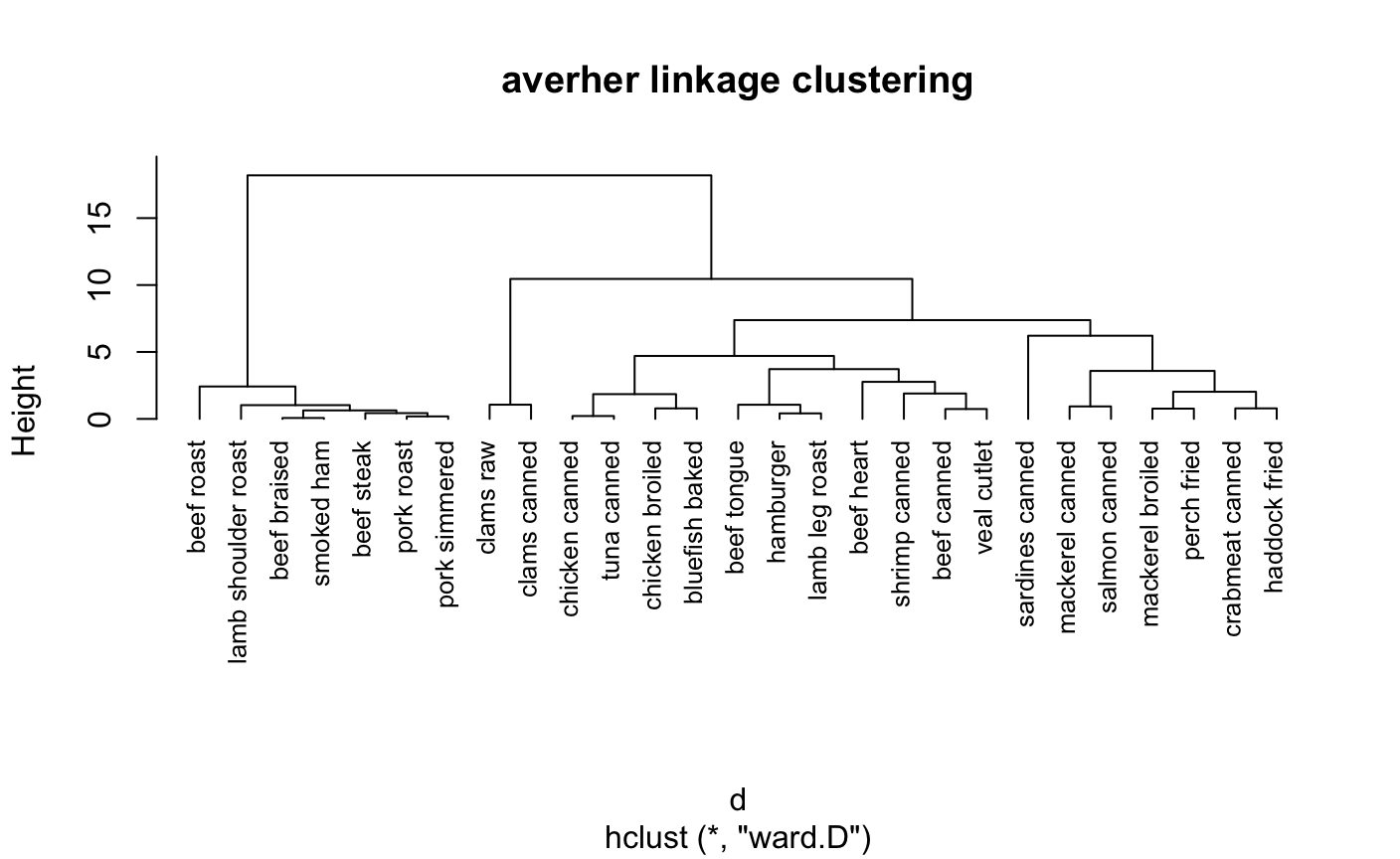
层次聚类
1、定义每一个观测量为一类
2、计算每一类与其他各类的距离
3、把距离最短的两类合为一类
4、重复步骤2和3,直到包含所有的观测量合并成单类时
> ##########################聚类算法 > ####层次聚类 > par(mfrow = c(1,1)) > data(nutrient,package = "flexclust") > row.names(nutrient)<-tolower(row.names(nutrient)) > #数据中心标准化scale() > nutrient_s<-scale(nutrient,center = T) > View(nutrient_s) > #用dist()函数求出距离euclidean-欧几里得距离常用 > d<-dist(nutrient_s,method = "euclidean") > #求出距离带入hclust函数中用ward方法聚类 > cnutrient<-hclust(d,method = "ward.D") > plot(cnutrient,hang = -1,cex=.8,main='averher linkage clustering')
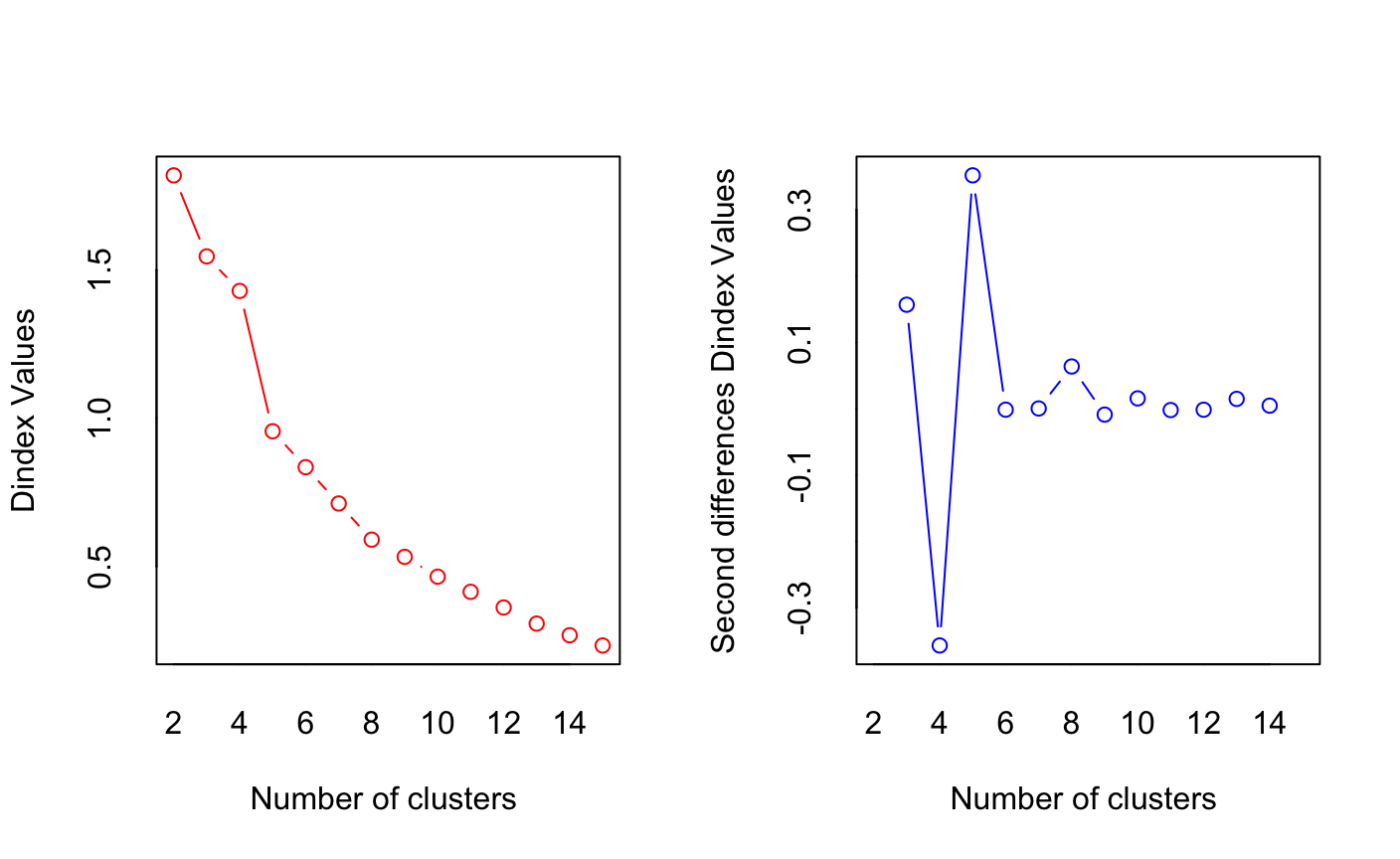
探究模型确定聚成几类合适
> ####用NbClust函数确定聚类K值 > library(NbClust) > NC<-NbClust(nutrient_s,distance = "euclidean",min.nc = 2,max.nc = 15,method = "average")
> table(NC$Best.n[1,])
0 1 2 3 4 5 9 10 13 14 15
2 1 4 4 2 4 1 1 2 1 4
> barplot(table(NC$Best.n[1,]))
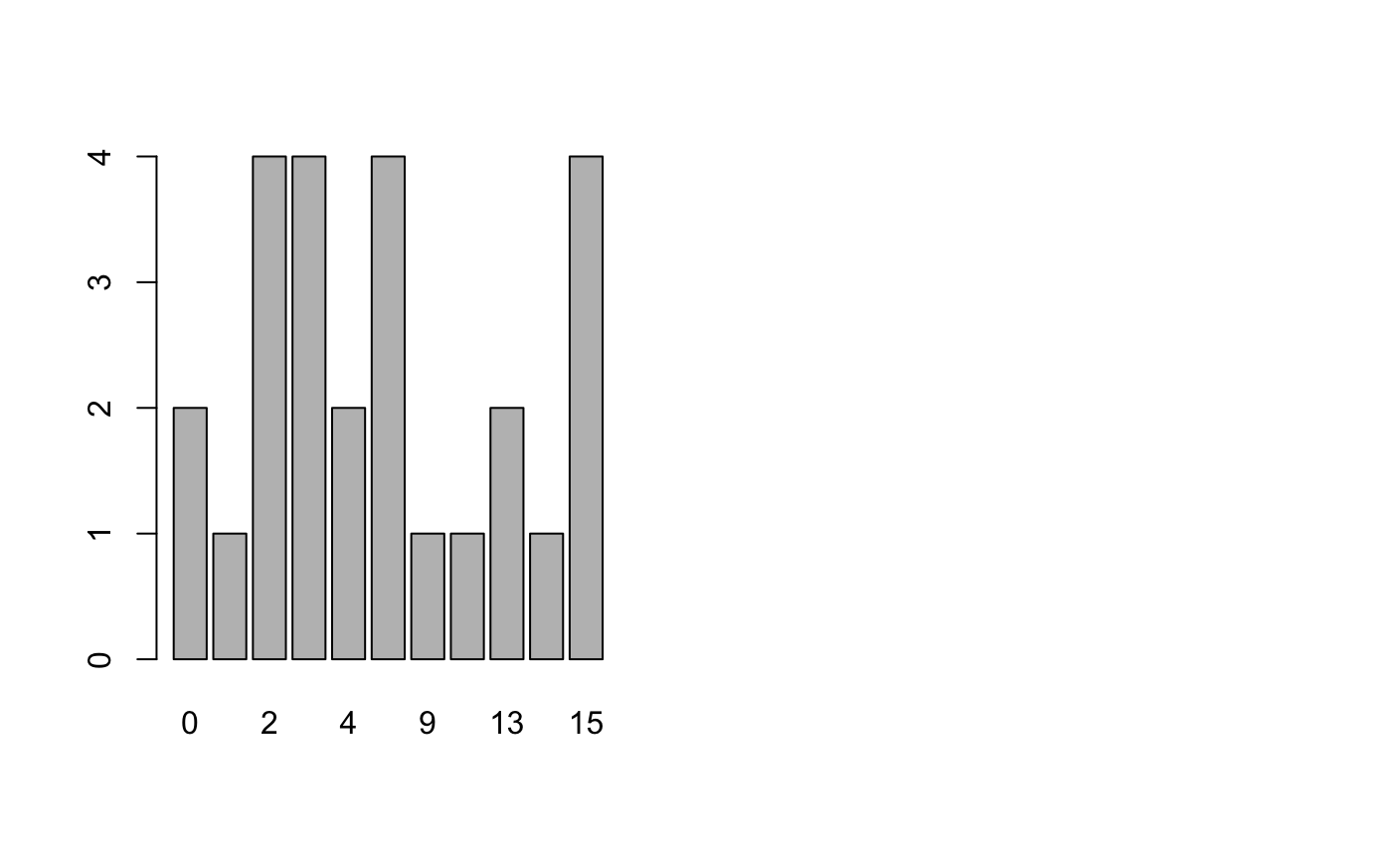
根据列表和柱状图我们可知聚为2、3、5、15类为不错的选项
下面我们看看聚为5类的结果
#####确定聚类个数后cut树 clusters<-cutree(cnutrient,k=5) table(clusters) plot(cnutrient,hang = -1,cex=.8,main='averher linkage clustering') rect.hclust(cnutrient,k=5)
