腾讯词向量介绍
腾讯词向量主页:https://ai.tencent.com/ailab/nlp/zh/embedding.html
词向量下载地址:https://ai.tencent.com/ailab/nlp/zh/data/Tencent_AILab_ChineseEmbedding.tar.gz
腾讯词向量(Tencent AI Lab Embedding Corpus for Chinese Words and Phrases)提供了预训练好的800万中文词汇的word embedding(200维词向量),可以应用于很多NLP的下游任务。
数据来源:新闻、网页、小说。
词表构建:维基百科、百度百科,以及Corpus-based Semantic Class Mining: Distributional vs. Pattern-Based Approaches论文中的方法发现新词。
训练方法:Directional Skip-Gram: Explicitly Distinguishing Left and Right Context for Word Embeddings论文中有介绍。
关于分词:可以使用任何开源分词工具,可以同时考虑细粒度和粗粒度的分词方式。
关于停用词、数字、标点:为了满足一些场景的需求,腾讯词向量并没有去掉这些,使用的时候需要自己构建词表并忽略其他无关词汇。
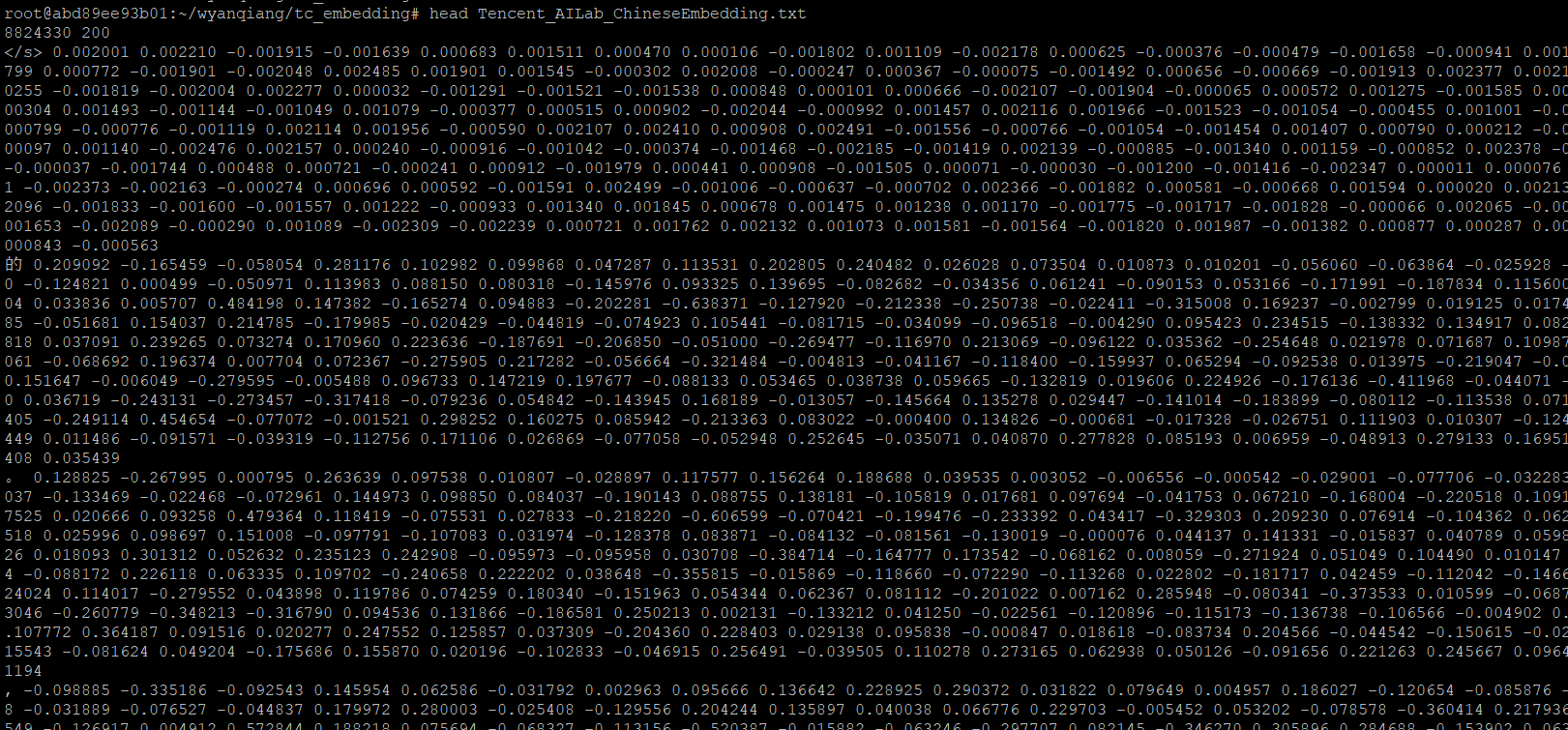
Tencent_AILab_ChineseEmbedding.txt文件内容:
第一行是词向量总数(8824330),和词向量维度(200)。
从第二行开始,每行是中文词以及它的词向量表示,每一维用空格分隔。
腾讯词向量使用举例
以查找近义词为例,介绍腾讯词向量的使用方法。
首先需要将已有的包含词和词向量的txt文件读入(使用KeyedVectors)
keyedVectors
可以很方便地从训练好的词向量中读取词的向量表示,快速生成 {词:词向量}
其中binary=False,加载的是txt文件,binary=True,加载的是二进制文件
然后构建词汇和索引的映射表,并用json格式离线保存,方便以后直接加载annoy索引时使用
基于腾讯词向量构建Annoy索引,annoy作用是在高维空间求近似最近邻
方法:
1、高维空间随意选两个点,做一个聚类数为2的kmeans,产生两个类,每类有中心点,这两个点为基准,找到垂直于二者连线的超平面,可以区分出两个集合
2、现在变成了两个集合,分别再进行第一步
3、设定一个k,最终每个类最多剩余k个点,停止
4、以上面区分两个集合的方法构建二叉树
5、如果查某个点的最近邻点,就在二叉树里搜索
AnnoyIndex(f, metric)
returns a new index that's read-write and stores vector of f dimensions. Metric can be "angular", "euclidean", "manhattan", "hamming", or "dot".
返回一个可以读写的index,并存储f维向量,度量可以是夹角、欧几里得距离、曼哈顿距离、汉明距离和点积。默认是夹角。
tc_index.build(10)
n_trees is provided during build time and affects the build time and the index size. A larger value will give more accurate results, but larger indexes.
n_trees影响构建时间和index大小,n_trees更大,则结果更精确,但是index也就更大,官方文档示例默认的是10
a.build(n_trees)
builds a forest of n_trees trees. More trees gives higher precision when querying. After calling build, no more items can be added.
构建一个有n_trees颗树的森林,树越多越精确。build完,就不能再增加了
import json
from collections import OrderedDict
from gensim.models import KeyedVectors
from annoy import AnnoyIndex
tc_wv_model = KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_format('Tencent_AILab_ChineseEmbedding.txt', binary=False)
# 把txt文件里的词和对应的向量,放入有序字典
word_index = OrderedDict()
for counter, key in enumerate(tc_wv_model.vocab.keys()):
word_index[key] = counter
# 本地保存
with open('tc_word_index.json', 'w') as fp:
json.dump(word_index, fp)
# 腾讯词向量是两百维的
tc_index = AnnoyIndex(200)
i = 0
for key in tc_wv_model.vocab.keys():
v = tc_wv_model[key]
tc_index.add_item(i, v)
i += 1
tc_index.build(10)
# 将这份index存到硬盘
tc_index.save('tc_index_build10.index')
# 反向id==>word映射词表
reverse_word_index = dict([(value, key) for (key, value) in word_index.items()])
# get_nns_by_item基于annoy查询词最近的10个向量,返回结果是个list,里面元素是索引
for item in tc_index.get_nns_by_item(word_index[u'卖空'], 10):
print(reverse_word_index[item]) # 用每个索引查询word