本文总结自:https://www.cnblogs.com/chengxiao/p/6059914.html
HashMap结构:
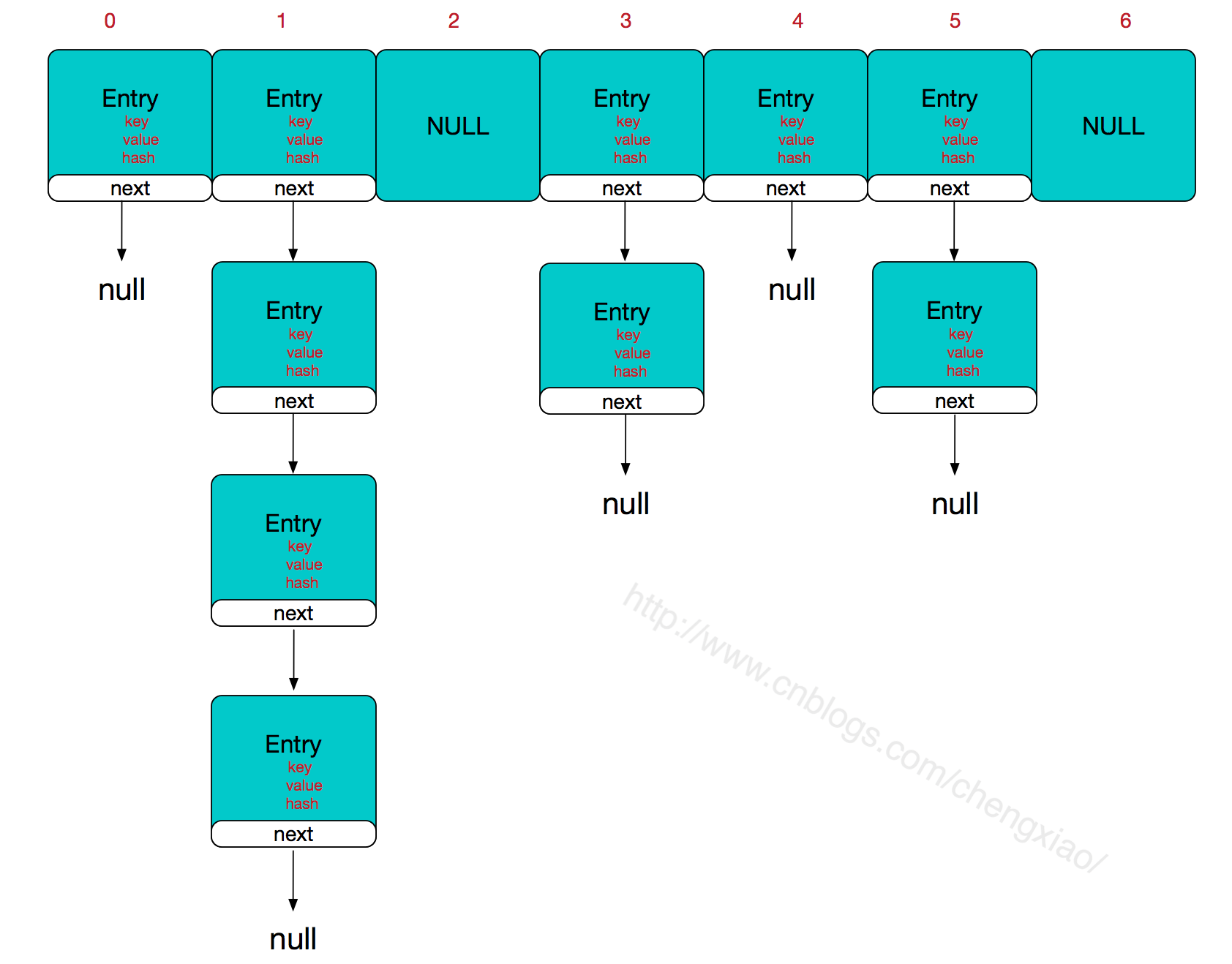
如上可知:HashMap的主干是一个Entry数组,每个元素是一个Entry链表,而每个Entry包含一个key、value(键值对)、hash(运算得到的hash值)、next(指向下一个Entry的引用)
备注:以下的table数组指的是Entry数组
为什么需要链表?
为了解决hash冲突,两个不同的元素通过哈希函数计算而得到的地址可能相同。
解决哈希冲突的方式有许多,有:开放定址法(发生冲突,继续寻找下一块未被占用的存储地址),再散列函数法,链地址法,而HashMap即是采用了链地址法(拉链法),也就是数组+链表的方式。
决定HashMap的几个重要属性
capacity 容量 (总容量)注:不会被完全填满
loadFactor 负载因子 (能填充到多少)
threshold 阈值(填充到啥大小后需要扩容)
构造函数
HashMap有4个构造器,可传initialCapacity 和loadFactor自定义,
不传则使用默认值:initialCapacity默认为16,loadFactory默认为0.75
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
核心方法分析:
构造函数

public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { //此处对传入的初始容量进行校验,最大不能超过MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1<<30(230) if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = initialCapacity; init();//init方法在HashMap中没有实际实现,不过在其子类如 linkedHashMap中就会有对应实现 }
可知:在常规构造器中,为hashMap进行了初始化,但并没有为数组分配内存空间(有一个入参为指定Map的构造器例外)
其实,一般是在执行put操作的时候才真正构建table数组。
put方法

public V put(K key, V value) { //如果table数组为空数组{},则进行数组填充(为table分配实际内存空间) if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); //inflate填充 } //如果key为null,存储位置为table[0]或table[0]的冲突链上?? if (key == null) //hashMap的元素可为null! return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key);//对key的hashcode进一步计算,确保散列均匀 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);//获取在table中的实际位置 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { //如果该位置已有数据,执行覆盖操作,并返回旧value Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++;//这是为了保证并发访问时,若HashMap内部结构发生变化,快速响应失败 addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//最后,新增一个entry return null; }
可知:
1.在执行put操作的时候才真正构建table数组
2.hashMap的元素可为null
3.hashMap并不适用于并发环境
inflateTable方法

//填充数组 private void inflateTable(int toSize) { int capacity = roundUpToPowerOf2(toSize);//根据函数名可知:capacity一定是2的次幂 threshold = (int) Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); //此处为threshold赋值,取capacity*loadFactor和MAXIMUM_CAPACITY+1的最小值,capaticy一定不会超过MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,除非loadFactor大于1 table = new Entry[capacity]; initHashSeedAsNeeded(capacity); }
可知:
1. 数组容量必须为2的次幂
2. threshold的值是取capacity*loadFactor和MAXIMUM_CAPACITY+1的最小值,capaticy一定不会超过MAXIMUM_CAPACITY,除非loadFactor大于1(不可能吧。。)
roundUpToPowerOf2方法
private static int roundUpToPowerOf2(int number) { // assert number >= 0 : "number must be non-negative"; return number >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : (number > 1) ? Integer.highestOneBit((number - 1) << 1) : 1; }
可知:roundUpToPowerOf2最终决定容量大小,而他使得数组容量必须为2的次幂
初始化并填充完数组后该进行元素插入位置的计算了~
hash方法

//对key的hashcode进一步进行计算以及二进制位的调整等来保证最终获取的存储位置尽量分布均匀 final int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); }
可知: hashMap会调整hashCode使得元素分布均匀
indexFor方法

/** * 最终返回数组下标 */ static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length-1); }
h&(length-1)是什么?
假设容量为16,length-1=15,h=18,运算得:
1 0 0 1 0
&0 1 1 1 1 __________________ 0 0 0 1 0 = 2
其实,这是为了保证获取的index一定在数组范围内
可知:indexOf方法获取下标并保证在数组范围内
那么,综上所述,获取下标分为:
![]()
最后,插入~
addEntry方法

void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { //当size超过临界阈值threshold,并且即将发生哈希冲突时进行扩容 resize(2 * table.length); //扩容都是两倍扩容 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); }
可知:
1. 当发生哈希冲突并且size大于阈值的时候,需要进行数组扩容
2. 扩容是都是进行双倍扩容
重点:填充数组时,数组容量一定是2次幂,数组扩容时,又是双倍扩容
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
那么,为什么数组的大小一定得是2次幂呢?
从一些方法上,我们可以看出些端倪,从resize入手:
resize方法

void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable, initHashSeedAsNeeded(newCapacity)); //重新计算元素的位置 table = newTable; //本质是把新数组赋值给旧数组 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); }
可知:
1.扩容时得重写计算元素的位置
2.扩容的本质是把新数组赋值给旧数组
transfer方法

void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { int newCapacity = newTable.length; //遍历数组 for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { while(null != e) { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; if (rehash) { e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); } int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //重新计算索引位置 //将当前entry的next链指向新的索引位置,newTable[i]有可能为空,有可能也是个entry链,如果是entry链,直接在链表头部插入。 e.next = newTable[i]; //重新计算索引位置,将老数组数据复制到新数组中去(数组不存储实际数据,所以仅仅是拷贝引用而已) newTable[i] = e; e = next; } } }
可知:
1. 数组其实并不存储实际数据
2. 重新计算位置依旧是indexOf方法
接下来,我们把焦点集中于indexOf方法的核心h&(length-1),他是此问题的核心所在
length为3次幂会为其带来哪些好处呢?
1. 如果length为2的次幂,则length-1转化为二进制后低位必定是11111..(例如16-1为15,二进制位1111),这样与操作的效率会非常快;
2. 如果length不是2的次幂,比如length为15,则length-1为14,对应的二进制为1110,根据与运算,运算结果的最低位永远为0,这样0001,0011,0101,1001,1011,0111,1101这几个位置永远都不能存放元素了,空间浪费相当大,
更糟的是这种情况中,数组可以使用的位置比数组长度小了很多,这增加了碰撞的几率(计算得到的下标相同),减慢了查询的效率。
