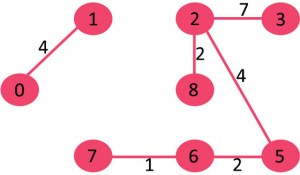
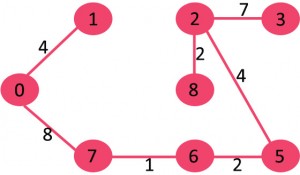
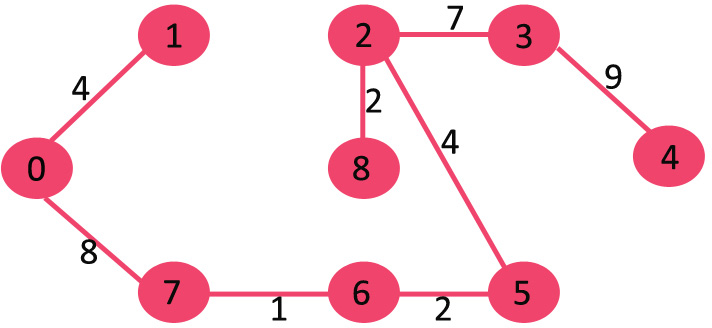
概述
给出一个连通的无向图,图的生成树是一个图的子图,并且是一棵连接了所有顶点的树。
一个图可以有很多个生成树,连通的有向图和无向图最小生成树或最小权重生成树是一棵权重小于其他所有的生成树的权重的生成树。
生成树的权重是生成树中所有边的权重的和。
算法
1. 对所有的边按照非降序排序
2.从中选择最小的边,并且检查它是否会和当前的树构成一个环。若不构成环,则将这条边加入最小生成树,若构成环,则抛弃它。
3.重复步骤2直至有V-1条边在生成树中。
注意
1.可以用Union Find(并查集)来检查是否存在环,(我认为也可以设定一个visited数组来记录该顶点是否加入mst)
2. 当一个图是连通的,如果我们需要连通所有的节点,我们至少需要V-1条边。
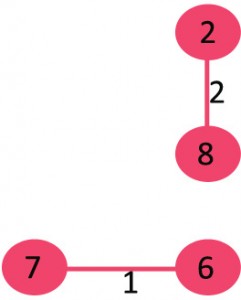
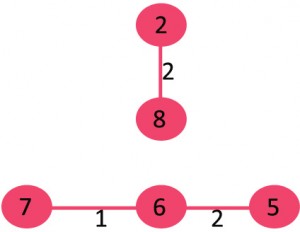
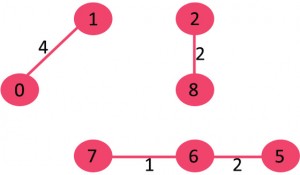
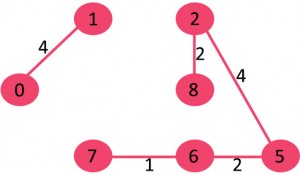
例子
图中含有9个节点,所以我们需要9-1 = 8条边来构成最小生成树
对边进行排序后:
After sorting: Weight Src Dest 1 7 6 2 8 2 2 6 5 4 0 1 4 2 5 6 8 6 7 2 3 7 7 8 8 0 7 8 1 2 9 3 4 10 5 4 11 1 7 14 3 5
6. 取出8-6:此时会形成环,不要该条边
8. P取出7-8:会生成环,不要该条边
10. 取出1-2:会生成环,不要这条变
因为此时已经有8条变了,所以算法停止。
实现
// C++ program for Kruskal's algorithm to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a given connected, undirected and weighted graph #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> // a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph struct Edge { int src, dest, weight; }; // a structure to represent a connected, undirected // and weighted graph struct Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges. // Since the graph is undirected, the edge // from src to dest is also edge from dest // to src. Both are counted as 1 edge here. struct Edge* edge; }; // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E) { struct Graph* graph = new Graph; graph->V = V; graph->E = E; graph->edge = new Edge[E]; return graph; } // A structure to represent a subset for union-find struct subset { int parent; int rank; }; // A utility function to find set of an element i // (uses path compression technique) int find(struct subset subsets[], int i) { // find root and make root as parent of i // (path compression) if (subsets[i].parent != i) subsets[i].parent = find(subsets, subsets[i].parent); return subsets[i].parent; } // A function that does union of two sets of x and y // (uses union by rank) void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y) { int xroot = find(subsets, x); int yroot = find(subsets, y); // Attach smaller rank tree under root of high // rank tree (Union by Rank) if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank) subsets[xroot].parent = yroot; else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank) subsets[yroot].parent = xroot; // If ranks are same, then make one as root and // increment its rank by one else { subsets[yroot].parent = xroot; subsets[xroot].rank++; } } // Compare two edges according to their weights. // Used in qsort() for sorting an array of edges int myComp(const void* a, const void* b) { struct Edge* a1 = (struct Edge*)a; struct Edge* b1 = (struct Edge*)b; return a1->weight > b1->weight; } // The main function to construct MST using Kruskal's algorithm void KruskalMST(struct Graph* graph) { int V = graph->V; struct Edge result[V]; // Tnis will store the resultant MST int e = 0; // An index variable, used for result[] int i = 0; // An index variable, used for sorted edges // Step 1: Sort all the edges in non-decreasing // order of their weight. If we are not allowed to // change the given graph, we can create a copy of // array of edges qsort(graph->edge, graph->E, sizeof(graph->edge[0]), myComp); // Allocate memory for creating V ssubsets struct subset *subsets = (struct subset*) malloc( V * sizeof(struct subset) ); // Create V subsets with single elements for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) { subsets[v].parent = v; subsets[v].rank = 0; } // Number of edges to be taken is equal to V-1 while (e < V - 1) { // Step 2: Pick the smallest edge. And increment // the index for next iteration struct Edge next_edge = graph->edge[i++]; int x = find(subsets, next_edge.src); int y = find(subsets, next_edge.dest); // If including this edge does't cause cycle, // include it in result and increment the index // of result for next edge if (x != y) { result[e++] = next_edge; Union(subsets, x, y); } // Else discard the next_edge } // print the contents of result[] to display the // built MST printf("Following are the edges in the constructed MST "); for (i = 0; i < e; ++i) printf("%d -- %d == %d ", result[i].src, result[i].dest, result[i].weight); return; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { /* Let us create following weighted graph 10 0--------1 | | 6| 5 |15 | | 2--------3 4 */ int V = 4; // Number of vertices in graph int E = 5; // Number of edges in graph struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 graph->edge[0].src = 0; graph->edge[0].dest = 1; graph->edge[0].weight = 10; // add edge 0-2 graph->edge[1].src = 0; graph->edge[1].dest = 2; graph->edge[1].weight = 6; // add edge 0-3 graph->edge[2].src = 0; graph->edge[2].dest = 3; graph->edge[2].weight = 5; // add edge 1-3 graph->edge[3].src = 1; graph->edge[3].dest = 3; graph->edge[3].weight = 15; // add edge 2-3 graph->edge[4].src = 2; graph->edge[4].dest = 3; graph->edge[4].weight = 4; KruskalMST(graph); return 0; }