定义
一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列。此队列按照 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序。队列的头部 是队列中时间最长的元素。队列的尾部 是队列中时间最短的元素。
新的元素插入到队列的尾部,队列获取操作从队列头部获得元素。当多个线程共享访问一个公共 collection 时,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是一个恰当的选择。此队列不允许使用 null 元素。
offer和poll
poll()
获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("哈哈哈"); System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println("从队列中poll:" + queue.poll()); System.out.println("pool后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); }
offer是往队列添加元素,poll是从队列取出元素并且删除该元素
执行结果
offer后,队列是否空?false 从队列中poll:哈哈哈 pool后,队列是否空?true
ConcurrentLinkedQueue中的add() 和 offer() 完全一样,都是往队列尾部添加元素
还有个取元素方法peek
peek()
获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null
public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("哈哈哈"); System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek()); System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek()); System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek()); System.out.println("pool后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); }
执行结果:
offer后,队列是否空?false 从队列中peek:哈哈哈 从队列中peek:哈哈哈 从队列中peek:哈哈哈 pool后,队列是否空?false
remove
remove(Object o)
从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)
public static void main(String[] args) { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("哈哈哈"); System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); System.out.println("从队列中remove已存在元素 :" + queue.remove("哈哈哈")); System.out.println("从队列中remove不存在元素:" + queue.remove("123")); System.out.println("remove后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty()); }
remove一个已存在元素,会返回true,remove不存在元素,返回false
执行结果:
offer后,队列是否空?false 从队列中remove已存在元素 :true 从队列中remove不存在元素:false remove后,队列是否空?true
size or isEmpty
size()
返回此队列中的元素数量
注意:
如果此队列包含的元素数大于 Integer.MAX_VALUE,则返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
需要小心的是,与大多数 collection 不同,此方法不是 一个固定时间操作。由于这些队列的异步特性,确定当前的元素数需要进行一次花费 O(n) 时间的遍历。
所以在需要判断队列是否为空时,尽量不要用 queue.size()>0,而是用 !queue.isEmpty()
比较size()和isEmpty() 效率的示例:
场景:10000个人去饭店吃饭,10张桌子供饭,分别比较size() 和 isEmpty() 的耗时
public class Test01ConcurrentLinkedQueue { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { int peopleNum = 10000;//吃饭人数 int tableNum = 10;//饭桌数量 ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>(); CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(tableNum);//计数器 //将吃饭人数放入队列(吃饭的人进行排队) for(int i=1;i<=peopleNum;i++){ queue.offer("消费者_" + i); } //执行10个线程从队列取出元素(10个桌子开始供饭) System.out.println("-----------------------------------开饭了-----------------------------------"); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(tableNum); for(int i=0;i<tableNum;i++) { executorService.submit(new Dinner("00" + (i+1), queue, count)); } //计数器等待,知道队列为空(所有人吃完) count.await(); long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - start; System.out.println("-----------------------------------所有人已经吃完-----------------------------------"); System.out.println("共耗时:" + time); //停止线程池 executorService.shutdown(); } private static class Dinner implements Runnable{ private String name; private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue; private CountDownLatch count; public Dinner(String name, ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue, CountDownLatch count) { this.name = name; this.queue = queue; this.count = count; } @Override public void run() { //while (queue.size() > 0){ while (!queue.isEmpty()){ //从队列取出一个元素 排队的人少一个 System.out.println("【" +queue.poll() + "】----已吃完..., 饭桌编号:" + name); } count.countDown();//计数器-1 } } }
执行结果:
使用size耗时:757ms
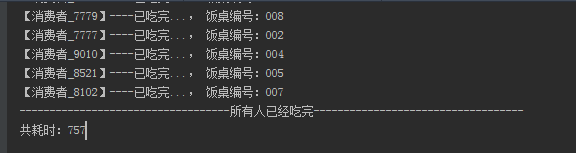
使用isEmpty耗时:210

当数据量越大,这种耗时差距越明显。所以这种判断用isEmpty 更加合理
contains
contains(Object o)
如果此队列包含指定元素,则返回 true
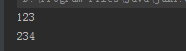
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue(); queue.offer("123"); System.out.println(queue.contains("123")); System.out.println(queue.contains("234")); }
执行结果:

toArray
toArray()
返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组
toArray(T[] a)
返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>(); queue.offer("123"); queue.offer("234"); Object[] objects = queue.toArray(); System.out.println(objects[0] + ", " + objects[1]); //将数据存储到指定数组 String[] strs = new String[2]; queue.toArray(strs); System.out.println(strs[0] + ", " + strs[1]); }
执行结果:

iterator
iterator()
返回在此队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>(); queue.offer("123"); queue.offer("234"); Iterator<String> iterator = queue.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()){ System.out.println(iterator.next()); } }
ConcurrentLinkedQueue文档说明:
| 构造方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
ConcurrentLinkedQueue() 创建一个最初为空的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue。 |
|
ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) 创建一个最初包含给定 collection 元素的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue,按照此 collection 迭代器的遍历顺序来添加元素。 |
|
| 方法摘要 | ||
|---|---|---|
boolean |
add(E e) 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
|
boolean |
contains(Object o) 如果此队列包含指定元素,则返回 true。 |
|
boolean |
isEmpty() 如果此队列不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 |
|
Iterator<E> |
iterator() 返回在此队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器。 |
|
boolean |
offer(E e) 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
|
E |
peek() 获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
|
E |
poll() 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
|
boolean |
remove(Object o) 从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。 |
|
int |
size() 返回此队列中的元素数量。 |
|
Object[] |
toArray() 返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组。 |
|
|
toArray(T[] a) 返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。 |
|