一、了解Spring IOC/DI
1:Spring有两大核心技术,控制反转(Inversion of Control, IOC)/依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI)和面向切面编程(Aspect Oriented Programming,AOP)
2. IOC/DI: 它用来管理所有的java类,类对象的创建和依赖关系都由IOC/DI进行控制。控制反转(IOC)和依赖注入(DI)在spring中表示同一种意思,只是看问题的角度不同,例如
当在A类中new一个B类时,控制权由A掌握,可以理解为控制正转,当A类使用的B类实例有spring创建时,控制权由spring掌握,就是控制反转;
依赖注入可以理解为A类依赖于spring,由spring注入B类。控制反转是抽象的概念,只是提出了一种“控制”的方式,而依赖注入是spring框架实现“控制反转”的具体方法。
3. IOC/DI工作原理:spring IOC/DI的更为直观的叫法是容器,这是因为spring可以管理很多类,当需要某一类对象的实例时,spring就会提供相应的实例,就像是一个容器里面
可以放入很多东西,需要什么就取什么。那么在spring容器中都有什么类可以使用呢?这需要预先定义在spring的配置文件中,默认的配置文件名称是applicationContext.xml
例如在配置文件中定义了A类和B类,而A类中使用到了B类,那么配置文件中再定义好这种依赖关系,即可由Spring自动地把B类实例注入到A类中,但是,这种注入是有条件的,
类需要符合Javabean的定义规范,在A类中需要定义对B类赋值的setter方法。这是Spring对管理的类唯一的要求,不需要像EJB那样实现框架本身的任何接口,也是spring被称
为轻量级框架的原因。
二、IOC/DI使用到的技术
1. JDOM:JDOM是对xml文件进行解析的技术,Spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml就是由JDOM进行解析的,它可以提取出xml文件中定义的标签和属性值。
1.1 环境的搭建:

1.2 StudentAction.java
public class StudentAction {
private StudentService studentService;
public void setStudentService(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
public void printName() {
System.out.println(studentService.getName());
}
}
1.3 StudentServiceImpl.java
public class StudentServiceImpl implements StudentService{
private StudentDao studentDao;
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public String getName() {
return studentDao.getName();
}
}
1.4 StudentService.java
public interface StudentService {
public String getName();
}
1.5 StudentDao.java
public interface StudentDao {
public String getName();
}
1.6 StudentDaoImpl.java
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
public String getName() {
return "Jike Wang";
}
}
1.7 测试
public class TestAction {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//使用ApplicationContext接口的实现类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载spring配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/applicationContext.xml");
//通过ApplicationContext接口的getBean方法获取id或name为studentAction的Bean实例
StudentAction studentAction = (StudentAction) applicationContext.getBean("studentAction");
//调用方法
studentAction.printName();
}
}
1.8 使用jdom模拟spring解析xml文件,读取关键信息
自定义XML代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans>
<!-- 定义StudentDaoImpl对象并指定id为studentDao -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.IOC.dao.impl.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<!-- 定义StudentServiceImpl对象并指定id为studentService-->
<bean id="studentService" class="com.IOC.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl">
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 定义StudentAction对象并指定id为studentAction -->
<bean id="studentAction" class="com.IOC.action.StudentAction">
<property name="studentService" ref="studentService"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
public class TestJDOM {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "src/main/resources/applicationContext.xml";//xml文件目录
//用于创建文档对象
SAXBuilder sb = new SAXBuilder();
//构造的XML文档对象
Document doc;
try {
//创建文档对象
doc = sb.build(path);
//得到文档的根元素<beans>
Element rootElement = doc.getRootElement();
