一、构建二叉树
我们构建一个如下图所示的二叉树:
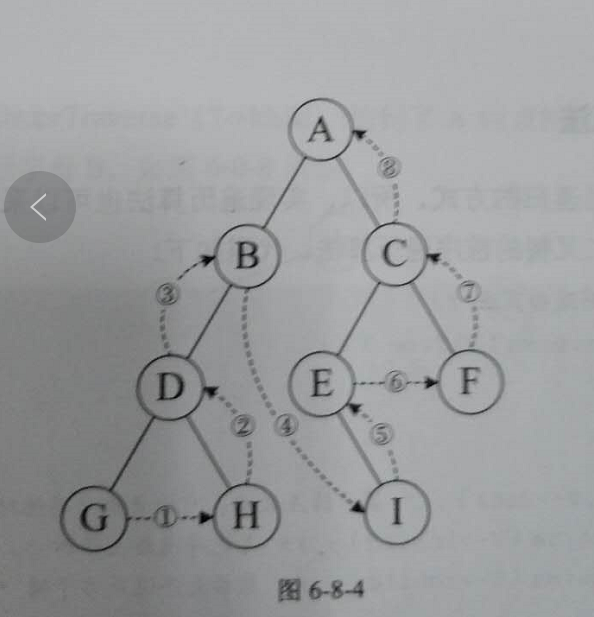
我们使用下面的数据结构来描绘出这个二叉树
1 public class Node { 2 private String name = ""; 3 public Node leftChild; 4 public Node rightChild; 5 6 public Node(String name) { 7 this.name = name; 8 } 9 10 public Node() { 11 } 12 13 public void setName(String name) { 14 this.name = name; 15 }
二、二叉树的遍历
前序遍历:
1 /** 2 * 前序遍历 3 */ 4 public String readPre() { 5 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); 6 result.append(name); //前序遍历 7 if (leftChild != null) { 8 result.append(leftChild.readPre()); 9 } 10 if (rightChild != null) { 11 result.append(rightChild.readPre()); 12 } 13 return result.toString(); 14 }
中序遍历:
1 /** 2 * 中序遍历 3 */ 4 public String readMid() { 5 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); 6 if (leftChild != null) { 7 result.append(leftChild.readMid()); 8 } 9 result.append(name); //中序遍历 10 if (rightChild != null) { 11 result.append(rightChild.readMid()); 12 } 13 return result.toString(); 14 }
后序遍历:
1 /** 2 * 后序遍历 3 */ 4 public String readEnd() { 5 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); 6 if (leftChild != null) { 7 result.append(leftChild.readEnd()); 8 } 9 if (rightChild != null) { 10 result.append(rightChild.readEnd()); 11 } 12 result.append(name); //后序遍历 13 return result.toString(); 14 }
从上面可以看到,前序、中序、后序遍历的算法基本上差不多,其主要是在对根节点的访问顺序不同,然后利用递归的方式来进行实现。
层序遍历:
1 /** 2 * 层序遍历 3 */ 4 public String readLevel() { 5 Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 6 StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); 7 queue.offer(this); 8 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 9 Node curNode = queue.poll(); 10 result.append(curNode.name); 11 if (curNode.leftChild != null) { 12 queue.offer(curNode.leftChild); 13 } 14 if (curNode.rightChild != null) { 15 queue.offer(curNode.rightChild); 16 } 17 } 18 return result.toString(); 19 }
跟其他遍历不同,层序遍历需要借助队列来进行实现。首先将根节点放到队列中,然后遍历循环,依次将左孩子和右孩子放置到队列中。
三、还原二叉树
在第二章节中,获得到前序、中序、后序、层序的结果依次如下:
1 String pre = "ABDGHCEIF"; //前序遍历 2 String mid = "GDHBAEICF"; //中序遍历 3 String end = "GHDBIEFCA"; //后序遍历 4 String level = "ABCDEFGHI"; //层序遍历
那能否通过上面的字符串还原出二叉树的的形状呢?这个分情况讨论
前序+中序:
思路:通过前序获得根节点的位置,利用根节点将中序序列分为左子树和右子树,然后不断的递归划分即可。
代码:
1 /** 2 * 根据前序和中序排序表获取树 3 */ 4 private static Node buildTreeByPreMid(char[] pre, int preBegin, int preEnd, char[] mid, int midBegin, int midEnd) { 5 Node root = new Node(); 6 root.setName(pre[preBegin] + ""); 7 8 int midRootLoc = 0; 9 for (int i = midBegin; i <= midEnd; i++) { 10 if (mid[i] == pre[preBegin]) { 11 midRootLoc = i; 12 break; 13 } 14 } 15 16 //递归得到左子树 17 if (preBegin + (midRootLoc - midBegin) >= preBegin + 1 && (midRootLoc - 1) >= midBegin) { 18 Node leftChild = buildTreeByPreMid(pre, preBegin + 1, preBegin + (midRootLoc - midBegin), 19 mid, midBegin, midRootLoc - 1); 20 root.leftChild = leftChild; 21 } 22 23 //递归得到右子树 24 if (preEnd >= (preEnd - (midEnd - midRootLoc) + 1) && (midEnd >= midRootLoc + 1)) { 25 Node rightChild = buildTreeByPreMid(pre, preEnd - (midEnd - midRootLoc) + 1, preEnd, 26 mid, midRootLoc + 1, midEnd); 27 root.rightChild = rightChild; 28 } 29 30 return root; 31 }