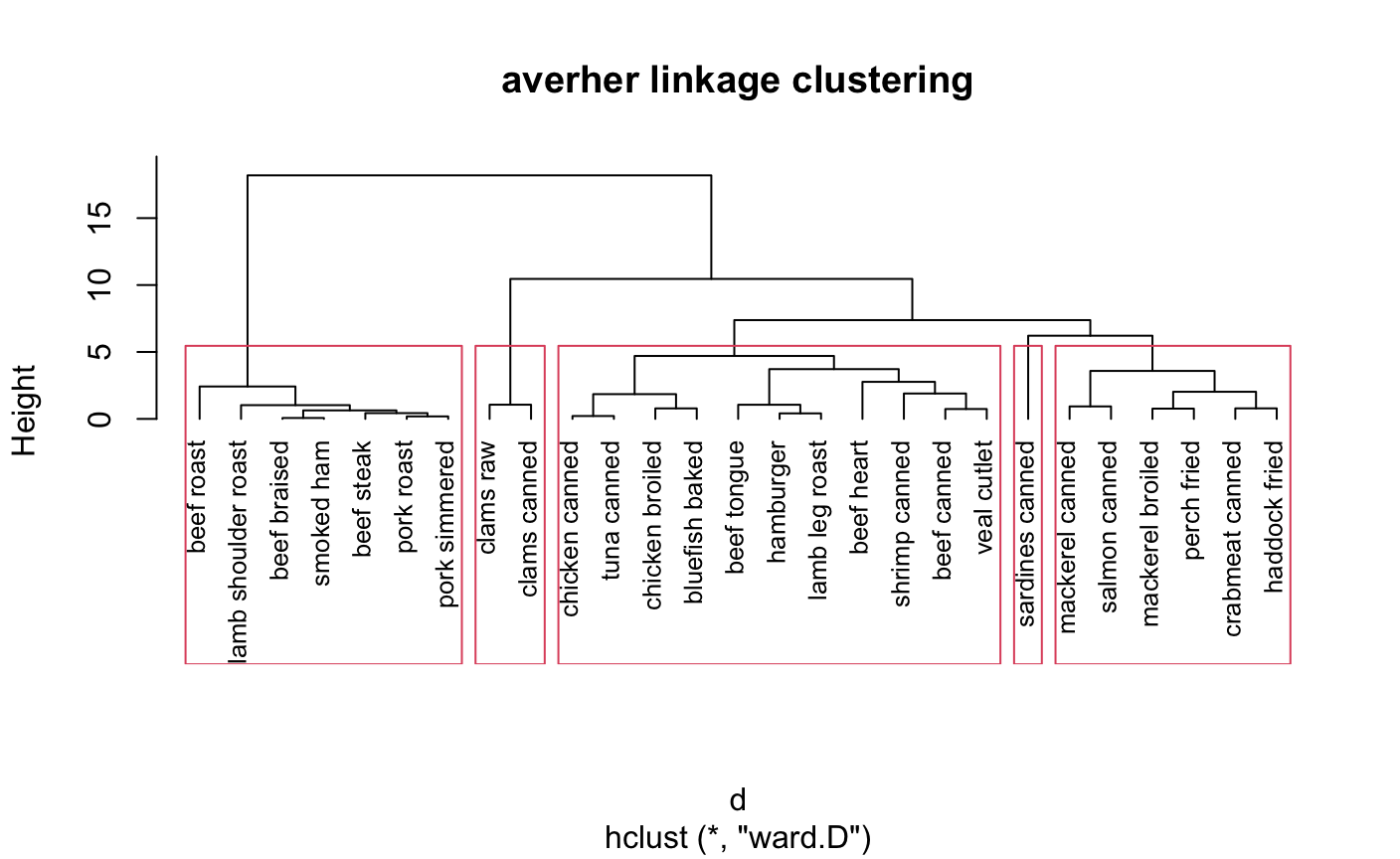
因为层次聚类计算距离非常复杂,所以能计算较小是数据集
K-Means聚类
1、选k个聚类中心点(随机生成)
2、把每个样本划分到距离最近的中心点
3、更新每类的中心点(可以把类的质心作为中心点)
4、重复2、3步骤,直至数据收敛
> #############k-means聚类 > data(wine,package = "rattle") > head(wine,3) Type Alcohol Malic Ash Alcalinity Magnesium Phenols Flavanoids Nonflavanoids 1 1 14.23 1.71 2.43 15.6 127 2.80 3.06 0.28 2 1 13.20 1.78 2.14 11.2 100 2.65 2.76 0.26 3 1 13.16 2.36 2.67 18.6 101 2.80 3.24 0.30 Proanthocyanins Color Hue Dilution Proline 1 2.29 5.64 1.04 3.92 1065 2 1.28 4.38 1.05 3.40 1050 3 