OCCT模块结构图

- 基础类: Foundation Classes module underlies all other OCCT classes;
- 模型数据: Modeling Data module supplies data structures to represent 2D and 3D geometric primitives and their compositions into CAD models;
- 模型算法: Modeling Algorithms module contains a vast range of geometrical and topological algorithms;
- 面? Mesh module implements tessellated representations of objects;
- 可视化 Visualization module provides complex mechanisms for graphical data representation;
- 数据交换 Data Exchange module inter-operates with popular data formats and relies on Shape Healing to improve compatibility between CAD software of different vendors;
- 程序框架 Application Framework module offers ready-to-use solutions for handling application-specific data (user attributes) and commonly used functionality (save/restore, undo/redo, copy/paste, tracking CAD modifications, etc).
基础类 Foundation Classes
基础类模提供了上层OCCT类需要的数据结构和服务.
-
原始类型 Primitive types, such as Boolean, Character, Integer or Real;
- 字符串 String classes that handle ASCII and Unicode strings;
- 集合类 Collection classes that handle statically or dynamically sized aggregates of data, such as arrays, lists, queues, sets and hash tables (data maps).
- 常用数值算法和基本线性代数 Classes providing commonly used numerical algorithms and basic linear algebra calculations (addition, multiplication, transposition of vectors and matrices, solving linear systems etc).
- 基础数据类型表示物理数量,支持日期和时间信息 Fundamental types representing physical quantities and supporting date and time information;
- 基本几何类型 Primitive geometry types providing implementation of basic geometric and algebraic entities that define and manipulate elementary data structures.
- 异常 Exception classes that describe situations, when the normal execution of program is abandoned;
本模块也提供了一系列通用服务 This module also provides a variety of general-purpose services, such as:
- 动态对象安全处理 Safe handling of dynamically created objects, ensuring automatic deletion of unreferenced objects (smart pointers);
- 可配置内容优化管理器 Configurable optimized memory manager increasing the performance of applications that intensively use dynamically created objects;
- RTTI扩展 Extended run-time type information (RTTI) mechanism maintaining a full type hierarchy and providing means to iterate over it;
- C++流封装 Encapsulation of C++ streams;
- 自动堆内存管理 Automated management of heap memory by means of specific allocators;
- 基础脚本解释器 Basic interpreter of expressions facilitating the creation of customized scripting tools, generic definition of expressions, etc.;
- 处理配置资源的工具 Tools for dealing with configuration resource files and customizable message files facilitating multi-language support in applications;
- 进度显示 Progress indication and user break interfaces, giving a possibility even for low-level algorithms to communicate with the user in a universal and convenient way;
- 其它 and many others...
详细说明见: 基础类用户指南
模型数据 Modeling Data
模型数据 提供了Brep表示法数据结构. 在BRep表示法中, shape表示为带拓扑关系几何体的集合. 几何体理解为shape的数学描述. topology是联结几何对象的数据结构.
Modeling Data supplies data structures to implement boundary representation (BRep) of objects in 3D. In BRep the shape is represented as an aggregation of geometry within topology. The geometry is understood as a mathematical description of a shape, e.g. as curves and surfaces (simple or canonical, Bezier, NURBS, etc). The topology is a data structure binding geometrical objects together.
几何类型和工具提供了几何数据结构和服务:
Geometry types and utilities provide geometric data structures and services for:
- Description of points, vectors, curves and surfaces:
- their positioning in 3D space using axis or coordinate systems, and
- their geometric transformation, by applying translations, rotations, symmetries, scaling transformations and combinations thereof.
- Creation of parametric curves and surfaces by interpolation and approximation;
- Algorithms of direct construction;
- Conversion of curves and surfaces to NURBS form;
- Computation of point coordinates on 2D and 3D curves;
- 几何对象之间的极值计算 Calculation of extrema between geometric objects.
Topology defines relationships between simple geometric entities. A shape, which is a basic topological entity, can be divided into components (sub-shapes):
- Vertex – a zero-dimensional shape corresponding to a point;
- Edge – a shape corresponding to a curve and bounded by a vertex at each extremity;
- Wire – a sequence of edges connected by their vertices;
- Face – a part of a plane (in 2D) or a surface (in 3D) bounded by wires;
- Shell – a collection of faces connected by edges of their wire boundaries;
- Solid – a finite closed part of 3D space bounded by shells;
- Compound solid – a collection of solids connected by faces of their shell boundaries.
Complex shapes can be defined as assemblies of simpler entities.
Please, see the details in Modeling Data User's Guide
3D geometric models can be stored in OCCT native BREP format. See BREP Format Description White Paper for details on the format.
See also: our E-learning & Training offerings.
模型算法 Modeling Algorithms
模型算法模块 包括一系列用于几何建模的拓扑和几何算法. 基本上, 分为两组:
Modeling Algorithms module groups a wide range of topological and geometric algorithms used in geometric modeling. Basically, there are two groups of algorithms in Open CASCADE Technology:
- High-level modeling routines used in the real design;
- Low-level mathematical support functions used as a groundwork for the modeling API;
- Low-level geometric tools provide the algorithms, which:
- Calculate the intersection of two curves, surfaces, or a curve and a surface;
- Project points onto 2D and 3D curves, points onto surfaces and 3D curves onto surfaces;
- Construct lines and circles from constraints;
- Construct free-form curves and surfaces from constraints (interpolation, approximation, skinning, gap filling, etc);
- Low-level topological tools provide the algorithms, which:
- 细分 Tessellate shapes;
- Check correct definition of shapes;
- Determine the local and global properties of shapes (derivatives, mass-inertia properties, etc);
- Perform affine transformations;
- Find planes in which edges are located;
- Convert shapes to NURBS geometry;
- Sew connected topologies (shells and wires) from separate topological elements (faces and edges).
Top-level API provides the following functionality:
- Construction of Primitives:
- Boxes;
- 棱柱 Prisms;
- Cylinders;
- Cones;
- Spheres;
- Toruses.
- Kinematic Modeling:
- Prisms – linear sweeps;
- Revolutions – rotational sweeps;
- Pipes – general-form sweeps;
- Lofting.

- Boolean Operations, which allow creating new shapes from the combinations of source shapes. For two shapes S1 and S2:
- Common contains all points that are in S1 and S2;
- Fuse contains all points that are in S1 or S2;
- Cut contains all points in that are in S1 and not in S2
See Boolean Operations User's Guide for detailed documentation.
- Algorithms for local modifications such as:
- Hollowing;
- Shelling;
- Creation of tapered shapes using draft angles;
- Algorithms to make fillets and chamfers on shape edges, including those with variable radius (chord).
- Algorithms for creation of mechanical features, i.e. depressions, protrusions, ribs and grooves or slots along planar or revolution surfaces
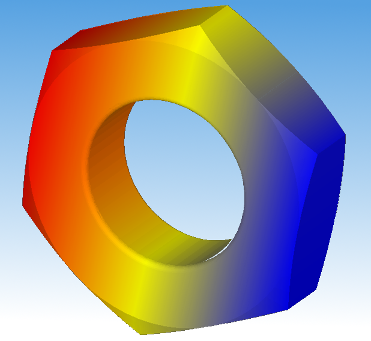
Please, see the details in Modeling Algorithms User's Guide.
See also: our E-learning & Training offerings.
Mesh
Mesh 模块提供了用三角面来表示对象的功能.
Mesh module provides the functionality to work with tessellated representations of objects in form of triangular facets. This module contains:
- data structures to store surface mesh data associated to shapes and basic algorithms to handle them;
- data structures and algorithms to a build triangular surface mesh from BRep objects (shapes);
- tools for displaying meshes with associated pre- and post-processor data (scalars or vectors).
Open CASCADE Technology includes two mesh converters:
- VRML converter translates Open CASCADE shapes to VRML 1.0 files (Virtual Reality Modeling Language). Two representation modes are possible: shaded, which presents shapes as sets of triangles computed by the mesh algorithm, or wireframe, which presents shapes as sets of curves.
- STL converter translates Open CASCADE shapes to STL files. STL (STtereoLithography) format is widely used for rapid prototyping (3D printing).
Open CASCADE SAS also offers Advanced Mesh Products:
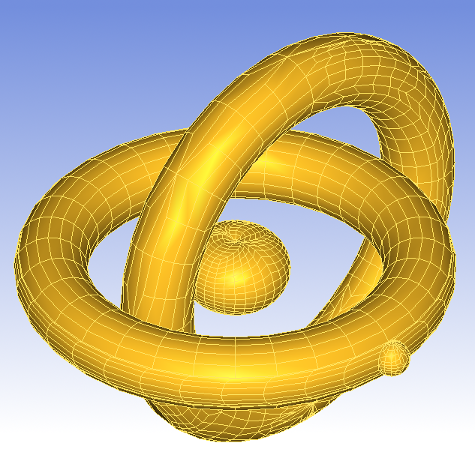
Visualization
Visualization module provides ready-to-use algorithms to create graphic presentations from various objects: shapes, meshes, etc.
In Open CASCADE Technology visualization is based on the separation of CAD data and its graphical presentation. The presentations can be customized to take the specificity of your application into account.
The module also supports a fast and powerful interactive selection mechanism.
The view facilities provided by OCCT range from low-level tools working with basic geometry and topology (such as NURBS visualization with control points and nodes, rendering of isolines to estimate speed and quality of parameterization, or rendering of a parametric profile of edges) to high-level tools for real time quality rendering of models using ray tracing: shades, reflections, transparency, anti-aliasing, etc.
Here are just a few examples:
- Camera-driven view projection and orientation. It is possible to choose between perspective, orthographic and stereographic projection.
- Real-time ray tracing technique using recursive Whitted's algorithm and Bounded Volume Hierarchy effective optimization structure.

- Support of GLSL shaders. The shader management is fully automatic, like with any other OpenGL resource.

Fragment shader implementing custom clipping surface
- Support of standard and custom materials, defined by transparency, diffuse, ambient and specular reflection and refraction index. The latter allows implementing transparent materials, such as glass, diamond and water.

- Optimization of rendering performance through the algorithms of:
- View frustum culling, which skips the presentation outside camera at the rendering stage and
- Back face culling, which reduces the rendered number of triangles and eliminates artifacts at shape boundaries.
- Definition of clipping planes through the plane equation coefficients. Ability to define visual attributes for cross-section at the level or individual clipping planes. In the image below different parts of the rocket are clipped with different planes and hatched.
- Possibility to flexibly adjust appearance of dimensions in a 3D view. The 3D text object represents a given text string as a true 3D object in the model space.
 Display of shape cross-section and dimensions
Display of shape cross-section and dimensions
For more details see Visualization User's Guide.
The visualization of OCCT topological shapes by means of VTK library provided by VIS component is described in a separate VTK Integration Services User's Guide.
See also: our E-learning & Training offerings.
Data Exchange
Data Exchange allows developing OCCT-based applications that can interact with other CAD systems by writing and reading CAD models to and from external data. The exchanges run smoothly regardless of the quality of external data or requirements to its internal representation, for example, to the data types, accepted geometric inaccuracies, etc.

Data Exchange is organized in a modular way as a set of interfaces that comply with various CAD formats: IGES, STEP, STL, VRML, etc. The interfaces allow software based on OCCT to exchange data with various CAD/PDM software packages, maintaining a good level of interoperability.
- Standardized Data Exchange interfaces allow querying and examining the input file, converting its contents to a CAD model and running validity checks on a fully translated shape. The following formats are currently supported.
- Extended data exchange (XDE) allows translating additional attributes attached to geometric data (colors, layers, names, materials etc).