后序+中序:
思路:通过后序获取根节点的位置,然后在中序中划分左子树和右子树,然后递归划分即可。
代码:
1 /** 2 * 根据后序和中序遍历还原树 3 */ 4 private static Node buildTreeByMidEnd(char[] mid, int midBegin, int midEnd, char[] end, int endBegin, int endEnd) { 5 Node root = new Node(); 6 root.setName(end[endEnd] + ""); 7 int midRootLoc = 0; 8 for (int i = midEnd; i >= midBegin; i--) { 9 if (mid[i] == end[endEnd]) { 10 midRootLoc = i; 11 break; 12 } 13 } 14 15 //还原左子树 16 if (midRootLoc - 1 >= midBegin && (endBegin + (midRootLoc - midBegin) - 1 >= endBegin)) { 17 Node leftChild = buildTreeByMidEnd(mid, midBegin, midRootLoc - 1, end, endBegin, endBegin + (midRootLoc - midBegin) - 1); 18 root.leftChild = leftChild; 19 } 20 21 //还原右子树 22 if (midEnd >= midRootLoc + 1 && (endEnd - 1 >= endEnd - (midEnd - midRootLoc))) { 23 Node rightChild = buildTreeByMidEnd(mid, midRootLoc + 1, midEnd, end, endEnd - (midEnd - midRootLoc), endEnd - 1); 24 root.rightChild = rightChild; 25 } 26 27 return root; 28 }
层序+中序:
思路:根据层序遍历获取根节点的位置,然后将中序划分为左子树和右子树,然后根据划分出的左子树和右子树分别在层序遍历中获取其对应的层序顺序,然后递归调用划分即可。
代码如下:
1 /** 2 * 根据层序遍历和中序遍历得到结果 3 * @return 4 */ 5 private static Node buildTreeByMidLevel(char[] mid, char[] level, int midBegin, int midEnd) { 6 Node root = new Node(level[0] + ""); 7 8 int midLoc = -1; 9 for (int i = midBegin; i <= midEnd; i++) { 10 if (mid[i] == level[0]) { 11 midLoc = i; 12 break; 13 } 14 } 15 16 if (level.length >= 2) { 17 if (isLeft(mid, level[0], level[1])) { 18 Node left = buildTreeByMidLevel(mid, getLevelStr(mid, midBegin, midLoc - 1, level), midBegin, midLoc - 1); 19 root.leftChild = left; 20 if (level.length >= 3 && !isLeft(mid, level[0], level[2])) { 21 Node right = buildTreeByMidLevel(mid, getLevelStr(mid, midLoc + 1, midEnd, level), midLoc + 1, midEnd); 22 root.rightChild = right; 23 } 24 } else { 25 Node right = buildTreeByMidLevel(mid, getLevelStr(mid, midLoc + 1, midEnd, level), midLoc + 1, midEnd); 26 root.rightChild = right; 27 } 28 } 29 return root; 30 } 31 32 /** 33 * 将中序序列中midBegin与MidEnd的字符依次从level中提取出来,保持level中的字符顺序不变 34 */ 35 private static char[] getLevelStr(char[] mid, int midBegin, int midEnd, char[] level) { 36 char[] result = new char[midEnd - midBegin + 1]; 37 int curLoc = 0; 38 for (int i = 0; i < level.length; i++) { 39 if (contains(mid, level[i], midBegin, midEnd)) { 40 result[curLoc++] = level[i]; 41 } 42 } 43 return result; 44 } 45 46 /** 47 * 如果str字符串的begin和end位置之间(包括begin和end)含有字符target,则返回true。 48 */ 49 private static boolean contains(char[] str, char target, int begin, int end) { 50 for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) { 51 if (str[i] == target) { 52 return true; 53 } 54 } 55 return false; 56 }
其他的遍历组合均不能还原出二叉树的形状,因为无法确认其左右孩子。例如,前序为AB,后序为AB,则无法确认出,B节点是A节点的左孩子还是右孩子,因此无法还原。
完整代码已经上传至GitHub: