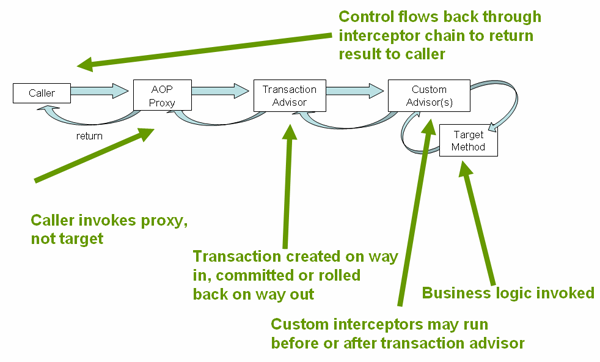
在事务代理上调用方法的执行路径示意图:
@Transactional注解配置
默认配置:
1、传播行为 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
2、隔离级别 ISOLATION_DEFAULT
3、事务是读写的 read-write
4、事务超时默认为基础事务系统的默认超时,如果不支持超时,则默认为无。
5、任何 RuntimeException 异常触发回滚,但是任何已检查异常不会
@Transactional注解属性介绍
1、propagation Spring事务传播机制:
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | Spring的默认传播级别,如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果不存在事务则新建事务执行。 |
| PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果没有事务则以非事务方式执行。 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 该传播级别要求上下文中必须存在事务,否则抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 该传播级别每次执行都会创建新事务,并同时将上下文中的事务挂起,执行完当前线程后再恢复上下文中事务。(子事务的执行结果不影响父事务的执行和回滚) |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 当上下文中有事务则挂起当前事务,执行完当前逻辑后再恢复上下文事务。(降低事务大小,将非核心的执行逻辑包裹执行。) |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 该传播级别要求上下文中不能存在事务,否则抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_NESTED | 嵌套事务,如果上下文中存在事务则嵌套执行,如果不存在则新建事务。(save point概念) |
常用传播机制:
1、PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
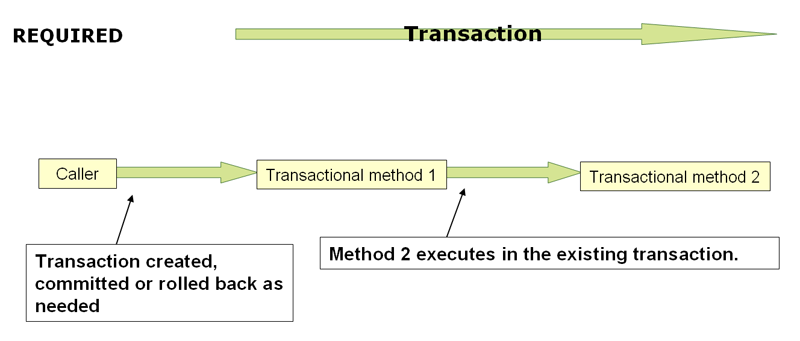
Spring的默认传播级别,如果上下文中存在事务则加入当前事务,如果不存在事务则新建事务执行。
2、PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
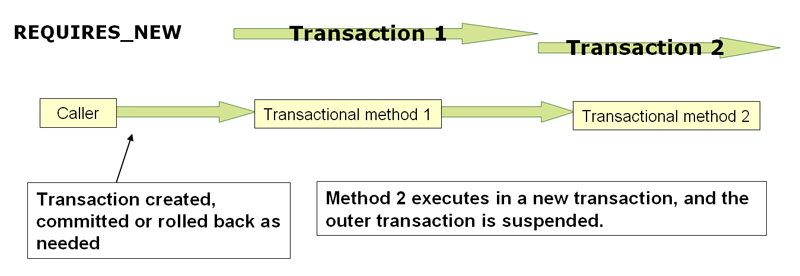
该传播级别每次执行都会创建新事务,并同时将上下文中的事务挂起,执行完当前线程后再恢复上下文中事务。(子事务的执行结果不影响父事务的执行和回滚)
3、PROPAGATION_NESTED
嵌套事务,如果上下文中存在事务则嵌套执行,如果不存在则新建事务。
PROPAGATION_NESTED 使用具有多个可还原到的保存点的单个物理事务。这种部分回滚使内部事务范围触发其范围的回滚,尽管某些操作已回滚,但外部事务仍能够继续物理事务。此设置通常映射到JDBC保存点,因此它仅适用于JDBC资源事务
2、isolation 隔离级别
| DEFAULT | 使用底层数据库默认的隔离级别 |
| READ_UNCOMMITTED | 读未提交 |
| READ_COMMITTED | 读已提交 |
| REPEATABLE_READ | 可重复度 |
| SERIALIZABLE | 串行化 |
3、timeout 事务超时时间
默认值为-1。如果超过该时间限制但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务
4、readOnly 事务是否为只读事务
默认值为 false;为了忽略那些不需要事务的方法,比如读取数据,可以设置 read-only 为 true。
5、rollbackFor
指定能够触发事务回滚的异常类型,可以指定多个异常类型。
6、noRollbackFor
抛出指定的异常类型,不回滚事务,也可以指定多个异常类型
一、Spring 单数据源xml事务配置
1、定义数据源
2、用DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器管理数据源
3、注册需要事务拦截的service <bean/>
4、要应用事务的方法规则 <tx:advice/>
5、aop切点配置,指定增强器,确保定义的事务通知在程序中的适当位置执行 <aop:config/>
<!-- from the file 'context.xml' --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional --> <bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/> <!-- the transactional advice (what 'happens'; see the <aop:advisor/> bean below) --> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager"> <!-- the transactional semantics... --> <tx:attributes> <!-- all methods starting with 'get' are read-only --> <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/> //rollback-for="Throwable" no-rollback-for="InstrumentNotFoundException" <!