有人会问,为啥要用这个叫啥Kudu的,Kudu是啥?
就像官网所说,Kudu是一个针对Apache hadoop 平台而开发的列式存储管理器,在本菜鸟看来,它是一种介于hdfs与hbase的一种存储。它的优势在于:
1、OLAP工作的快速处理,也就是针对于查询,很快,很牛逼。
2、针对同时运行顺序和随机工作负载的情况性能很好。
3、高可用,Table server和master使用Raft Consensus Algorithm节点来保证高可用,什么是Raft Consunsus Algorith?参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/mindwind/p/5231986.html),只要有一半以上的副本可用,该tablet便可用于读写。
4、结构化数据模型(可以理解为带schema)。
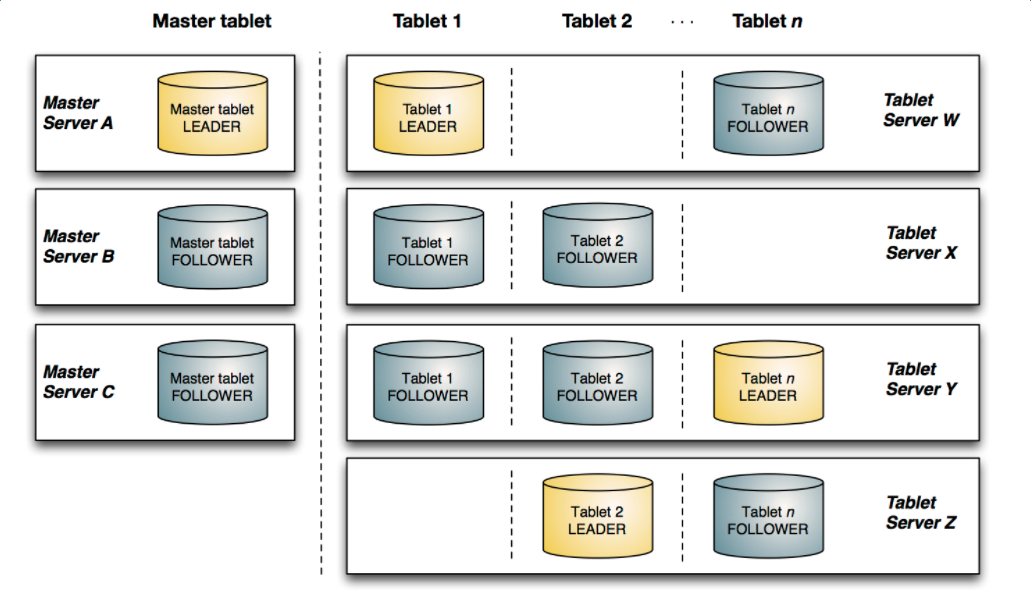
该图显示了一个具有三个 master 和多个 tablet server 的 Kudu 集群,每个服务器都支持多个 tablet。它说明了如何使用 Raft 共识来允许 master 和 tablet server 的 leader 和 f ollow。此外,tablet server 可以成为某些 tablet 的 leader,也可以是其他 tablet 的 follower。leader 以金色显示,而 follower 则显示为蓝色。
下面是一些基本概念:
Table(表)
一张 talbe 是数据存储在 Kudu 的位置。表具有 schema 和全局有序的 primary key(主键)。table 被分成称为 tablets 的 segments。
Tablet
一个 tablet 是一张 table 连续的 segment,与其它数据存储引擎或关系型数据库中的 partition(分区)相似。给定的 tablet 冗余到多个 tablet 服务器上,并且在任何给定的时间点,其中一个副本被认为是 leader tablet。任何副本都可以对读取进行服务,并且写入时需要在为 tablet 服务的一组 tablet server之间达成一致性。
Tablet Server
一个 tablet server 存储 tablet 和为 tablet 向 client 提供服务。对于给定的 tablet,一个 tablet server 充当 leader,其他 tablet server 充当该 tablet 的 follower 副本。只有 leader服务写请求,然而 leader 或 followers 为每个服务提供读请求。leader 使用 Raft Consunsus Algorithm来进行选举 。一个 tablet server 可以服务多个 tablets ,并且一个 tablet 可以被多个 tablet servers 服务着。
具体我还没有那么深入,写了些api调用玩了一把,下面慢慢讲述,Kudu的API比较恶心的哈。。
kudu的sql语法与传统的sql语法比较相似,但也不尽相同,直接解析时,具体sql语法请参考官网,下面以类似hive metastore表结构的方式封装了下。以下列sql为例:
create table combined_t6 (x int64, s string, s2 string, primary key (x, s))
partition by hash (x) partitions 10, range (x)
(
partition 0 <= values <= 49, partition 50 <= values <= 100
) REPLICAS 1
public Boolean create(Table table,String operator) { LOGGER.info("kudu Table properties:" + table.getKvInfos().toString()); List<ColumnSchema> columns = new ArrayList(table.getTableColumnList().size());
KuduTableGenerateUtil.generateKuduColumn(table.getTableColumnList(),columns); Schema schema = new Schema(columns); KuduPartitionSchema kuduPartitionSchema = KuduTableGenerateUtil.parserPartition(table); CreateTableOptions tableOptions = KuduTableGenerateUtil.generateKuduTableOptions(table,schema,kuduPartitionSchema); try { getKuduClient(table).createTable(table.getTableName(), schema,tableOptions); } catch (KuduException e) { throw new MetadataInvalidObjectException(e, " create kudu storage table error!!"); } return true; }
kudu的column属性中,包含有primarfyKey、encoding、compression algorithm、null table 、default value 、block size等属性,所以从上述代码中需要先将kuduColumn进行封装,构造ColumnSchema对象:
new ColumnSchema.ColumnSchemaBuilder(tableColumn.getColumnName(), getKuduColumnType(tableColumn.getDataType())) .key(checkBoolKey(columnCondition.get(MetadataConfigKey.COLUMN_KUDU_PRIMARY_KEY))) .nullable(checkBoolKey(columnCondition.get(MetadataConfigKey.COLUMN_KUDU_SCHEMA_IS_NULLTABLE))) .defaultValue(defaultValue) .desiredBlockSize(getDesiredBlockSize(columnCondition.get(MetadataConfigKey.COLUMN_KUDU_SCHEMA_DESIRED_BLOCKSIZE))) .encoding(getColumnEncoding(columnCondition.get(MetadataConfigKey.COLUMN_KUDU_SCHEMA_ENCODING))) .compressionAlgorithm(getCompressionType(columnCondition.get(MetadataConfigKey.COLUMN_KUDU_SCHEMA_COMPRESSION_ALGORITHM))) .build();
对于column的数据类型,有很多种,如下:
private static Type getKuduColumnType(String dataType) { switch (dataType.toUpperCase()) { case "INT8": return Type.INT8; case "INT16": return Type.INT16; case "INT32": return Type.INT32; case "INT64": return Type.INT64; case "BINARY": return Type.BINARY; case "STRING": return Type.STRING; case "BOOL": return Type.BOOL; case "FLOAT": return Type.FLOAT; case "DOUBLE": return Type.DOUBLE; case "UNIXTIME_MICROS": return Type.UNIXTIME_MICROS; default: return Type.STRING; } }
压缩方式包括:
public static CompressionAlgorithm getCompressionType(String compressionType) { if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(compressionType)) { switch (compressionType.toUpperCase()) { case "UNKNOWN": return CompressionAlgorithm.UNKNOWN; case "DEFAULT_COMPRESSION": return CompressionAlgorithm.DEFAULT_COMPRESSION; case "NO_COMPRESSION": return CompressionAlgorithm.NO_COMPRESSION; case "SNAPPY": return CompressionAlgorithm.SNAPPY; case "LZ4": return CompressionAlgorithm.LZ4; case "ZLIB": return CompressionAlgorithm.UNKNOWN.ZLIB; default: return null; } } return null; }
随之我们要构造,Kudu Partition,Kudu Partition包含两种类型,一种是hashPartition,一种是rangePartition,其实从字面意思应该也能够想到,一种是用于对某个字段进行hash散列,一种是进行分区区间的设置,从而在查询时达到优化的效果,这里通过将sql解析后的转换的KuduPartitionSchema对象分别进行range与hash partition的组装,也就是将sql中 Partition表达式 partition 0 <= values <= 49, partition 50 <= values <= 100 封装:
public static void generateHashPartition(CreateTableOptions tableOptions, List<HashPartitionSchema> hashPartitionSchemas) { if (null != hashPartitionSchemas && hashPartitionSchemas.size() != 0) {
hashPartitionSchemas.forEach(hashPartitionSchema ->{
tableOptions.addHashPartitions(hashPartitionSchema.getColumns(), hashPartitionSchema.getBucket());
});
}
}
public static void generateRangePartition(Schema schema, CreateTableOptions tableOptions, RangePartitionSchema rangePartitionSchema) { tableOptions.setRangePartitionColumns(rangePartitionSchema.getColumns()); List<RangeSplit> ranges = rangePartitionSchema.getRanges(); ranges.forEach(range -> { tableOptions.addRangePartition( getPartialRow( range.getLower(), schema, rangePartitionSchema.getColumns()), getPartialRow( range.getUpper(), schema, rangePartitionSchema.getColumns()), getRangePartitionBound( range.getLowerBoundType()), getRangePartitionBound( range.getUpperBoundType()) ); }); }
public static RangePartitionBound getRangePartitionBound(String boundType) { if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(boundType)) { switch (boundType) { case "EXCLUSIVE_BOUND": return RangePartitionBound.EXCLUSIVE_BOUND; case "INCLUSIVE_BOUND": return RangePartitionBound.INCLUSIVE_BOUND; default: return null; } } return null; }
最后构造,CreateTableOptions对象:
public static CreateTableOptions generateKuduTableOptions(Table table, Schema schema, KuduPartitionSchema kuduPartitionSchema) { CreateTableOptions tableOptions = new CreateTableOptions(); String numReplicas = table.getKvInfos().get(MetadataConfigKey.TABLE_KUDU_REPLICAS); if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(numReplicas)) { tableOptions.setNumReplicas(Integer.valueOf(numReplicas)); } if (kuduPartitionSchema.getHashPartitionSchemaList() != null && kuduPartitionSchema.getHashPartitionSchemaList().size() != 0) { generateHashPartition(tableOptions, kuduPartitionSchema.getHashPartitionSchemaList()); } if (kuduPartitionSchema.getRangePartitionSchema() != null) { generateRangePartition(schema, tableOptions, kuduPartitionSchema.getRangePartitionSchema()); } return tableOptions; }
没有hbase编程便捷。。不过对于kudu的连接而言,只需要配置kudu master的地址,便可创建连接。
public KuduClient getKuduClient(Table table){ if(null == kuduClient){ try{ String kuduMaster = table.getStorageClusterKvs().get(MetadataConfigKey.CLUSTER_KUDU_MASTER); kuduClient = new KuduClient.KuduClientBuilder(kuduMaster).build(); }catch(Exception e){ throw new MetadataRuntimeException(e, " create kuduClient error!!"); } } return kuduClient; }
活儿干不完啊~改天再深入完 哈哈~