官网解释说 tensorflow 读取数据有 3 种方式
1. feed:供给数据,每次迭代 临时 生成数据,喂给 模型
2. 从文件中读取:本文主讲
3. 预加载数据:定义常量或者变量来保存数据,仅适用小数据量
从文件读取有 3 大步骤
1. 生成读取器,不同类型的文件有对应的读取器
2. 把文件名列表生成队列
3. 用读取器的 read 方法读取队列中的文件
文件读取器
不同类型的文件对应不同的文件读取器,我们称为 reader对象;
该对象的 read 方法自动读取文件,并创建数据队列,输出key/文件名,value/文件内容;
reader = tf.TextLineReader() ### 一行一行读取,适用于所有文本文件 reader = tf.TFRecordReader() ### A Reader that outputs the records from a TFRecords file reader = tf.WholeFileReader() ### 一次读取整个文件,适用图片
生成文件名队列
生成文件名队列主要方法是 string_input_producer 和 slice_input_producer;
string_input_producer
把输入的 list 生成队列
def string_input_producer(string_tensor, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True, seed=None, capacity=32, shared_name=None, name=None, cancel_op=None)
string_tensor:A 1-D string tensor with the strings to produce
num_epochs:回合数,表示 string_tensor 中每个元素的使用次数 注意:如果它不是None,则此函数创建本地计数器 epochs,需要使用local_variables_initializer()初始化局部变量
shuffle:每个回合中元素顺序是否打乱
seed:随机种子,取值为整数
capacity:队列容量
tf.train.start_queue_runners
注意,在调用tf.train.string_input_producer后,文件名并没有被真正加入文件名队列,而只是创建了一个空队列,此时如果直接计算,系统会陷入阻塞状态。
此时需要启动队列,就是调用tf.train.start_queue_runners
代码示例
filenames = ['f%s.csv'%i for i in range(5)] file_queue1 = tf.train.string_input_producer(filenames, num_epochs=2, shuffle=True) # 创建一个空的文件名队列 attrs = dir(file_queue1) ### 可查看属性 sess = tf.Session() print(sess.run(file_queue1.size())) # 0 空的 sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # 不能是 tf.global_variables_initializer() 哦 tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # 启动队列 print(sess.run(file_queue1.size())) # 10 # 此处可以看到epochs的功能
slice_input_producer
基本同 string_input_producer
def slice_input_producer(tensor_list, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True, seed=None, capacity=32, shared_name=None, name=None)
tensor_list:A list of `Tensor` objects
注意:也需要启动队列
代码示例1
filelist = ['2.png', '3.png'] getfile = tf.train.slice_input_producer([filelist], num_epochs=2, shuffle=False) # 注意 filelist 必须加 [],此处filelist为list with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # must tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # must while 1: try: print(sess.run(getfile)) except: break # [b'2.png'] # [b'3.png'] # [b'2.png'] # [b'3.png']
注意,在使用中,传入的 list 需要另外加个[ ]
getfile 表示每次从队列中取一个元素,读取方式类似于 python 中的 queue
代码示例2
filelist2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(filelist) # 转换成tensor getfile2 = tf.train.slice_input_producer([filelist2], num_epochs=2, shuffle=True) # filelist为tensor with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # must tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # must print(sess.run(getfile2)) # [b'3.png']
输入的 list 中每个元素为 tensor
读取文件
各种文件读取方法基本一致
csv
每次读取一行
########## 文件名队列 ########## # xx2 有空值 filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["myfiles/xx1.csv", "myfiles/xx2.csv"], shuffle=False) ########## reader对象 (文件阅读器)########## reader = tf.TextLineReader() ########## read 方法 ########## key, value = reader.read(filename_queue) # 为数据设定默认格式,如果出现空值,就替换为这种格式的默认值 # 注意格式必须一样,因为输出的格式是统一的,如下 # [array([ 4. , 0. , 34.322323, 1. ], dtype=float32)] record_defaults = [[1.], [1.], [1.], [1.]] col1, col2, col3, col4 = tf.decode_csv(value, record_defaults=record_defaults) # decode_csv features = tf.concat([[col1], [col2], [col3], [col4]], 0) with tf.Session() as sess: coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord) # 启动队列,相当于是启动了多个线程,并将coord传入每个线程 for i in range(12): example = sess.run([features]) print(example) coord.request_stop() # coord.join(threads) # 等待结束
