1.DelayQueue介绍
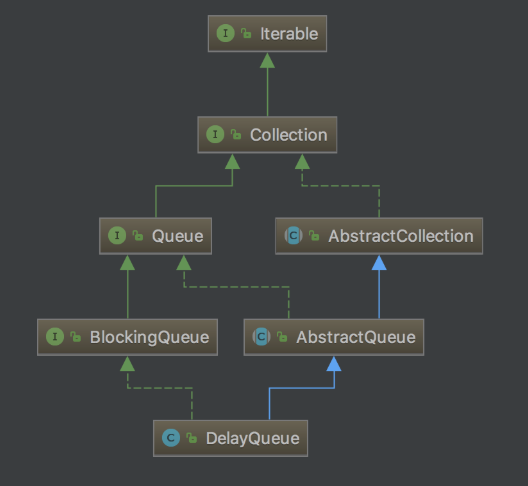
DelayQueue用于存放拥有过期时间的元素阻塞队列,只有当元素过期,才能从队列中取出。什么时候元素过期?当元素的getDelay()方法返回值小于等于0。
DelayQueue内部用PriorityQueue实现,可认为DelayQueue=BlockingQueue+PriorityQueue+Delayed
1.1Delayed接口
public interface Comparable<T> { public int compareTo(T o); } //实现该接口的对象带有时间延迟属性,只有当对象的时间延迟过期,才能对对象进行操作 public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed> { //返回当前对象的剩余时间延迟。0或者负数表示对象已过期。 long getDelay(TimeUnit unit); }
因此,DelayQueue中存放的对象需要实现compareTo()方法和getDelay()方法。
2.DelayQueue源码分析
2.1领导者/追随者(Leader/Follower)模式
2.1.1半同步/半异步(Half-Sync/Half-Async)模式
在我们编写网络服务程序时,比较简单的方式是per client per thread模型,这种模型当客户端连接数快速增长是就会出现性能瓶颈,我们不能不断的开启新的线程,当然我们肯定是会使用线程池,但是线程的管理和频繁的线程调度也会影响性能。
java 1.4给我们带来了NIO编程模型,由于它的读写操作都是无阻塞的,这样使我们能够只用一个线程处理所有的IO事件,当然我们不会真的只用一个线程来处理,比较常见的编写NIO网络服务程序的模型是半同步-半异步模式,其实现原理大体上是单线程同步处理网络IO请求,当有请求到达时,将该请求放入一个工作队列中,由另外的线程处理,主线程继续等待新的网络IO请求。
这种编程模型的缺点主要是:
1).使用工作队列带来的内存的动态分配问题。
2).每次网络IO请求,总是分配给另外一个线程处理,这样频繁的线程的context switching也会影响性能
2.1.2领导者/追随者(Leader/Follower)模式
针对以上缺点,解决的方案是使用Leader-Follower线程模型,它的基本思想是所有的线程被分配成两种角色:
Leader和Follower,一般同时只有一个Leader线程,所有的Follower线程排队等待成为Leader线程,线程池启动时自动产生一个Leader负责等待网络IO事件,当有一个事件产生时,Leader线程首先通知一个Follower线程,并将其提拔为新的Leader,然后自己去处理这个网络事件,处理完毕后加入Follower线程等待队列,等待重新成为Leader.
关键点:
(1)只有1个leader线程,可以有若干的follower线程;
(2)线程有3种状态:leading/processing/following;
(3)有一把锁,抢到的就是leading;
(4)事件来到时,leading线程会对其进行处理,从而转化为processing状态;
(5)处理完成后,尝试抢锁,抢到则又变为leading,否则变为followering;
(6)followering不干事,就是抢锁,力图成为leading;
这种线程模型的优点:
1)这个线程模型主要解决了内存的动态分配问题,我们不需要不断的将到来的网络IO事件放入队列,
2)并且等待网络IO事件的线程在等到网络事件的发生后,是自己处理的这个事件,也就是说没有context switching的过程.
