IO 面向流,堵塞
管道可以理解为水管,可以直接运输水流(字节数据)
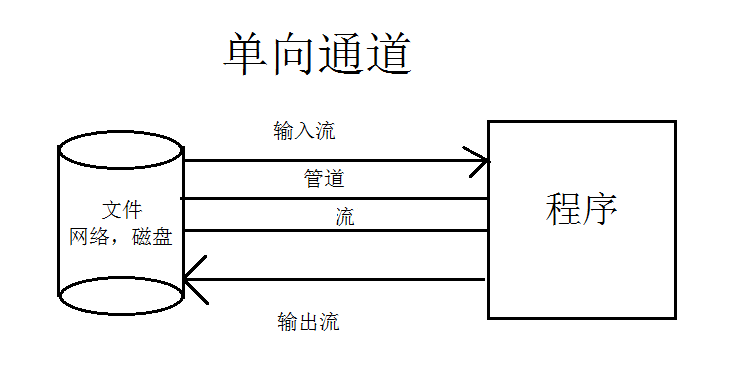
NIO 面向缓冲区,非堵塞
管道可以理解铁路,需要依赖火车(缓冲区)才能运输数据。
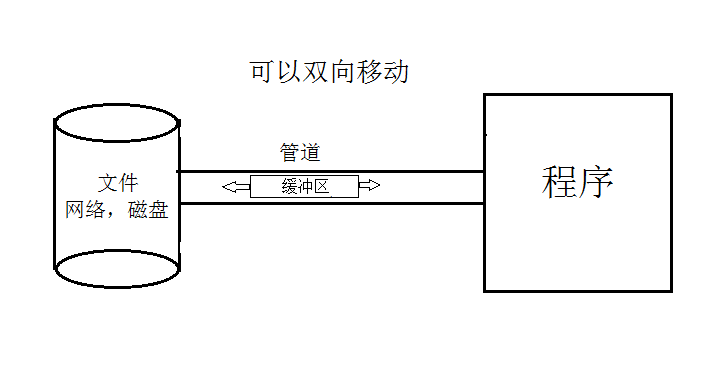
Java NIO系统的核心在于:通道/管道(Channel)和缓冲区(Buffer)。通道表示打开到I0设备(例如:文件、套接字)的连接。若需要使用NIO系统,需要获取用于连接I0设备的通道以及用于容纳数据的缓冲区。然后操作缓冲区,对数据进行处理。简而言之,Channel负责传输,Buffer负责存储
缓冲区
概念
缓冲区就是数组,用户存储不同数据类型的数据,根据数据类型不同(boolean除外),提供了相应类型的缓冲区
ByteBuffer
CharBuffer
ShortBuffer
IntBuffer
LongBuffer
FloatBuffer
DoubleBuffer
上述缓冲区的管理方式几乎一致,通过allocate()获取缓冲区,缓冲区存储数据的连个核心方法 put()、get()
缓冲区中的四个核心属性:
capacity:容量,表示缓冲区中最大存储数据的容量。一旦声明不能改变。 limit: 界限,表示缓冲区中可以操作数据的大小。(limit后数据不能进行读写) position:位置,表示缓冲区中正在操作数据的位置。 mark:标记,表示记录当前position的位置。可以通过reset()恢复到mark的位置 0<=mark<=position<=limit<=capacity
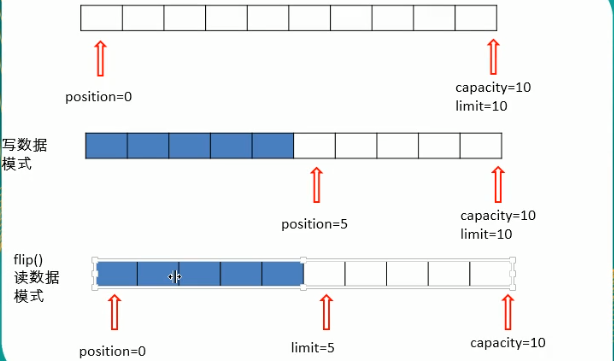
基本操作
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//test1();
test2();
}
public static void test1(){
ByteBuffer byteBuffer= ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
System.out.println("-----allocate-----");
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
byteBuffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
System.out.println("-----put()-----");
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
//切换读取模式
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println("-----flip()-----");
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
System.out.println("-----get()-----");
byte[] bytes = new byte[byteBuffer.limit()];
byteBuffer.get(bytes);//如果bytes的空间大于byteBuffer.limit(),会报错
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,byteBuffer.limit()));
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
//可重复读取数据
byteBuffer.rewind();
System.out.println("-----rewind()-----");
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
//清空缓冲区(缓冲区的数据并没有真正意义上的清空,但处于被遗忘的状态)
byteBuffer.clear();
System.out.println("-----clear()-----");
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.limit());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.capacity());
}
public static void test2(){
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
byteBuffer.get(bytes, 0, 2);
byteBuffer.mark();
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,2));
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
byteBuffer.get(bytes, 0, 2);
//position又回到了mark标记的配置
byteBuffer.reset();
byteBuffer.get(bytes, 0, 2);
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,2));
System.out.println(byteBuffer.position());
}
}
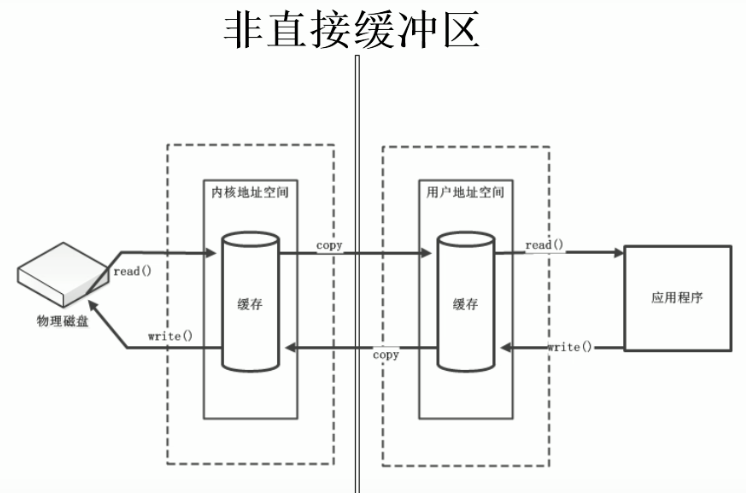
直接缓冲区和非直接缓冲区
非直接缓冲区:通过allocate()方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在JVM的内存中
直接缓冲区:通过allocateDirect()方法分配直接缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在物理内存中。可以提高效率

内核空间与用户空间