2.81 5.68 1.03 3.17 1185 > df<-scale(wine[,-1],center = T) > #确定聚类个数 > library(NbClust) > nck<-NbClust(df,distance = "euclidean",min.nc = 2,max.nc = 15,method = "kmeans")

> table(nck$Best.n[1,])
0 1 2 3 14 15
2 1 2 19 1 1
> barplot(table(nck$Best.n[1,]))

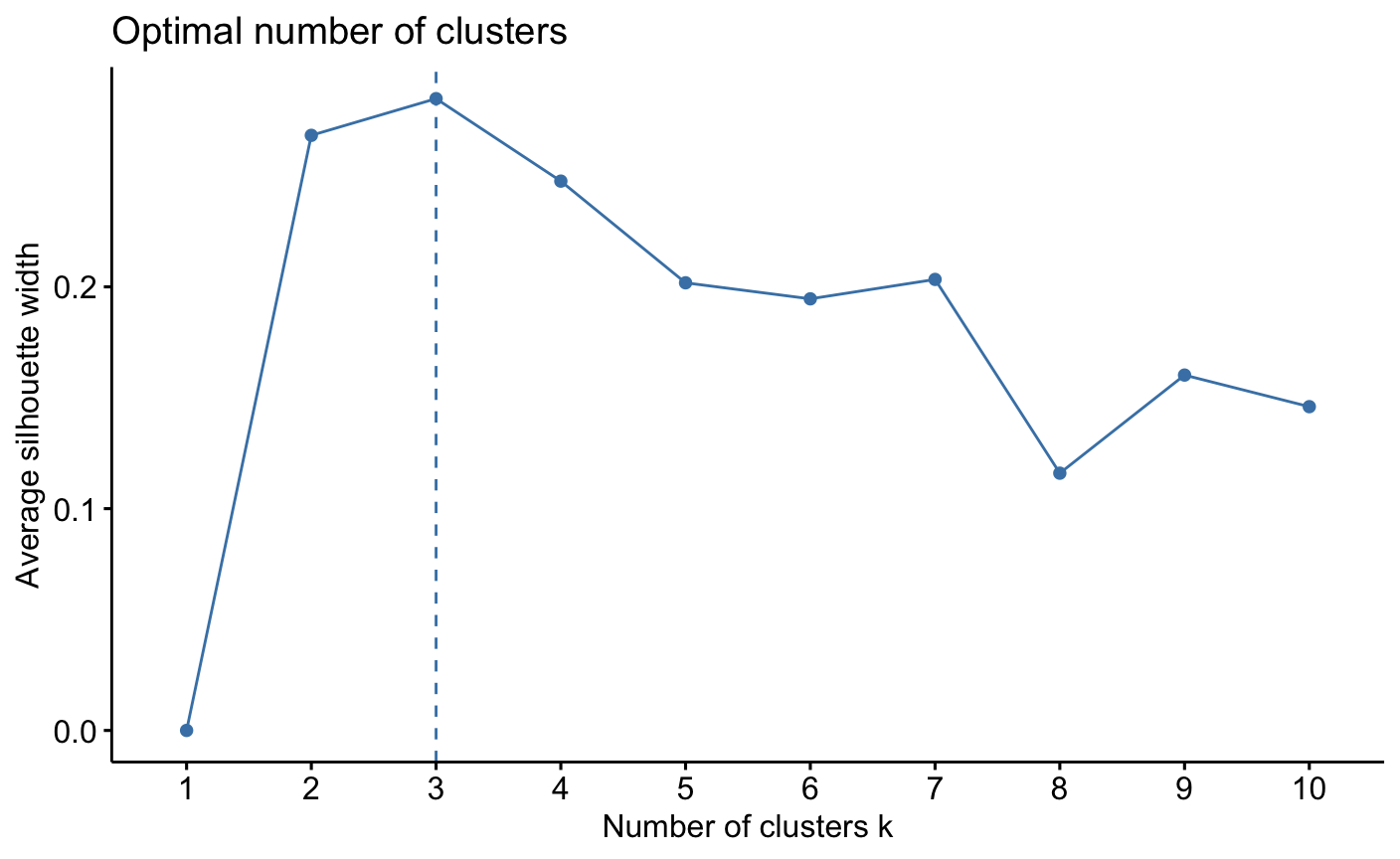
从数据和图像可知聚为3类最好。
下面进行聚类:
> #kmeans输出详解 > #cluster:样本归属群号的向量 > #centers:聚类中心的矩阵,每一条记录,代表相应聚类的中心点 > #totss:所有数据的平方和 > #withinss:群内样本点进行scale(x,scale=F)后的平方和 > #tot.withinss:对所有群withinss的汇总 > #betweenss:totss与tot.withinss的差 > #size:每个群中的样本个数 > #iter:迭代的次数 > #ifault:指示可能的算法问题(专家使用),比如当一些点非常靠近的时候,算法也许不会收敛,就会返回ifault=4 > set.seed(1234) > dfk<-kmeans(df,3,nstart = 25) > #每类的大小 > dfk$size [1] 62 65 51 > dfk$cluster [1] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 [44] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 [87] 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 [130] 2 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 [173] 3 3 3 3 3 3 > dfk$centers Alcohol Malic Ash Alcalinity Magnesium Phenols Flavanoids 1 0.8328826 -0.3029551 0.3636801 -0.6084749 0.57596208 0.88274724 0.97506900 2 -0.9234669 -0.3929331 -0.4931257 0.1701220 -0.49032869 -0.07576891 0.02075402 3 0.1644436 0.8690954 0.1863726 0.5228924 -0.07526047 -0.97657548 -1.21182921 Nonflavanoids Proanthocyanins Color Hue Dilution Proline 1 -0.56050853 0.57865427 0.1705823 0.4726504 0.7770551 1.1220202 2 -0.03343924 0.05810161 -0.8993770 0.4605046 0.2700025 -0.7517257 3 0.72402116 -0.77751312 0.9388902 -1.1615122 -1.2887761 -0.4059428 > table(dfk$cluster,wine$Type)#table(x,y) 1 2 3 1 59 3 0 2 0 65 0 3 0 3 48
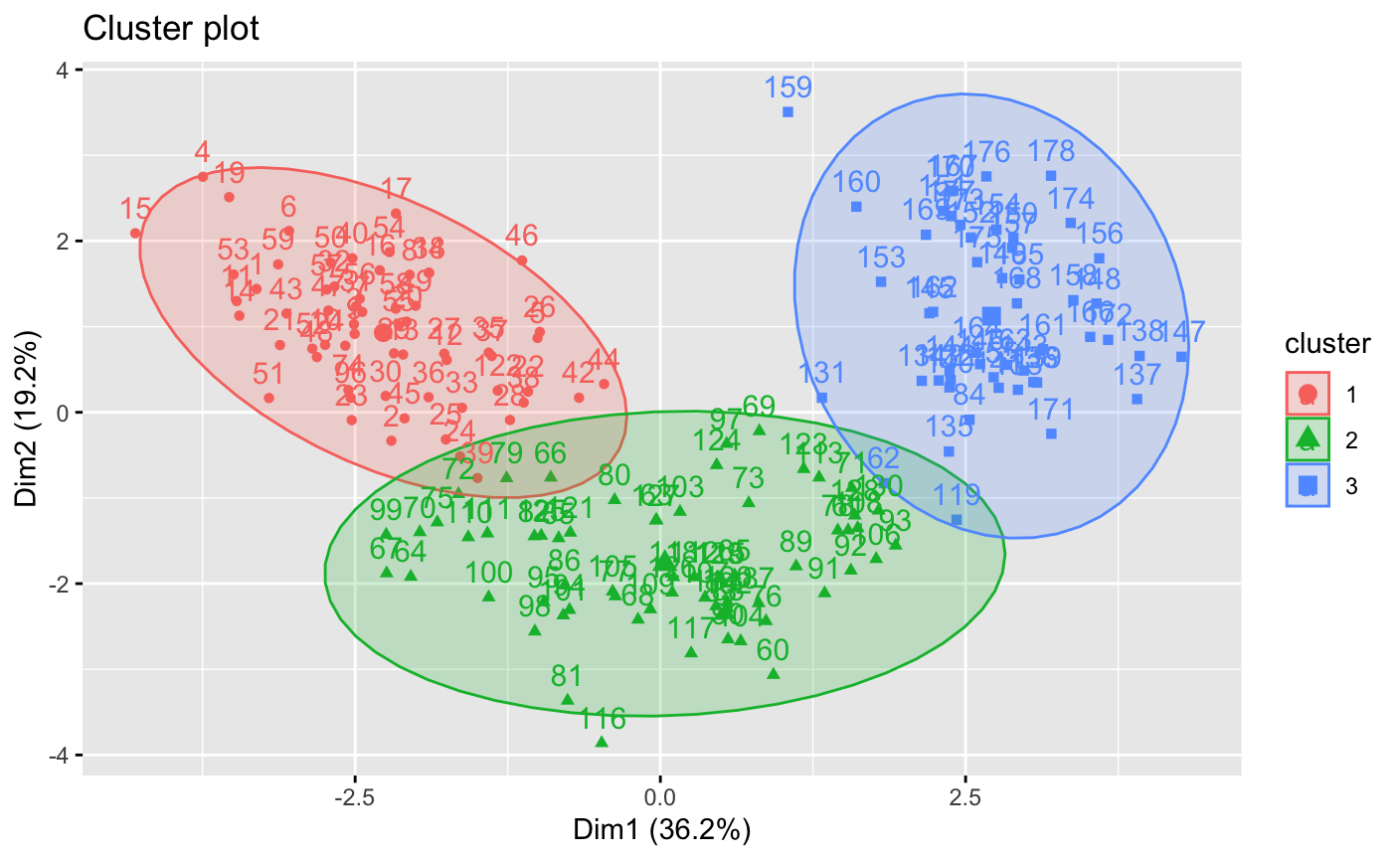