打个比方:
-
话说一个地方有一群有组织无纪律的人从事山贼这个很有前途的职业。
-
一般就是有一个山贼在山路口察看,其他人在林子里面睡觉。
-
假如发现有落单的过往客商,望风的山贼就会弄醒一个睡觉的山贼,然后自己去打劫。
-
醒来的山贼接替作望风的事情。
-
打劫的山贼搞定以后,就会去睡觉,直到被其他望风的山贼叫醒来望风为止。
-
有时候过往客商太多,而山贼数量不够,有些客商就能侥幸平安通过山岭(所有山贼都去打劫其他客商了)。
计算机版本:
-
有若干个线程(一般组成线程池)用来处理大量的事件
-
有一个线程作为领导者,等待事件的发生;其他的线程作为追随者,仅仅是睡眠。
-
假如有事件需要处理,领导者会从追随者中指定一个新的领导者,自己去处理事件。
-
唤醒的追随者作为新的领导者等待事件的发生。
-
处理事件的线程处理完毕以后,就会成为追随者的一员,直到被唤醒成为领导者。
-
假如需要处理的事件太多,而线程数量不够(能够动态创建线程处理另当别论),则有的事件可能会得不到处理。
简单理解,就是最多只有一个线程在处理,其他线程在睡眠。
2.2创建
public DelayQueue() {} //内部使用优先级队列PriorityQueue来实现对元素的排序,PriorityQueue默认为小根堆 private final PriorityQueue<E> q = new PriorityQueue<E>(); //锁 private final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //与锁关联的available条件。 a.当队头元素延迟时间过期,变得可用,b.或者新的线程需要成为leader,通过调用available.signal()方法唤醒阻塞的线程。 private final Condition available = lock.newCondition(); //使用Leader-Follower模式来等待队头的元素变为available(即时间延迟过期),最小化等待时间。 //1.当一个线程成为leader,它只等待下一个时间延迟过期的元素,其他线程则无限等待。 //2.lead线程必须在从take()、poll()方法返回之前,唤醒某个线程,除非在此期间某个线程成为leader。 //3.无论何时队头元素被更早过期的元素替代,leader属性将通过重置为null使其失效,并且某个等待的线程(不一定是当前leader)被唤醒。 //4.所以,线程们在等待的时候必须等待着获得或失去领导权。 /** Thread designated to wait for the element at the head of * the queue. This variant of the Leader-Follower pattern * (http://www.cs.wustl.edu/~schmidt/POSA/POSA2/) serves to * minimize unnecessary timed waiting. When a thread becomes * the leader, it waits only for the next delay to elapse, but * other threads await indefinitely. The leader thread must * signal some other thread before returning from take() or * poll(...), unless some other thread becomes leader in the * interim. Whenever the head of the queue is replaced with * an element with an earlier expiration time, the leader * field is invalidated by being reset to null, and some * waiting thread, but not necessarily the current leader, is * signalled. So waiting threads must be prepared to acquire * and lose leadership while waiting. */ private Thread leader = null;
2.3 put方法
//插入元素到队列中 //由于队列是无界的,此方法永远不会阻塞 public void put(E e) { offer(e); } public boolean offer(E e) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //获得锁 lock.lock(); try { //元素入队 q.offer(e); //如果入队后,队头元素(即小根堆的堆顶元素)为当前元素 if (q.peek() == e) {//不是很理解,为什么是这个判断条件 //将leader置为null,并唤醒某个阻塞的线程,让其成为leader leader = null; //唤醒阻塞在available上的线程 available.signal(); } return true; } finally { //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } }
2.4take方法
//移除队头元素。 //如果队头元素(即时间延迟最小的元素)时间延迟未过期,阻塞等待,直到其过期 public E take() throws InterruptedException { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //获得锁 lock.lockInterruptibly(); try { for (;;) { E first = q.peek(); //如果队列为空,当前线程在available上阻塞等待 if (first == null) available.await(); else { //如果队头元素的时间延迟已过期,元素出队 long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS); if (delay <= 0) return q.poll(); //如果队头元素的时间延迟未过期 first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting //【使用leader/follower模式】 if (leader != null) //如果leader为null,当前线程阻塞等待 available.await(); else {//如果leader不为空,当前线程成为leader,并等待delay时间 Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread(); leader = thisThread; try { available.awaitNanos(delay); } finally { //等待delay时间后,队头元素的时间延迟已过期,当前leader任务完成,将leader置为null if (leader == thisThread) leader = null; } } } } } finally { //如果队列中有元素,且leader为null,将唤醒某个阻塞的线程,让其成为leader if (leader == null && q.peek() != null) available.signal(); //释放锁 lock.unlock(); } }
3.DelayQueue的应用场景
3.1使用DelayQueue模拟实现session
3.1.1场景分析
Session有以下特点:
1、以唯一键key来插入和获取对象
2、Session有自动过期时间,到期后系统会自动清理。
3、每次获取session对象,该key值所在的对象生命周期重置,过期时间从当前时间开始重新计算。
3.1.2实现思路
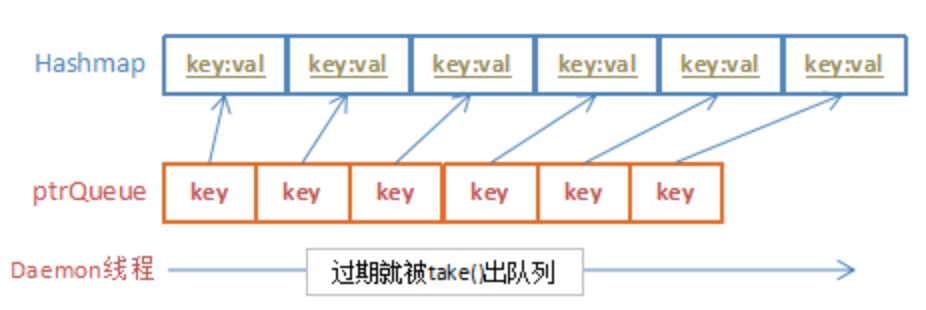
1、对于特点1,采用hashmap来保存session存储对象
2、对于特点2,3,利用DelayQueue延迟队列来实现:
创建一个延迟队列ptrqueue,每当有session插入hashmap时,就同步往ptrqueue队列插入一个与session的key同名的指针对象(该指针实现了Delayed接口,通过key值指向hashmap中对应元素);
每当读取session操作时,就更新ptrqueue队列中对应指针的到期时间;
专门开启一个守护线程(阻塞式)从ptrqueue队列中获取过期的指针,再根据指针删除hashmap中对应元素