内核空间主要指操作系统用于程序调度、虚拟内存的使用或者连接硬件资源等的程序逻辑。为了保证操作系统的稳定向,运行在操作系统中的用户进程不能访问操作系统所使用的内存空间。如果用户程需要访问硬件资源,如网络连接等,可以调用操作系统提供的接口来实现,这个接口的调用其实也是系统调用。每次系统调用都会存在两个内存空间的切换,通常的网络传输也是一次系统调用,通过网络传输的数据先是从内核空间从远程主机接受数据,然后再从内核空间复制到用户空间,供程序使用。这种复制手段很费时,虽然包住了程序运行时的安全性与稳定性,但是也牺牲了部分效率。现在linux系统上提供了sendfile文件传输方式来减少这种复制方式的成本。
内核空间和用户空间大小分配也是个需要权衡的问题,如果是一台登录服务器要分配更多的内核空间,因为没有个登录用户操作系统都会初始化一个用户进程,这个进程大部分在内核空间运行。当前windows内核:用户为1:1(也就是大约2G内核空间,2G用户空间),linux为1:3。

补充参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012129558/article/details/82878994
通道
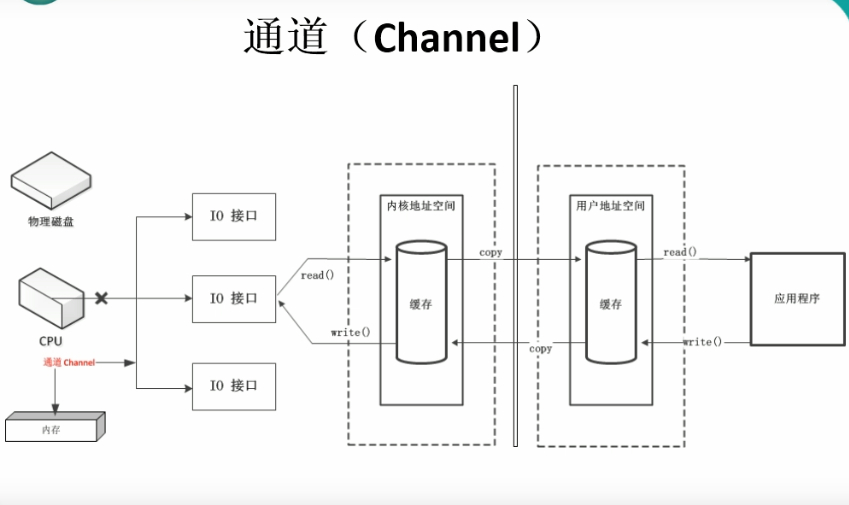
DMA技术的重要性在于,利用它进行数据传送时不需要CPU的参与。每台电脑主机板上都有DMA控制器,通常计算机对其编程,并用一个适配器上的ROM(如软盘驱动控制器上的ROM)来储存程序,这些程序控制DMA传送数据。一旦控制器初始化完成,数据开始传送,DMA就可以脱离CPU,独立完成数据传送。
参考:https://baike.baidu.com/item/DMA%E9%80%9A%E9%81%93/7492727?fr=aladdin
通道(Channe1):用于源节点与目标节点的连接。在Java NIO中负责缓冲区中数据的传输。Channe1本身不存储数据,因此需要配合缓冲区进行传输。
通道的主要实现类

注意FileChannel不能切换非堵塞模式,通过上面的图可以看出SelectableChannel(监听器),下面没有FileChannel
获取通道
1.Java针对支持通道的类提供了getChanne1()方法
本地IO:
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
RandomAccessFile
网络IO:
Socket
ServerSocket
DatagramSocket
2.在JDK1.7中的NIO.2针对各个通道提供了静态方法open()
3.在JDK 1.7中的NIO.2的Files 工具类的newByteChannel()
1、利用通道完成文件复制(使用非直接缓存区),速度比面向流块
public static void main(String[] args) {
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\t.txt";
copyFile(from_file,to_file);
}
private static void copyFile(String from_file, String to_file) {
try {
//创建输入文件通道
FileChannel fcIn = new FileInputStream(from_file).getChannel();
//创建输出文件通道
FileChannel fcOut = new FileOutputStream(to_file).getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(fcIn.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
fcOut.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
fcIn.close();
fcOut.close();
System.out.println("copy successful");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2、利用通道完成文件复制(使用直接缓存区,内存映射),速度比非直接缓冲区块
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\t.txt";
copyFile(from_file,to_file);
}
private static void copyFile(String from_file, String to_file) throws IOException {
FileChannel inchannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(from_file), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outchannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(to_file), StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//内存映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inByteBuffer = inchannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inchannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outByteBuffer = outchannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inchannel.size());
//直接对缓冲区进行数据读写操作
byte bytes[] = new byte[1024];
for(int i=0;i<inchannel.size();i++){
outByteBuffer.put(inByteBuffer.get());
}
inchannel.close();
outchannel.close();
}
2、利用通道完成文件复制(使用直接缓存区,内存映射),速度比非直接缓冲区快(transferTo、transferFrom)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\t.txt";
copyFile(from_file,to_file);
}
private static void copyFile(String from_file, String to_file) throws IOException {
FileChannel inchannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(from_file), StandardOpenOption.READ);
FileChannel outchannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(to_file), StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
inchannel.transferTo(0,inchannel.size(),outchannel);
inchannel.close();
outchannel.close();
}
分散和聚集
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String from_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt";
String to_file = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\t.txt";
copyFile(from_file,to_file);
}
private static void copyFile(String from_file, String to_file) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
RandomAccessFile r = new RandomAccessFile(from_file, "rw");
RandomAccessFile rw = new RandomAccessFile(to_file, "rw");
FileChannel rChannel = r.getChannel();
FileChannel rwChannel = rw.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//分散读取数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffers[] = {byteBuffer1,byteBuffer2};
rChannel.read(byteBuffers);
while (rChannel.read(byteBuffers)!=-1){
for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer:byteBuffers){
byteBuffer.flip();
}
//聚合写入数据
rwChannel.write(byteBuffers);
for (ByteBuffer byteBuffer:byteBuffers){
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
r.close();
rw.close();
}
字符集编码和解码
private static void charsettest() throws IOException {
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
ByteBuffer estr = charset.encode("sdfsd的df");
//estr.flip();
CharBuffer decode = charset.decode(estr);
System.out.println(decode.toString());
estr.rewind();
Charset gbk = Charset.forName("GBK");
CharBuffer decode1 = gbk.decode(estr);
//会出现乱码
System.out.println(decode1.toString());
}
NIO核心非堵塞
注意堵塞和非堵塞以及同步和异步的区别
网络过程中IO堵塞
假如服务器只有一个线程来处理用户请求,由于某种原因(数据还没到达)造成线程堵塞(线程放弃了CPU执行权),此时如果有其他的用户请求,该线程就不能及时的处理该请求。传统的解决方式就是开一个线程池,多线程来处理用户请求,但是这样可能依然会造成堵塞的情况。
NIO解决非堵塞
利用的是select选择器。将用户的请求注册到select上,select来监听所有的请求数据(通过单独的一个线程),如果请求的数据准备完毕,才将该请求任务分配到服务器的一个或者多个线程上执行。
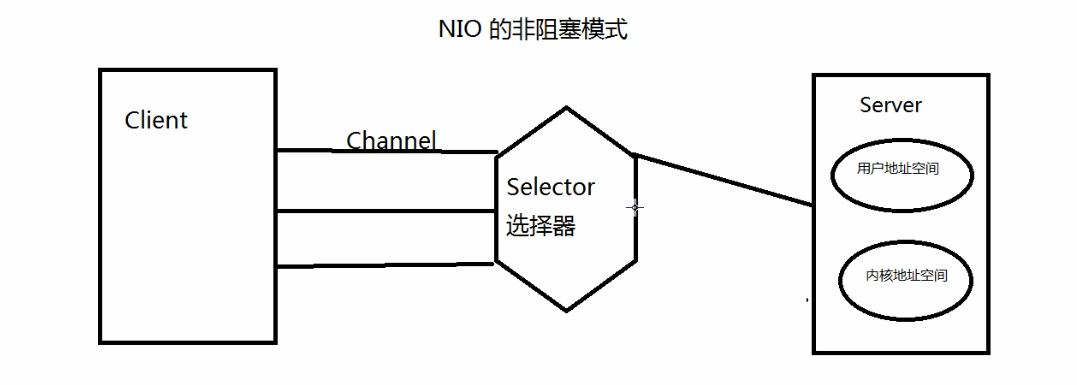
1、使用NIO,阻塞式完成通讯
服务端
//服务端
public class BlockNIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8090));
while (true){
//获取客户端连接通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("连接成功,等待用户发送数据");
SocketAddress remoteAddress = socketChannel.getRemoteAddress();
String s = remoteAddress.toString();
String[] split = s.split(":");
//写入本地
String path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\"+split[1]+".txt";
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(path), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//接受客户端的数据并且写入文件
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