聚类结果可视化
> ##进行绘图 > library(ggplot2) > #factoextra包中fviz_nbclust可以确定最佳簇数,fviz_cluster画出聚类图 > library(factoextra) > fviz_nbclust(df,kmeans,method = "silhouette")
fviz_cluster(dfk, df, ellipse.type = "norm")
kmeans算法优点:有效率,而且不容易受初始值选择的影响
缺点:不能处理非球形簇,对离群值敏感。
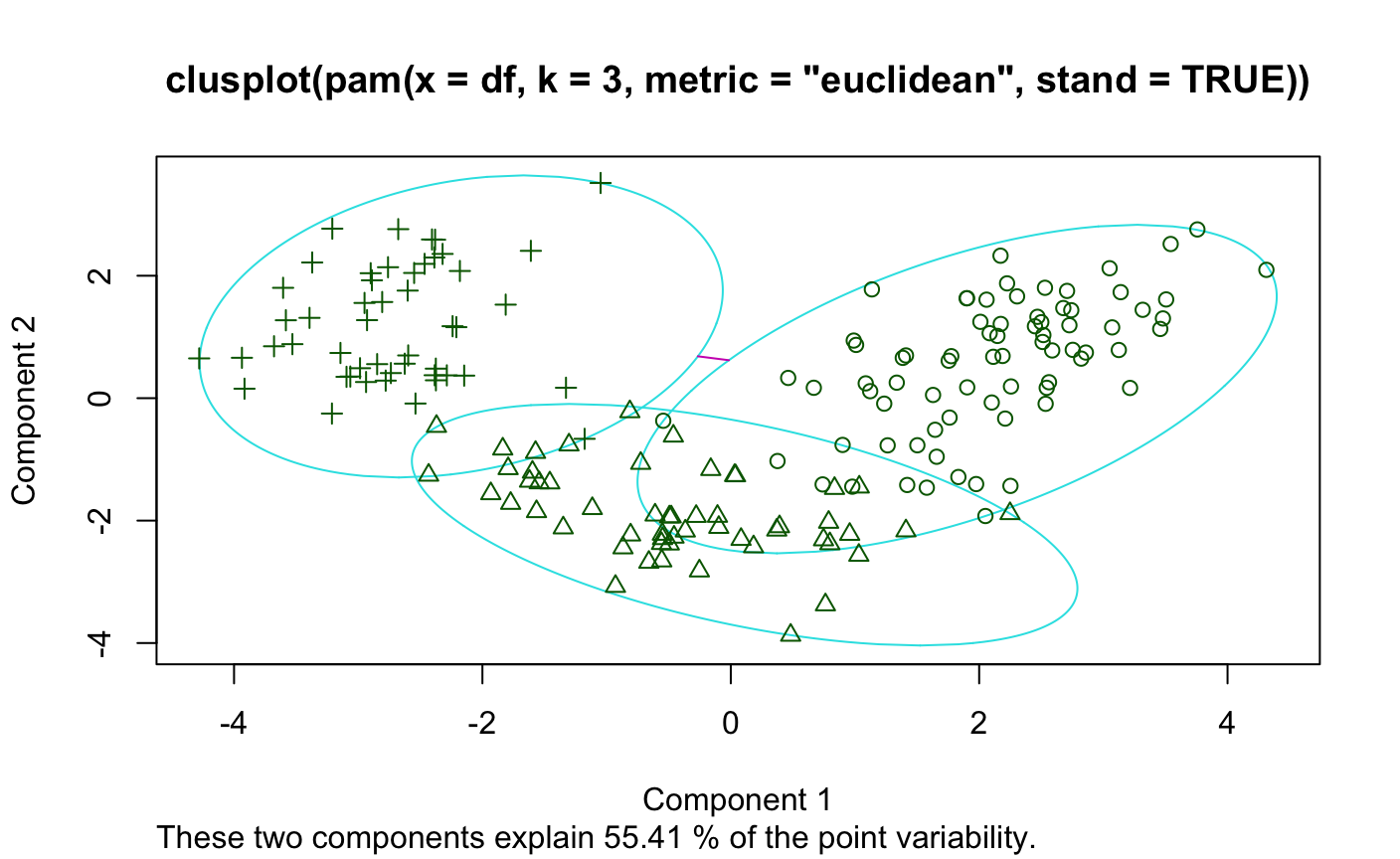
PAM
> ####k中心点PAM聚类 > library(cluster) > set.seed(12) > kp<-pam(df,k=3,metric="euclidean",stand = TRUE) > table(kp$clustering,wine$Type) 1 2 3 1 59 16 0 2 0 53 1 3 0 2 47 > kp$medoids Alcohol Malic Ash Alcalinity Magnesium Phenols Flavanoids [1,] 0.5904981 -0.4711544 0.1584986 0.3009543 0.01809398 0.6469393 0.9518166597 [2,] -0.9246039 -0.5427655 -0.8985684 -0.1482061 -1.38222271 -1.0307762 0.0007311716 [3,] 0.4919549 1.4086355 0.4136527 1.0495551 0.15812565 -0.7911025 -1.2807313808 Nonflavanoids Proanthocyanins Color Hue Dilution Proline [1,] -0.81841060 0.47016154 0.01807806 0.3611585 1.2089101 0.549706678 [2,] 0.06545479 0.06831575 -0.71522236 0.1861586 0.7863692 -0.752263054 [3,] 0.54756319 -0.31605849 0.96705508 -1.1263406 -1.4812670 0.009865569 > par(mfrow=c(1,1)) > clusplot(kp)