-- other methods use the default transaction settings (see below) --> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!-- ensure that the above transactional advice runs for any execution of an operation defined by the FooService interface --> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="fooServiceOperation" expression="execution(* x.y.service.FooService.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="fooServiceOperation"/> </aop:config> <!-- don't forget the DataSource --> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close"> <property name="driverClassName" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@rj-t42:1521:elvis"/> <property name="username" value="scott"/> <property name="password" value="tiger"/> </bean> <!-- similarly, don't forget the PlatformTransactionManager --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- other <bean/> definitions here --> </beans>
二、Spring 单数据源声明式事务配置
1、将@Transactional 注解声明在方法或类上;声明在类上,则声明类及其子类的所有方法都执行事务通知。注意:只作用于public修饰的方法。
2、若使用JavaConfig配置,则要在其中一个有@Configuration注解的配置类上@EnableTransactionManagement
3、在xml中使用<tx:annotation-driven/>
<!-- from the file 'context.xml' --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- this is the service object that we want to make transactional --> <bean id="fooService" class="x.y.service.DefaultFooService"/> <!-- enable the configuration of transactional behavior based on annotations --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/><!-- a PlatformTransactionManager is still required --> <bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <!-- (this dependency is defined somewhere else) --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!-- other <bean/> definitions here --> </beans>
注意:
@EnableTransactionManagement and <tx:annotation-driven/> looks for @Transactional only on beans in the same application context in which they are defined.
This means that, if you put annotation-driven configuration in a WebApplicationContext for a DispatcherServlet, it checks for @Transactional beans only in
your controllers and not your services. See MVC for more information.
@EnableTransactionManagement 注解和<tx:annotation-driven/>仅在定义和他们的相同应用程序上下文中的bean上去查找@Transactional注解。也就是说,如果将<tx:annotation-driven/>注解驱动的配置放在DispatcherServlet的WebApplicationContext中,它将仅在控制器controller中而不是service中检查@Transactional bean。
三、Spring多数据源声明式事务配置
四、Spring动态数据源AbstractRoutingDataSource声明式事务配置
手动回滚事务
有些情况下需要捕获异常,那么就需要手动回滚事务,在catch块中
// 手动回滚 TransactionAspectSupport.currentTransactionStatus().setRollbackOnly();