//可以给客户端提供反馈信息
byteBuffer.put("数据已经接受完毕...".getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("写入数据成功....");
}
}
}
客户端
//客户端
public class BlockNIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8090));
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
//System.out.println("模拟10秒之后发送数据...");
//可以开启两个客户端,一个睡10秒发送数据(先请求),一个不用睡眠(后请求),发现,必须等第一个用户处理完毕之后,第二个用户才可以被处理
//Thread.sleep(10000);
//分配缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取本地文件发送到服务器
while (fileChannel.read(byteBuffer)!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
//告诉服务器,我的数据已经发送完毕
socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
//接受服务器返回来的消息
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
int len =-1;
while ((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer))!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
stringBuffer.append(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
socketChannel.close();
fileChannel.close();
}
}
1、使用NIO,非阻塞式完成通讯(通过select作为监听器)
服务端
//服务端
public class BlockNIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//切换非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8090));
//获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//将该通道注册到select中,让select监听该通道的连接是否准备就绪
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = null;
//通过选择器轮询获取已经准备就绪的事件
while (selector.select()>0){
iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
//如果获取的是准备连接就绪的事件
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
System.out.println("有客户端已经准备好连接了....");
//开始接受连接客户端
SocketChannel accept = serverSocketChannel.accept();
//切换非阻塞模式
accept.configureBlocking(false);
//将通道注册到selector中,让select监听该通道的数据是否准备就绪
accept.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
else if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(100);
String path = "C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\"+i+".txt";
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(path), StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (socketChannel.read(byteBuffer)!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
fileChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
byteBuffer.put("数据已经接受完毕...".getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
fileChannel.close();
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("写入数据成功....");
}
//取消选择键
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
客户端
//客户端
public class BlockNIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8090));
FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("C:\Users\zhengyan\Desktop\test1\x.txt"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
//System.out.println("模拟10秒之后发送数据...");
//可以开启两个客户端,一个睡10秒发送数据(先请求),一个不用睡眠(后请求),发现,必须等第一个用户处理完毕之后,第二个用户才可以被处理
//Thread.sleep(20000);
//分配缓冲区大小