- Advanced Data Exchange Components are available in addition to standard Data Exchange interfaces to support interoperability and data adaptation (also using Shape Healing) with CAD software using the following proprietary formats:
These components are based on the same architecture as interfaces with STEP and IGES.
Shape Healing
Shape Healing library provides algorithms to correct and adapt the geometry and topology of shapes imported to OCCT from other CAD systems.
Shape Healing algorithms include, but are not limited to, the following operations:
- analyze shape characteristics and, in particular, identify the shapes that do not comply with OCCT geometry and topology validity rules by analyzing geometrical objects and topology:
- check edge and wire consistency;
- check edge order in a wire;
- check the orientation of face boundaries;
- analyze shape tolerances;
- identify closed and open wires in a boundary.
- fix incorrect or incomplete shapes:
- provide consistency between a 3D curve and its corresponding parametric curve;
- repair defective wires;
- fit the shapes to a user-defined tolerance value;
- fill gaps between patches and edges.
- upgrade and change shape characteristics:
- reduce curve and surface degree;
- split shapes to obtain C1 continuity;
- convert any types of curves or surfaces to Bezier or B-Spline curves or surfaces and back;
- split closed surfaces and revolution surfaces.
Each sub-domain of Shape Healing has its own scope of functionality:
| Sub-domain | Description | Impact on the shape |
|---|---|---|
| Analysis | Explores shape properties, computes shape features, detects violation of OCCT requirements. | The shape itself is not modified. |
| Fixing | Fixes the shape to meet the OCCT requirements. | The shape may change its original form: modification, removal or creation of sub-shapes, etc.) |
| Upgrade | Improves the shape to fit some particular algorithms. | The shape is replaced with a new one, but geometrically they are the same. |
| Customization | Modifies the shape representation to fit specific needs. | The shape is not modified, only the mathematical form of its internal representation is changed. |
| Processing | Mechanism of shape modification via a user-editable resource file. |
For more details refer to Shape Healing User's guide.
See also: our E-learning & Training offerings.
Application Framework
Open CASCADE Application Framework (OCAF) handles Application Data basing on the Application/Document paradigm. It uses an associativity engine to simplify the development of a CAD application thanks to the following ready-to-use features and services:
- Data attributes managing the application data, which can be organized according to the development needs;
- Data storage and persistence (open/save);
- Possibility to modify and recompute attributes in documents. With OCAF it is easy to represent the history of modification and parametric dependencies within your model;
- Possibility to manage multiple documents;
- Predefined attributes common to CAD/CAM/CAE applications (e.g. to store dimensions);
- Undo-Redo and Copy-Paste functions.
Since OCAF handles the application structure, the only development task is the creation of application-specific data and GUIs.
OCAF differs from any other CAD framework in the organization of application data, as there the data structures are based on reference keys rather than on shapes. In a model, such attributes as shape data, color and material are attached to an invariant structure, which is deeper than the shapes. A shape object becomes the value of Shape attribute, in the same way as an integer number is the value of Integer attribute and a string is the value of Name attribute.
OCAF organizes and embeds these attributes in a document. OCAF documents, in their turn, are managed by an OCAF application.
For more details see OCAF User's Guide.
See also: our E-learning & Training offerings.
Draw Test Harness
Test Harness or Draw is a convenient testing tool for OCCT libraries. It can be used to test and prototype various algorithms before building an entire application. It includes:
- A command interpreter based on the TCL language;
- A number of 2D and 3D viewers;
- A set of predefined commands.
The viewers support operations such as zoom, pan, rotation and full-screen views.
The basic commands provide general-purpose services such as:
- Getting help;
- Evaluating a script from a file;
- Capturing commands in a file;
- Managing views;
- Displaying objects.
In addition, Test Harness provides commands to create and manipulate curves and surfaces (geometry) and shapes, access visualization services, work with OCAF documents, perform data exchange, etc.
You can add custom commands to test or demonstrate any new functionalities, which you develop.
For more details see Draw Test Harness Manual.