Description
Peter has a sequence 










 and he define a function on the sequence --
and he define a function on the sequence -- 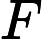
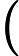












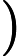

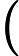
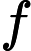


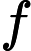






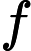

 , where
, where 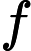
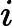 is the length of the longest increasing subsequence ending with
is the length of the longest increasing subsequence ending with 
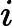 .
.
Peter would like to find another sequence










 in such a manner that
in such a manner that 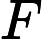
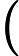












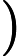 equals to
equals to 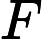
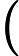












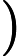 . Among all the possible sequences consisting of only positive integers, Peter wants the lexicographically smallest one.
. Among all the possible sequences consisting of only positive integers, Peter wants the lexicographically smallest one.
The sequence










 is lexicographically smaller than sequence
is lexicographically smaller than sequence 










 , if there is such number
, if there is such number 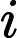 from
from  to
to 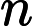 , that
, that 
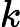


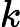 for
for 

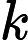
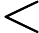
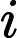 and
and 
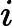


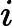 .
.











 and he define a function on the sequence --
and he define a function on the sequence -- 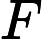
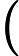












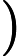

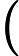
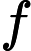


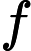






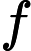

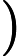 , where
, where 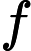
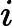 is the length of the longest increasing subsequence ending with
is the length of the longest increasing subsequence ending with 
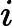 .
. Peter would like to find another sequence











 in such a manner that
in such a manner that 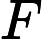
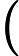












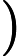 equals to
equals to 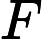












 . Among all the possible sequences consisting of only positive integers, Peter wants the lexicographically smallest one.
. Among all the possible sequences consisting of only positive integers, Peter wants the lexicographically smallest one. The sequence











 is lexicographically smaller than sequence
is lexicographically smaller than sequence 










 , if there is such number
, if there is such number 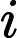 from
from  to
to 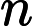 , that
, that 
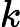


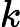 for
for 

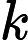

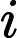 and
and 
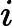


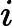 .
.Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input contains an integer  , indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
, indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first contains an integer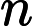


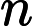







 -- the length of the sequence. The second line contains
-- the length of the sequence. The second line contains 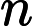 integers
integers 











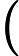



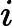



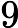
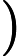 .
.
 , indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
, indicating the number of test cases. For each test case: The first contains an integer
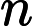


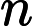







 -- the length of the sequence. The second line contains
-- the length of the sequence. The second line contains 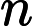 integers
integers 











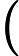



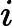



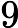
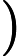 .
.Output
For each test case, output 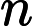 integers
integers 











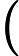



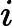



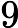
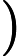 denoting the lexicographically smallest sequence.
denoting the lexicographically smallest sequence.
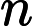 integers
integers 











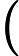






 denoting the lexicographically smallest sequence.
denoting the lexicographically smallest sequence. Sample Input
3 1 10 5 5 4 3 2 1 3 1 3 5
Sample Output
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3
英语题目很难度,但是题意很简单,给你一个整数序列,输出以每个数结尾的最长上升子序列的长度。
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #define INF 0x3f3f3f3f 4 using namespace std; 5 int dp[100005]; 6 int a[100005]; 7 int b[100005]; 8 int main() 9 { 10 int t; 11 scanf("%d",&t); 12 while(t--) 13 { 14 int n,i,j; 15 scanf("%d",&n); 16 for(i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) 17 { 18 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 19 dp[i]=0; 20 b[i]=INF; 21 } 22 for(i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++) 23 { 24 int k=lower_bound(b+1,b+n+1,a[i])-b; //函数返回值为大于a[i]的第一个值的位置,比如序列1 1 4 5,a[i]为2,返回值为3 25 dp[i]=k; //与二分法类似,将数放入新数组 26 b[k]=a[i]; 27 } 28 for(i = 1 ; i < n ; i++) 29 printf("%d ",dp[i]); 30 printf("%d ",dp[n]); 31 } 32 }