文件阅读器每次从文件内读取一行,如果有空值,就根据默认格式自动填补,decode_csv 将读取内容解析成张量;
将上述代码与多线程 QueueRunner 代码对比,不难发现,其实 string_input_producer 生成的就是一个 QueueRunner; 【多线程机制】
图片
每次读取全部图片内容,不是一行一行
with tf.Session() as sess: filename = ['myfiles\2.png', 'myfiles\3.png'] filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filename, shuffle=False, num_epochs=2) ### 文件名队列 reader = tf.WholeFileReader() ### 文件读取器 key, value = reader.read(filename_queue) ### 读取文件 tf.local_variables_initializer().run() threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) ### 启动队列 i = 0 while True: i += 1 image_data = sess.run(value) with open('test_%d.jpg' % i, 'wb') as f: f.write(image_data) # 获取图片数据并保存
TFrecords
这部分内容很多,参考我的博客
读取数据的多线程机制
tensorflow 读取数据都是多线程的;
多线程读取数据也是基于 Queue 的多线程编程;
主线程读取数据,然后计算,在读数据这部分有两个线程,一个线程读取文件名,生成文件名队列,另一个线程从文件名队列中获取文件名,并读取相应文件,生成数据队列。
图示如下
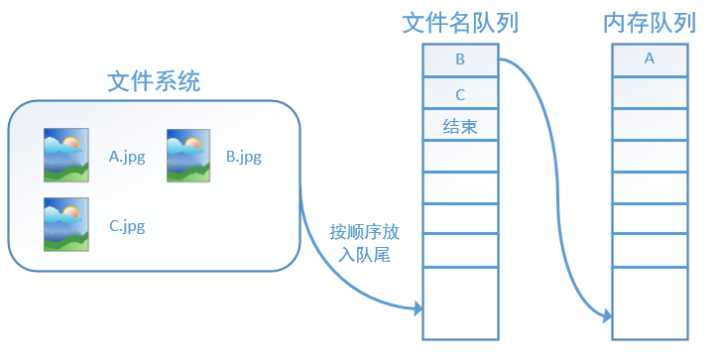
tensorflow 在队列中加入“结束”标记符,当读取线程检测到该标记符时,会抛出异常 OutOfRange,后续代码会捕捉该异常,从而结束线程
批量读取
images = ['wgb1', 'wgb2', 'wgb3'] # images, labels 元素类型必须一致 labels= ['1','2','3'] getfile3 = tf.train.slice_input_producer([images, labels], num_epochs=2, shuffle=True) # 直接生成2x3个元素,每次取2个 file_batch = tf.train.batch([getfile3], batch_size=2, capacity=10) # 每次执行getfile3两次,批量读取 # file_batch = tf.train.batch([getfile3], batch_size=2, capacity=1) # 这个队列大小貌似没影响 ## 随机取元素,此处因为slice_input_producer已经随机,所以无需shuffle_batch # file_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) while 1: try: print(sess.run(file_batch)) except: break # [[b'wgb1' b'1'] # [b'wgb2' b'2']] # [[b'wgb3' b'3'] # [b'wgb3' b'3']] # [[b'wgb1' b'1'] # [b'wgb2' b'2']]
1. tf.train.batch 实现了批量读取,相当于是执行了n次读取队列操作
2. 此处在队列中同时填入了两个list,在读取时,同时读取两个list中的同位置的元素,类似于 zip
3. slice_input_producer 直接生成 epochs个list
这两个方法都可以结合多线程来实现并发读取,方法类似于python中的多线程,具体可参考我的其他博客。
tf.train.batch
多次执行操作
tf.train.batch( tensors, batch_size, num_threads=1, capacity=32, enqueue_many=False, shapes=None, dynamic_pad=False, allow_smaller_final_batch=False, shared_name=None, name=None )
参数解释:
Args: tensors: The list or dictionary of tensors to enqueue. batch_size: The new batch size pulled from the queue. num_threads: The number of threads enqueuing tensors. The batching will be nondeterministic if num_threads > 1. capacity: An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue. #进行shuffle的输入是否为单个tensor enqueue_many: Whether each tensor in tensors is a single example. shapes: (Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the inferred shapes for tensors. dynamic_pad: Boolean. Allow variable dimensions in input shapes. The given dimensions are padded upon dequeue so that tensors within a batch have the same shapes. allow_smaller_final_batch: (Optional) Boolean. If True, allow the final batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue. shared_name: (Optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given name across multiple sessions. name: (Optional) A name for the operations.
实际用法见上例
参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/heiheiya/article/details/80967301 string_input_producer参数详解
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30666517/article/details/79715045