/software_install/Anaconda1105/envs/pytorch0.4.1/lib/python3.6/site-packages/torch/autograd/__init__.py", line 90, in backward
allow_unreachable=True) # allow_unreachable flag
RuntimeError: CuDNN error: CUDNN_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED
搜cudnn的,都是乱七八糟的,没有可用的。
但是仔细看上面还有一个提示:
line=271 error=59 : device-side assert triggered
这句话百度,有人解答说是标签超过类别数了。
于是我就开始怀疑我的16万数据里面是不是有超过类别数的标签,分割的标签图看起来都是黑的,里面的像素值代表类别,我是26类,那么标签范围是0-25,所以
我就用上了np.unique这个函数,检查数据的代码如下:
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
txt_list = '/data_2/2019biaozhushuju/seg-chewaiguan/seg_chewaigaun_ding/se_chewaiguan_data/20190618_new/train.txt'
with open(txt_list,'r')as fr:
lines = fr.readlines()
for line in lines:
line = line.strip().split(' ')
_target = Image.open(line[1]).convert('L')
# _target.show()
targe = np.array(_target)
a = np.unique(targe)
max_val = max(a)
if max_val >= 26:
print (max_val, "::", line[1])
!!!果真,有打印!!!原来真有几张图片超过标签,坑爹啊,这个错误排查了2-3个小时!!!
根据标签图和颜色表显示标签图

import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
from PIL import Image
mmm = cv2.imread("/data_2/fengjing.jpg")
cv2.imshow("m",mmm)
cv2.waitKey(0)
#BGR
color_segmentation=np.asarray([
[0,0,0], #[0]背景
[180,120,120],
[6,230,230],
[80,50,50],
[4,200,3],
[120,120,80],
[140,140,140],
[204,5,255],
[230,230,230],
[4,250,7],
[40,150,255],
[235,255,7],
[150,5,61],
[120,120,70],
[8,255,51],
[255,6,82],
[143,255,140],
[204,255,4],
[255,51,7],
[204,70,3],
[0,102,200],
[61,230,250],
[255,6,51],
[11,102,255],
[255,7,71],
[255,9,224],
[9,7,230],
[220,220,220],
[255, 9, 92]
],dtype=np.uint8)
def decode_segmap(label_mask,n_classes = 21):
r = label_mask.copy()
g = label_mask.copy()
b = label_mask.copy()
for ll in range(0, n_classes):
# aaa = color_segmentation[ll, 1]
# position = label_mask == ll
b[label_mask == ll] = color_segmentation[ll, 0]
g[label_mask == ll] = color_segmentation[ll, 1]
r[label_mask == ll] = color_segmentation[ll, 2]
rgb = np.zeros((label_mask.shape[0], label_mask.shape[1], 3))
print(rgb[240][240])
rgb[:, :, 0] = b
rgb[:, :, 1] = g
rgb[:, :, 2] = r
# rgb[:, :, 0] = b / 255.0
# rgb[:, :, 1] = g / 255.0
# rgb[:, :, 2] = r /255.0
rgb = rgb.astype(np.uint8) ##重要! 要不然opencv显示有问题
print(rgb[240][240])
return rgb
root_dir = "/data_2/2019biaozhushuju/others/voc/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/SegmentationClassAug/"
list_gray_img = os.listdir(root_dir)
for img_name in list_gray_img:
path_gray = root_dir + img_name
laber_mask = cv2.imread(path_gray,0) ##灰度 单通道读取
# print(laber_mask.shape)
color_img = decode_segmap(laber_mask)
# print(color_img.shape)
# img1 = Image.fromarray(color_img.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
# img1.show()
cv2.imshow("laber_mask", laber_mask*20)
cv2.imshow("color",color_img)
cv2.waitKey()
这里直接放的正确的代码,一开始显示的图片有问题啊,没有颜色

找问题找了半天
aaa = color_segmentation[ll, 1]
print(rgb[240][240])
上面这个在代码里面打印出来的像素值是正常的,都是比如我上面的颜色表里面的,既然像素正常那显示为啥没有颜色呢?难道是我opencv出问题了吗。然后可以看开头我直接读取一张图片显示,是可以正常显示的,然后我加PIL库来显示,
img1 = Image.fromarray(color_img.astype('uint8')).convert('RGB')
显示出来的图像是彩色的,那为啥opencv显示有问题呢,然后我rgb[:, :, 0] = b / 255.0,然后发现opencv显示就正常了,好奇怪啊,/255就变为0-1之间了啊。。。反正很奇怪,找了很久,然后突然想到可以是数据格式的问题!果断打断点:
发现我加载的那张图片格式是:dtype=uint8格式的,而color这个图格式是float64格式的!所以问题就出现在这里!!
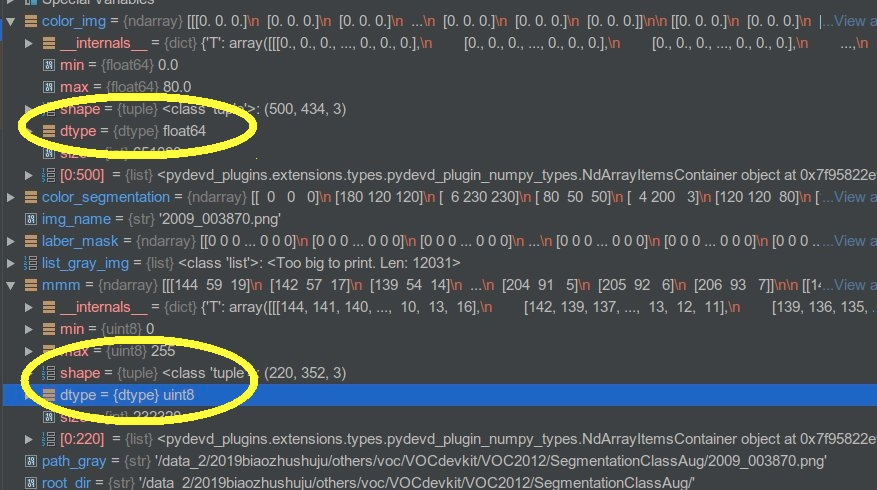
一定要加上这句话
rgb = rgb.astype(np.uint8) ##重要! 要不然opencv显示有问题
好了,只是把我发现问题,解决问题的思路过程写在这里。
这里主要要学习numpy的几个操作:
1.
r = label_mask.copy()
g = label_mask.copy()
b = label_mask.copy()
for ll in range(0, n_classes):
b[label_mask == ll] = color_segmentation[ll, 0]
g[label_mask == ll] = color_segmentation[ll, 1]
r[label_mask == ll] = color_segmentation[ll, 2]
这里我一开始的直观理解就是label_mask == ll返回的是位置,b[label_mask == ll],比如图片像素值等于2的位置都填充后面的值。但是我
position = label_mask == ll
看了一下,其实不是,这里的position是和图一样大小,里面的值都是True或者False
明白了,其实返回的相当于一个mask,只在true的位置上填充后面的值
2.
rgb = np.zeros((label_mask.shape[0], label_mask.shape[1], 3))
rgb[:, :, 0] = b
rgb[:, :, 1] = g
rgb[:, :, 2] = r
这里rgb都是单通道的,就是把这三个合并一个图。首先就是申请了一个三通的。这里需要注意的是opencv的格式都是hwc。
rgb[:, :, 0]代表的第一个通道
还有上面我调试的代码
print(rgb[240][240])
这里打印出来的是这样的
[80. 50. 50.]
想想为啥吧!
@@@@@@@@@@
有个相反操作的,就是把colormap图映射为标签图
def encode_segmap(mask):
"""Encode segmentation label images as pascal classes
Args:
mask (np.ndarray): raw segmentation label image of dimension
(M, N, 3), in which the Pascal classes are encoded as colours.
Returns:
(np.ndarray): class map with dimensions (M,N), where the value at
a given location is the integer denoting the class index.
"""
mask = mask.astype(int)
label_mask = np.zeros((mask.shape[0], mask.shape[1]), dtype=np.int16)
for ii, label in enumerate(get_pascal_labels()):
label_mask[np.where(np.all(mask == label, axis=-1))[:2]] = ii
label_mask = label_mask.astype(int)
return label_mask
pytorch继承的Dataset类的自己定义的OrientClassifyDataset,可以用iter next来迭代访问
train_dataset = OrientClassifyDataset(
train_root,
transform=train_transform,
)
aa = iter(train_dataset)
a = next(aa)
print('train data:', len(train_dataset))
train_loader = data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=num_workers, drop_last=True, collate_fn=align_collate_train)
to_tensor || transforms.functional.to_tensor
将numpy数组或PIL.Image读的图片转换成(C,H, W)的Tensor格式且/255归一化到[0,1.0]之间
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
class Normalize(object):
def __init__(self):
pass
def __call__(self, img):
img = transforms.functional.to_tensor(img)
img.sub_(0.5).div_(0.5)
return img
pytorch数据处理,继承的Dataset类的函数的单元测试
反向操作,之前减均值,除方差操作现在反着来恢复原图变显示
本文大部分代码参考这个仓库:https://github.com/jfzhang95/pytorch-deeplab-xception
voc_train = VOCSegmentation(args, split='train')
dataloader = DataLoader(voc_train, batch_size=5, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
for ii, sample in enumerate(dataloader):
for jj in range(sample["image"].size()[0]):
img = sample['image'].numpy()
gt = sample['label'].numpy()
tmp = np.array(gt[jj]).astype(np.uint8)
segmap = decode_segmap(tmp, dataset='pascal')
img_tmp = np.transpose(img[jj], axes=[1, 2, 0])
img_tmp *= (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)
img_tmp += (0.485, 0.456, 0.406)
img_tmp *= 255.0
img_tmp = img_tmp.astype(np.uint8)
plt.figure()
plt.title('display')
plt.subplot(211)
plt.imshow(img_tmp)
plt.subplot(212)
plt.imshow(segmap)
if ii == 1:
break
plt.show(block=True)
pytorch保存模型两种方式
保存和加载模型参数有两种方式:
方式一:
torch.save(net.state_dict(),path):
功能:保存训练完的网络的各层参数(即weights和bias)
其中:net.state_dict()获取各层参数,path是文件存放路径(通常保存文件格式为.pt或.pth)
net2.load_state_dict(torch.load(path)):
功能:加载保存到path中的各层参数到神经网络
注意:不可以直接为torch.load_state_dict(path),此函数不能直接接收字符串类型参数
方式二:
torch.save(net,path):
功能:保存训练完的整个网络模型(不止weights和bias)
net2=torch.load(path):
功能:加载保存到path中的整个神经网络
说明:官方推荐方式一,原因自然是保存的内容少,速度会更快。
shape[1,6] + shape[6,1] = shape[6,6]
>>> a = np.array([[3,2,1,1,2,3]])
>>> b = np.array([[3],[2],[1],[1],[2],[3]])
>>> print(a.shape),print(b.shape)
(1, 6)
(6, 1)
(None, None)
>>> c = a+b
>>> print(a)
[[3 2 1 1 2 3]]
>>> print(b)
[[3]
[2]
[1]
[1]
[2]
[3]]
>>> print(c)
[[6 5 4 4 5 6]
[5 4 3 3 4 5]
[4 3 2 2 3 4]
[4 3 2 2 3 4]
[5 4 3 3 4 5]
[6 5 4 4 5 6]]
numpy 数组,[x1,y1,x2,y2,score,cls] 比如我有形状[100,6]这样的一个numpy数组,需要保留score大于0.8的,其余不要。如何写?
问群里人,得到三种答案:
import numpy as np
a = [[1, 2, 3, 4, 0.75, 1],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 0.85, 2],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 0.95, 3],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 0.61, 4],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 0.97, 5],
[1, 2, 3, 4, 0.82, 6],]
a = np.array(a)
####11111
s = a[np.apply_along_axis(lambda x:x[4]>0.8,axis=1,arr=a)]
print(s)
print()
####2222
mask = a[:,4] > 0.8
print(mask)
print(a[mask])
print()
####333
print(a[a[:,4]>0.8,:])
#######################################
[[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.85 2. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.95 3. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.97 5. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.82 6. ]]
[False True True False True True]
[[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.85 2. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.95 3. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.97 5. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.82 6. ]]
[[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.85 2. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.95 3. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.97 5. ]
[1. 2. 3. 4. 0.82 6. ]]
Process finished with exit code 0
图片保持长宽比,缩放到固定尺寸
int input_w = 512;
int input_h = 512;
float scale = cv::min(float(input_w)/img.cols,float(input_h)/img.rows);
auto scaleSize = cv::Size(img.cols * scale,img.rows * scale);
cv::Mat resized;
cv::resize(img, resized,scaleSize,0,0);
cv::Mat cropped = cv::Mat::zeros(input_h,input_w,CV_8UC3);
cv::Rect rect((input_w- scaleSize.width)/2, (input_h-scaleSize.height)/2, scaleSize.width,scaleSize.height);
resized.copyTo(cropped(rect));