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取本地文件发送到服务器
while (fileChannel.read(byteBuffer)!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
//告诉服务器,我的数据已经发送完毕
socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
//接受服务器返回来的消息
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
int len =-1;
while ((len=socketChannel.read(byteBuffer))!=-1){
byteBuffer.flip();
stringBuffer.append(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,len));
byteBuffer.clear();
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer);
socketChannel.close();
fileChannel.close();
}
}
使用UDP
服务端
//服务端
public class BlockNIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取通道
DatagramChannel datagramChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
//切换非阻塞模式
datagramChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//绑定端口
datagramChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8090));
//获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//只需要监听数据是否到来
datagramChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
while (selector.select()>0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
DatagramChannel channel = (DatagramChannel) selectionKey.channel();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
channel.receive(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit()));
}
//取消选择键
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
}
客户端
//客户端
public class BlockNIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
DatagramChannel datagramChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
buf.put(new Date().toString().getBytes());
buf.flip();
datagramChannel.send(buf,new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8090));
buf.clear();
datagramChannel.close();
}
}
管道(Pipe)
Java NIO 管道是两个线程之间的单向数据连接。Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。
public class PipeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取管道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open();
new Thread(new MyThread1(pipe)).start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
new Thread(new MyThread2(pipe)).start();
}
}
class MyThread1 implements Runnable{
private Pipe pipe;
public MyThread1(Pipe pipe){
this.pipe = pipe;
}
@Override
public void run() {
Pipe.SinkChannel sink = pipe.sink();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put("ssss".getBytes());
byteBuffer.flip();
try {
sink.write(byteBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
byteBuffer.clear();
}
}
class MyThread2 implements Runnable{
private Pipe pipe;
public MyThread2(Pipe pipe){
this.pipe = pipe;
}
@Override
public void run() {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Pipe.SourceChannel source = pipe.source();
try {
source.read(byteBuffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array(),0,byteBuffer.limit()));
}
}