C++11里新的容器unorderedmap,其底层是一个hashtable,在C++98中,unorderedmap其实已经有过,叫做hashmap。
unorderedmap(hashmap)是一个模板,模板参数有5个,以下是可能的伪代码(不同的编译器有不同的实现)
1 template <class Key,
2 class Value,
3 class HashFcn = hash<Key>,
4 class EqualKey = equals_to<Key>,
5 class Alloc = alloc>
6 class hash_map
7 {
8 ...
9 };
Key是键值类型,Value是实值类型,HashFcn是一个用来寻找bucket位置的函数,稍后重点讲述,EqualKey是用来确定两个对象如何算相等,Alloc是内存分配相关。
hashtale实际上是由一层vector形成一个bucket的集合,每个bucket上挂有一个链表,在不同编译器下链表实现可能不同。既是所谓的sperate chaning开链法,分开链接。
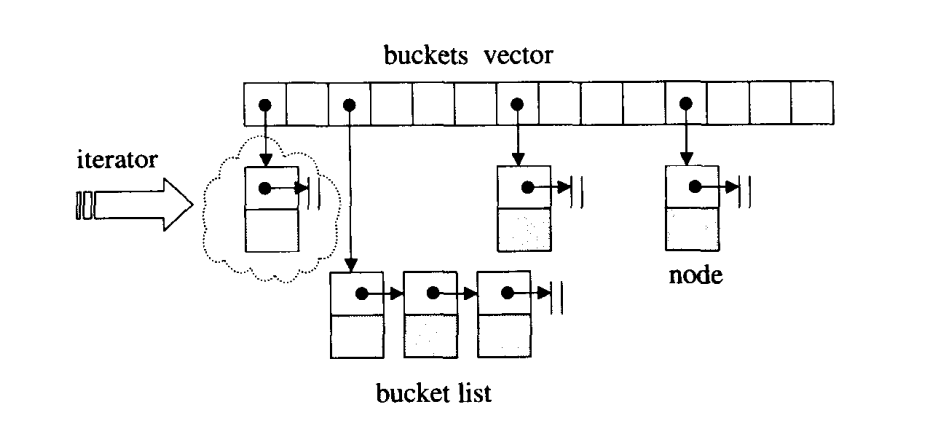
一个元素想要插入到hashtable,必须要算出挂在哪一个bucket上,再插入到bucket上的链表后端。
计算出插入到哪一个bucket上的操作,便是hashfunction的工作。
hashmap是通过Key来决定一个元素的在hashtable中的位置的,因此Key的类型尤为关键。
如果Key是一个简单的系统类型,比如int,char。那么STL已经帮我们定义好了对应的hashfunction。
class HashFcn = hash<Key>
我们注意到HashFcn模板的缺省参数hash<Key>,便是STL给我们实现好的hashfunciton。
举例hashfunction之前,先用讲到一个计算元素在bucket落脚处的函数bkt_num_key
1 size_type bkt_num_key(const key_type& key, size_t n) const
2 {
3 return hash(key) % n;
4 }
STL最终都会走到hash(key)来计算元素的bucket位置。
STL通过偏特化的方式实现了一些简单类型的hashfunction。举几个例子:
1 template <class Key> struct hash {};
2
3 template<> struct hash<char> {
4 size_t operator()(char x) const { return x; }
5 };
6
7 template<> struct hash<int> {
8 size_t operator()(int x) const { return x; }
9 };
那么其实简单类型的hashfunction就是返回自己本身。有稍微复杂一些的char*
1 template<> struct hash<const char*> {
2 size_t operator()(const char* s) const { return __stl_hash_string; }
3 }
4
5 // hash function越乱越好
6 inline size_t __stl_hash_string(const char* s)
7 {
8 unsigned_long h = 0;
9 for (: *s; ++s)
10 h = 5*h + *s;
11
12 return size_t(h);
13 }
那么如果一个Key是自定义的类型,hashfunction应该怎么做呢。
假定我们的自定义类型如下:
struct CustomerInfo
{
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int z = 0;
}
这个自定义结构当成unordermap的key,如果你不定义hashfunction应该是不能过编译的。
也许你会简单想一个hashfunction,三个int分别用STL的hashfunction版本,然后加起来!天才=_=。
1 struct HashFuncCustomer
2 {
3 std::size_t operator()(const CustomerInfo &c) const
4 {
5 using std::size_t;
6 using std::hash;
7
8 return hash<int>()(c.x)
9 + hash<int>()(c.y)
10 + hash<int>()(c.z));
11 }
12 };
能过编译。但是其实这个hashfunction所造成的碰撞是很多的。hashfunction的目标应该是越散越好,因此哈希表又叫散列表。
碰撞的时候,新加的元素会挂在bucket碰撞位置的链表后面。hashtable的查找复杂度应该是O(1)~O(n),明显碰撞越多复杂度越趋近于O(n)。
TR1版本(简单理解成C++98和C++11之间的过渡版本)提供了一种万用的hashfunction,外层调用如下即可:
1 struct HashFuncCustomer
2 {
3 std::size_t operator()(const CustomerInfo &c) const
4 {
5 using std::size_t;
6 using std::hash;
7
8 return hash_value(c.x, c.y, c.z);
9 }
10 };
内部的实现其实并不重要,内部的实现是个数学问题=_=。这里面内部用了黄金分割比例,移位等各种操作。
另外一个版本,我在实际项目中使用过的一个版本:
1 struct HashFuncCustomer
2 {
3 std::size_t operator()(const CustomerInfo &c) const
4 {
5 using std::size_t;
6 using std::hash;
7
8 return ((hash<int>()(c.x)
9 ^ (hash<int>()(c.y) << 1)) >> 1)
10 ^ (hash<int>()(c.z) << 1);
11 }
12 };
仅供参考。
hashfunction怎么写的好,应该是个数学问题。