//得到文档的所有<bean>
List<Element> list = rootElement.getChildren("bean");
for (Element element : list) {
//得到<bean>的id属性值
String id = element.getAttributeValue("id");
//得到<bean>的class属性值
String classValue = element.getAttributeValue("class");
//得到<bean>的子元素<property>
Element propertyElement = element.getChild("property");
String propertyName = null;
String propertyRef = null;
if (propertyElement != null) {
//得到<property>的name属性值
propertyName = propertyElement.getAttributeValue("name");
//得到property的内容
propertyRef = propertyElement.getAttributeValue("ref");
}
System.out.println("========================");
System.out.println("id="+id);
System.out.println("class="+classValue);
System.out.println("propertyName="+propertyName);
System.out.println("propertyRef="+propertyRef);
System.out.println("========================");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
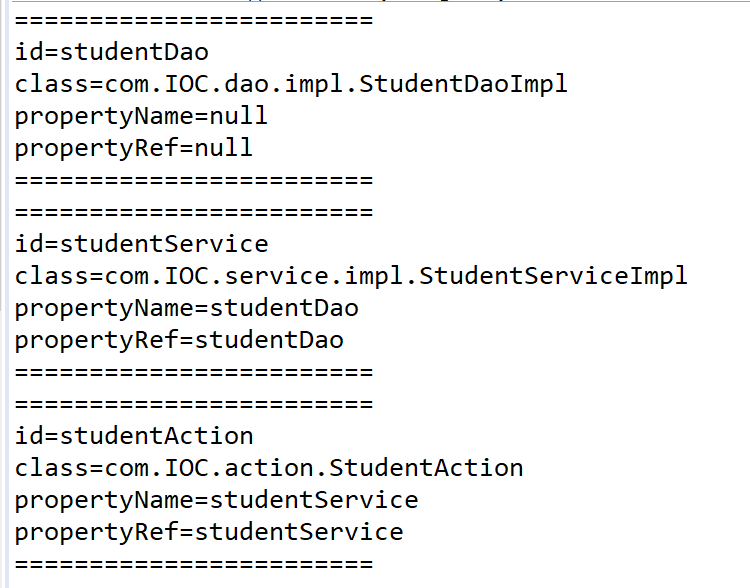
测试结果:
2. 反射机制:对配置文件中的类名使用反射机制可以实现类加载初始化等工作,也可以调用类的方法进行属性注入,java.lang.reflect提供了反射相关的工具
public class TestReflect {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//表示StudentDao接口全路径
String studentDao = "com.IOC.dao.StudentDao";
//表示StudentService接口全路径
String studentService = "com.IOC.service.StudentService";
//表示StudentDaoImpl类全路径
String studentDaoImpl = "com.IOC.dao.impl.StudentDaoImpl";
//表示StudentServiceImpl
String studentServiceImpl = "com.IOC.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl";
//表示StudentAction类全路径
String studentAction = "com.IOC.action.StudentAction";
//表示setStudentService方法的字符串
String setStudentService = "setStudentService";
//表示setStudentDao方法的字符串
String setStudentDao = "setStudentDao";
try {
//使用全路径字符串加载StudentDao类别
Class studentDaoClass = Class.forName(studentDao);
//使用全路径字符串加载StudentService类别
Class studentServiceClass = Class.forName(studentService);
//使用全路径字符串加载StudentDaoImpl类别
Class studentDaoImplClass = Class.forName(studentDaoImpl);
//使用全路径字符串加载StudentServiceImpl类别
Class studentServiceImplClass = Class.forName(studentServiceImpl);
//使用全路径字符串加载StudentAction类别
Class studentActionClass = Class.forName(studentAction);
//setStudentDao方法签名,相当于获取次此方法,使用类别获取setStudentDao方法
Method setDaoMethod = studentServiceImplClass.getMethod(setStudentDao, studentDaoClass);
//setStudentService方法签名,使用类别获取setStudentService方法
Method setServiceMethod = studentActionClass.getMethod(setStudentService, studentServiceClass);
//创建StudentDaoImpl对象,相当于new StudentDaoImpl(),但返回的是Object对象
Object studentDaoImplnstance = studentDaoImplClass.newInstance();
//创建StudentServiceImpl对象,相当于new StudentServiceImpl(),但返回的是Object对象
Object studentServiceImplInstance = studentServiceImplClass.newInstance();
//创建StudentAction对象,相当于new StudentAction(),但返回的是Object对象
Object studentActionInstance = studentActionClass.newInstance();
//使用反射机制调用StudentServiceImpl的setStudentDao方法,参数是StudentDaoImpl对象,
//第一个参数是执行方法的类实例,第二个参数是方法参数
setDaoMethod.invoke(studentServiceImplInstance, studentDaoImplnstance);
setServiceMethod.invoke(studentActionInstance, studentServiceImplInstance);
//调用StudentAction的printName方法
((StudentAction)studentActionInstance).printName();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
测试结果:

