一. 动态组件和keep-alive
1. 背景
比如我们要做一个动态组件的切换,传统的做法是通过v-if进行判断切换,核心代码如下:

2. 动态组件
(1). 基本使用
动态组件是使用 component 组件,通过一个特殊的attribute is 来实现:
代码分享:
<template> <div> <button v-for="(item,index) in tabs" :key="index" @click="tabClick(item)" :class="{active:currentTab===item}">{{item}}</button> <!-- 方案2:动态组件Component --> <!--2.1 is属性里存放的是Components里注册的组件名称 --> <component :is="currentTab"></component> </div> </template> <script> import Home1 from './pages/Home1.vue'; import Home2 from './pages/Home2.vue'; import Home3 from './pages/Home3.vue'; export default { components: { Home1, Home2, Home3 }, data() { return { tabs: ['home1', 'home2', 'home3'], currentTab: 'home1', myAge: 20 }; }, methods: { tabClick(item) { this.currentTab = item; } } } </script>
(2). 传值给子组件 和 监听子组件事件
与普通的父子组件类似,子组件通过props接收,通过$emit对外传递。
父组件
<template> <div> <button v-for="(item,index) in tabs" :key="index" @click="tabClick(item)" :class="{active:currentTab===item}">{{item}}</button> <!-- 方案2:动态组件Component --> <!-- 2.2 传值和事件监听 在Home3组件上实现--> <component :is="currentTab" name="lmr" :age='myAge' @pageClick="pageClick"></component> </div> </template> <script> import Home1 from './pages/Home1.vue'; import Home2 from './pages/Home2.vue'; import Home3 from './pages/Home3.vue'; export default { components: { Home1, Home2, Home3 }, data() { return { tabs: ['home1', 'home2', 'home3'], currentTab: 'home1', myAge: 20 }; }, methods: { tabClick(item) { this.currentTab = item; }, pageClick(v1, v2) { console.log(v1, v2); } } } </script> <style scoped> .active { color: red; } </style>
子组件Home3
<template> <div @click="myClick1"> 我是Home3组件,{{name}}--{{age}} </div> </template> <script> export default { name:'myHome3', props: { name: { type: String, default: 'ypf' }, age: { type: Number, default: 18 } }, emits: ['pageClick'], data() { return {}; }, methods: { myClick1() { this.$emit('pageClick', 20, 30, 40); } } } </script>
3. keep-alive缓存
默认情况下,切换组件,原组件就被销毁了,再次回来会重新创建组件。
代码分享:
<!-- 方案3 keep-alive保持状态 --> <!-- 注意:不写include 默认所有都缓存,存在include时,优先匹配首先检查组件自身的 name 选项 --> <!-- 缓存生命周期测试,在Home2组件上改造 --> <keep-alive include="myHome1,myHome2"> <component :is='currentTab' name='lmr' :age='myAge' @pageClick="pageClick"></component> </keep-alive>
剖析:

4. keep-alive缓存生命周期

二. Webpack分包和异步组件
1. Webpack实现js分包
(1). 背景
默认情况下,在构建整个组件树的过程中,因为组件和组件之间是通过模块化直接依赖的,那么webpack在打包时就会将组件模块打包到一起(比如 自己编写的一些业务都在这个app.xxxx.js中,一些三方依赖都打包在chunk-vendors.xxx.js中)
这个时候随着项目的不断庞大,app.js文件的内容过大,会造成首屏的渲染速度变慢;

(2). 代码分包
所以,对于一些不需要立即使用的组件,我们可以单独对它们进行拆分,拆分成一些小的代码块chunk.js; 这些chunk.js会在需要时从服务器加载下来,并且运行代码,显示对应的内容。
比如在mainjs入口中导入一段js代码,进行打包
// 普通导入js import {sum} from './components/11_异步组件的使用/utils/test.js'; console.log(sum(10,20));

改成分包写法,进行打包
// 分包的写法 import("./components/11_异步组件的使用/utils/test.js").then(({sum})=>{ console.log(sum(10,20)); });

2. Vue中实现异步组件
(1). 背景
A. 如果我们的项目过大了,对于某些组件我们希望通过异步的方式来进行加载(目的是可以对其进行分包处理),那么Vue中给我们提供了一个函数:defineAsyncComponent。
B. defineAsyncComponent接受两种类型的参数:
类型一:工厂函数,该工厂函数需要返回一个Promise对象;
类型二:接受一个对象类型,对异步函数进行配置;
(2). 代码分享
<script>
// 同步写法
import Loading from './Loading.vue';
// 导入异步组件
import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';
// 写法1
const AsyncCpn1 = defineAsyncComponent(() => import('./AsyncCpn1.vue'));
// 写法2
const AsyncCpn2 = defineAsyncComponent({
loader: () => import("./AsyncCpn2.vue"),
// 加载异步组件时要使用的组件
loadingComponent: Loading,
// 在显示 loadingComponent 之前的延迟 | 默认值:200(单位 ms)
delay: 200,
/**
*
* @param {*} error 错误信息对象
* @param {*} retry 一个函数,用于指示当 promise 加载器 reject 时,加载器是否应该重试
* @param {*} fail 一个函数,指示加载程序结束退出
* @param {*} attempts 允许的最大重试次数
*/
onError: function(err, retry, attempts) {
}
})
export default {
components: {
AsyncCpn1,
AsyncCpn2,
Loading
},
data() {
return {};
}
}
</script>
打包后的资源文件如下图:

3. Suspense
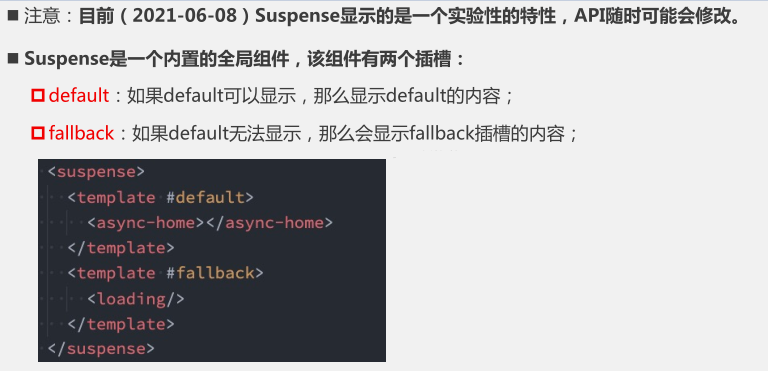
三. 引用元素/组件($ref等)
1. $ref
某些情况下,我们在组件中想要直接获取到元素对象或者子组件实例:
(1). 在Vue开发中我们是不推荐进行DOM操作的。
(2). 这个时候,我们可以给元素或者组件绑定一个ref的attribute属性。
(1). 获取元素 或 组件
子组件代码

<template> <div> {{msg}} <p><button @click="getfather">获取父亲组件和根组件</button></p> </div> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { msg: 'hello Vue3' }; }, methods:{ getfather(){ console.log('-----------------我是子组件中业务---------------------'); // 1.获取父元素 { console.log(this.$parent); // 不建议这么用,因为一个组件会被多个父组件调用,并不是每一个父组件里都有test1属性和getInfo方法 console.log(this.$parent.test1); this.$parent.getInfo(); } // 2. 获取根元素 // { // console.log(this.$root); // console.log(this.$root.test1); // this.$root.getInfo(); // } } } } </script>
父组件代码
<template> <div> <!-- ref绑定到元素上 --> <div ref="t1">hello ypf</div> <!-- ref绑定到组件上 --> <child-msg1 ref='cMsg'></child-msg1> <p><button @click="getInfo">获取信息</button></p> </div> </template> <script> import ChildMsg1 from './ChildMsg1.vue'; export default { components: { ChildMsg1 }, data() { return { test1: '我是test1' }; }, methods: { getInfo() { // 1.获取普通元素 { console.log(this.$refs.t1); console.log(this.$refs.t1.innerHTML); } // 2. 获取组件元素 { console.log(this.$refs.cMsg); // 获取组件中data数据 console.log(this.$refs.cMsg.msg); // 调用组件中的方法 this.$refs.cMsg.getfather(); } } } } </script>
2. $parent 和 $root
$parent获取父元素。
$root获取根元素。
注意:在Vue3中已经移除了$children的属性,所以不可以使用了。
代码同上
四. 组件生命周期
1. 简介
(1). 什么是生命周期呢?
每个组件都可能会经历从创建、挂载、更新、卸载等一系列的过程;
在这个过程中的某一个阶段,用于可能会想要添加一些属于自己的代码逻辑(比如组件创建完后就请求一些服务器数据);
但是我们如何可以知道目前组件正在哪一个过程呢?Vue给我们提供了组件的生命周期函数;
(2). 生命周期函数:
生命周期函数是一些钩子函数,在某个时间会被Vue源码内部进行回调;
通过对生命周期函数的回调,我们可以知道目前组件正在经历什么阶段;
那么我们就可以在该生命周期中编写属于自己的逻辑代码了;
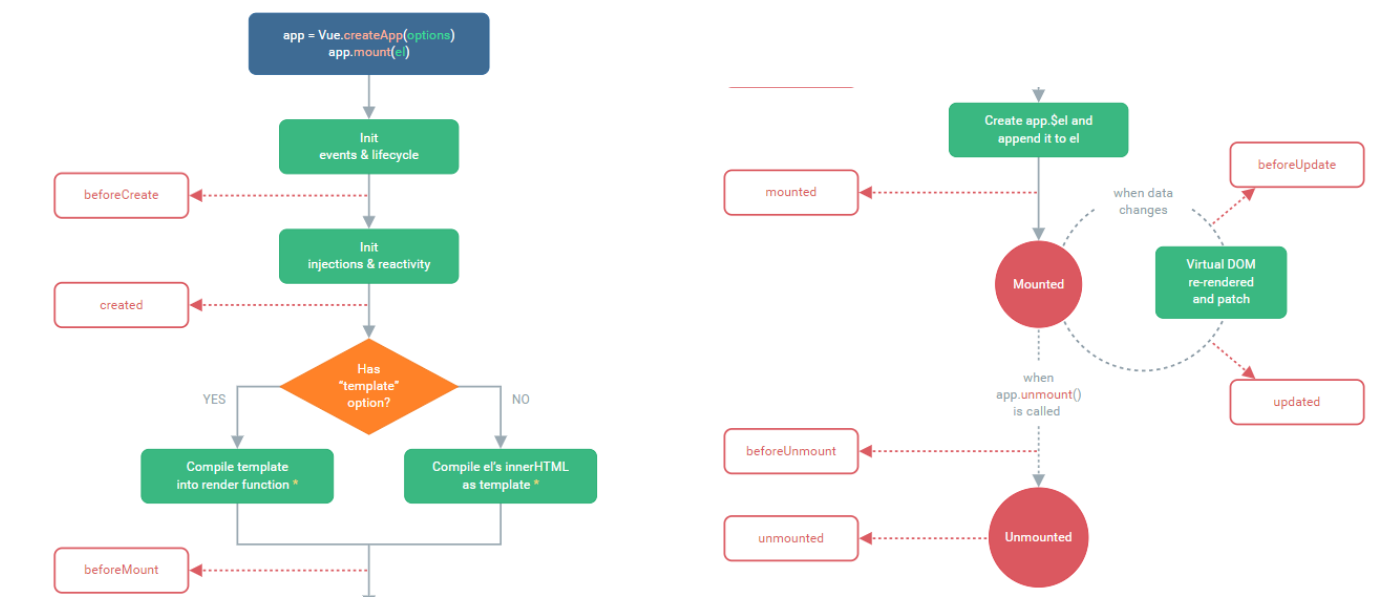
2. 图例
每个钩子函数的作用详见:https://v3.cn.vuejs.org/api/options-lifecycle-hooks.html#beforecreate
3. 实操
代码分享:

<template>
<div>
<h4 ref="title"> {{msg}}</h4>
<button @click="changeMessage">修改message</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
msg: 'Hello Home'
};
},
methods: {
changeMessage() {
this.msg = "你好啊, 李马儒"
}
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log("home beforeCreate");
},
created() {
console.log("home created");
},
beforeMount() {
console.log("home beforeMount");
},
mounted() {
console.log("home mounted");
},
beforeUnmount() {
console.log("home beforeUnmount");
},
unmounted() {
console.log("home unmounted");
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log(this.$refs.title.innerHTML);
console.log("home beforeUpdate");
},
updated() {
console.log(this.$refs.title.innerHTML);
console.log("home updated");
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
五. 组件的v-model
1. 回顾input中使用v-model实现属性绑定
这里的v-model实现了两件事,v-bind:value的数据绑定和@input的事件监听。
<div>{{message}}</div> <input v-model="message"> <input :value="message" @input="message=$event.target.value">
2. 组件v-model的使用
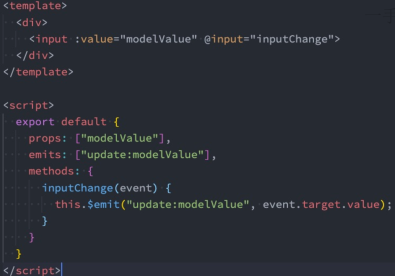
(1). 组件的写法
<template> <div> <input v-model="value"> </div> </template> <script> export default { props: ['modelValue'], emits: ['update:modelValue'], computed: { // 这里是固定值,名字就得叫value value: { set(value) { this.$emit('update:modelValue', value); }, get() { return this.modelValue; } } } } </script>
也可以用@input监听
(2). 调用
<!-- 2.1 按部就班调用--> <hy-input1 :modelValue="message" @update:modelValue="message = $event"></hy-input1> <!-- 2.2 直接使用v-model,等价于上面的代码 --> <hy-input1 v-model="message"></hy-input1>
3. 组件v-model绑定多个属性
(1). 子组件
<template> <div> <input v-model="value"> <input v-model="myTitle"> </div> </template> <script> export default { props: ['modelValue', 'title'], emits: ['update:modelValue', 'update:title'], computed: { value: { set(value) { this.$emit('update:modelValue', value); }, get() { return this.modelValue; } }, myTitle: { set(myTitle) { this.$emit('update:title', myTitle); }, get() { return this.title; } } } } </script>
(2). 调用
<hy-input2 v-model="message" v-model:title="title"></hy-input2>
!
- 作 者 : Yaopengfei(姚鹏飞)
- 博客地址 : http://www.cnblogs.com/yaopengfei/
- 声 明1 : 如有错误,欢迎讨论,请勿谩骂^_^。
- 声 明2 : 原创博客请在转载时保留原文链接或在文章开头加上本人博客地址,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