3.1.3实现代码
public class DelayedDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { TSession sessionService=new TSession(); sessionService.ConnectionAndStart(); /*模拟客户端调用*/ sessionService.put("userIdentity", "tangwenming"); Thread.sleep(4000); sessionService.put("userGroup", "super"); sessionService.get("userIdentity"); sessionService.get("userGroup"); Thread.sleep(2000); sessionService.get("userGroup"); Thread.sleep(2000); sessionService.get("userGroup"); Thread.sleep(2000); sessionService.get("userGroup"); Thread.sleep(5500); sessionService.get("userGroup"); sessionService.get("userIdentity"); } } class TSession{ /*从conf中获取session自动过期时间,单位:秒*/ private static int liveTime=Integer.valueOf(getConfig("livetime")); /*指针保存队列*/ DelayQueue<Itemptr> ptrqueue=new DelayQueue<Itemptr>(); /*Session数据存储map*/ public ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> datapool = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(); public void put(String key,Object value){ /*插入session数据池*/ datapool.put(key, value); /*插入对应key值的指针*/ Itemptr ptr=new Itemptr(key,liveTime); ptrqueue.remove(ptr);/*更新过期时间step1*/ ptrqueue.put(ptr);/*更新过期时间step2*/ System.out.println("插入"+key+":"+value+",生命周期初始化:"+liveTime+"秒"); } public Object get(String key){ Object resultObject= datapool.get(key); if(resultObject!=null){ /*刷新对应key值的指针*/ Itemptr ptr=new Itemptr(key,liveTime); ptrqueue.remove(ptr); ptrqueue.put(ptr); System.out.println("获取"+key+"成功:"+resultObject+",生命周期重新计算"); }else{ /*从session池中返回对象*/ System.out.println("获取"+key+"失败:"+resultObject+"。对象已过期"); } return resultObject; } private void sesseion_gc(){ Itemptr ptr; while (true){ try { /*阻塞线程等待直到获取超时的元素指针 *获取成功后从队列中删除节点 在while true循环块中确实比非阻塞式的poll节省资源*/ ptr = ptrqueue.take(); /*根据指针删除session对象*/ datapool.remove(ptr.getKey()); System.out.println("删除过期key="+ptr.getKey()+"的元素"); /*降低cpu负担,根据业务需要和硬件调整*/ Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } private static String getConfig(String key){ return "5";/*单位:秒*/ } /*以守护进程运行gc回收方法*/ public void ConnectionAndStart(){ Thread sessionThread=new Thread(){ @Override public void run(){ sesseion_gc(); } }; sessionThread.setDaemon(true); sessionThread.start(); } } class Itemptr implements Delayed{ private String key; public String getKey() { return key; } private long liveTime ; private long removeTime; public long getRemoveTime() { return removeTime; } public Itemptr(String key,long liveTime){ this.key=key; this.liveTime = liveTime; this.removeTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.convert(liveTime, TimeUnit.SECONDS) + System.nanoTime(); } @Override public int compareTo(Delayed o) { if (o == null) return 1; if (o == this) return 0; if (o instanceof Itemptr){ Itemptr ptr = (Itemptr)o; /*用过期时间排序,确定优先级。 * DelayQueue按照升序(由小到大)排序的,也就是临近当前时间的优先出队*/ if (removeTime > ptr.getRemoveTime() ) { return 1; }else if (removeTime == ptr.getRemoveTime()) { return 0; }else { return -1; } } return 1; } @Override public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { return unit.convert(removeTime - System.nanoTime(), TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS); } /* * 队列remove()判断时使用equals比较:指针队列只需要判断key字符相同即可 * remove(Object o) * Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present, whether or not it has expired. */ @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (obj instanceof Itemptr) { if (obj==this) return true; return ((Itemptr)obj).getKey() == this.getKey() ?true:false; } return false; } }
4.参考资料
http://www.cs.wustl.edu/~schmidt/POSA/POSA2/ 《面向模式的软件体系结构2:用于并发和网络化对象的模式》官网
http://blog.csdn.net/jmxyandy/article/details/7338896 Leader Follower线程模型简单实现
http://www.cnblogs.com/duzouzhe/archive/2009/09/28/1575813.html 领导者/追随者模式
http://blog.csdn.net/goldlevi/article/details/7705180 Leader/Follower多线程网络模型介绍
http://blog.csdn.net/soonfly/article/details/58599087 Java多线程/并发27、DelayQueue延迟队列模拟实现Session