一、OGNL概述
1.1 什么是OGNL
OGNL的全称是对象图导航语言( object-graph Navigation Language),它是一种功能强大的开源表达式语言,使用这种表达式语言,可以通过某种表达式语法,存取Java对象的任意属性,调用Java对象的方法,同时能够自动实现必要的类型转换。如果把表达式看作是一个带有语义的字符串,那么OGNL无疑成为了这个语义字符串与Java对象之间沟通的桥梁。
1.2 OGNL的作用
Struts2默认的表达式语言就是OGNL,它具有以下特点:
● 支持对象方法调用。例如: objName. methodName( )。
● 支持类静态方法调用和值访问,表达式的格式为@[类全名(包括包路径)]@[ 方法名|值名 ]。例如:@java.lang.String@format( "foo%s","bar")。
● 支持赋值操作和表达式串联,例如: price=100, discount=0.8, calculatePrice( ),在方法中进行乘法计算会返回80。
● 访问OGNL上下文( OGNL context)和 ActionContext。
● 操作集合对象。
1.3 OGNL的要素
了解什么是OGNL及其特点后,接下来,分析一下OGNL的结构。OGNL的操作实际上就是围绕着OGNL结构的三个要素而进行的,分别是表达式(Expression)、根对象(Root Object)、上下文环境(Context),下面分别讲解这三个要素,具体如下:
1、表达式
表达式是整个OGNL的核心,OGNL会根据表达式去对象中取值。所有OGNL操作都是针对表达式解析后进行的。它表明了此次OGNL操作要”做什么”。表达式就是一个带有语法含义的字符串,这个字符串规定了操作的类型和操作的内容。OGNL支持大量的表达式语法,不仅支持这种”链式”对象访问路径,还支持在表达式中进行简单的计算。
2、根对象(Root)
Root对象可以理解为OGNL的操作对象,表达式规定了”做什么”,而Root对象则规定了”对谁操作”。OGNL称为对象导航语言,所谓对象图,即以任意一个对象为根,通过OGNL可以访问与这个对象关联的其他对象。
3、Context对象
实际上OGNL的取值还需要一个上下文环境。设置了Root对象,OGNL可以对Root对象进行取值或写值等操作,Root对象所在环境就是OGNL的上下文环境(Context)。上下文环境规定了OGNL的操作”在哪里进行”。上下文环境Context是一个Map类型的对象,在表达式中访问Context中的对象,需要使用”#”号加上对象名称,即”#对象名称”的形式。
总结来说:OGNL是一种表达式语言,之前我们学过el表达式,el表达式用于在JSP页面中获取域对象里面的值,但OGNL表达式比el表达式功能更加强大,我们使用OGNL表达式主要做的事情是在Struts2里面获取值栈中的数据(OGNL在Struts2里面经常和Struts2标签一起使用)。这就是我们接下来要重点讲解的内容,即在Struts2里面如何获取值栈中数据。
我们还需要注意一点:OGNL本身不是Struts2框架的一部分,而是一个单独的项目,只不过它经常和Struts2框架一起使用而已。要使用OGNL表达式,首先要导入Jar包,Struts2的包中已经包含了OGNL表达式的Jar包:![]() ,所以不需要导入额外的jar包。
,所以不需要导入额外的jar包。
二、OGNL的入门
2.1 取值环境
OGNL表达式作为一种与EL表达式性质相同的语言,主要都是用于取值的语言。我们首先要给这个语言的取值准备一个取值的环境。
我们先回顾一下EL表达式的取值环境。EL表达式的取值范围是11大内置对象,分别为:requestScope,sessionScope,applicationScope,pageScope,pageContext,param,paramValues,header,headerValues,cookie,initParam。
那么OGNL的取值环境在哪呢?我们需要给它准备一个对象OgnlContext,你写OGNL表达式的时候,就会从OgnlContext这个对象中取值。OgnlContext由两部分构成:一部分是Root,可以放置任何对象作为root,在整个OgnlContext中有且最多只能有一个根对象,可以通过调用OgnlContext.setRoot(obj)设置为根对象;一部分是Context,这里必须是Map,即键值对的形式存放。OGNL就在ROOT和Context这两部分中取值。
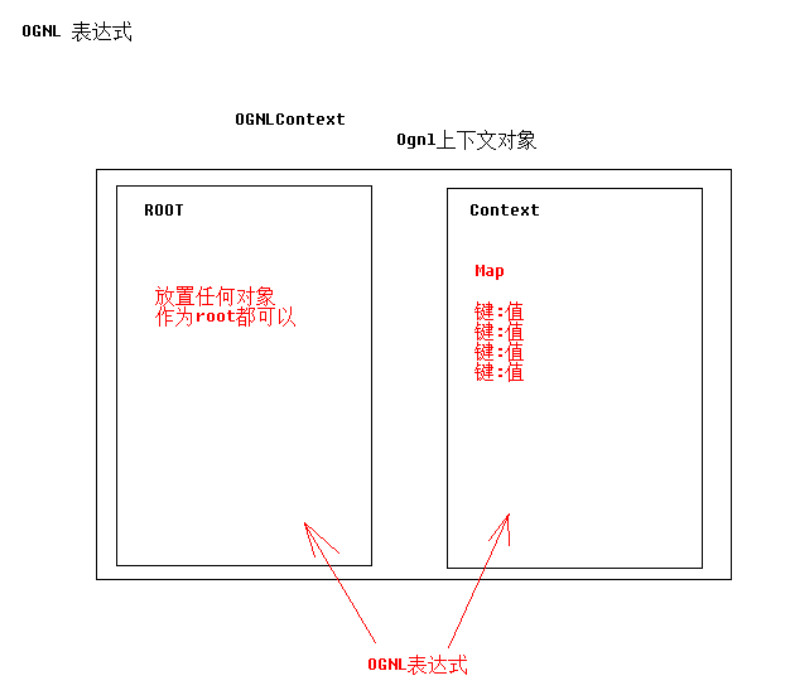
2.2 语法
- 取值
public void demo1() throws Exception { // 准备OGNLContext // 准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom", 18); // 准备Context Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<>(); context.put("user1", new User("jack", 20)); context.put("user2", new User("rose", 24)); // OgnlContext实现了Map接口 OgnlContext ognlContext = new OgnlContext(); // 将rootUser作为Root部分 ognlContext.setRoot(rootUser); // 将Context这个Map作为Context部分 ognlContext.setValues(context); // ----------------------------------------------------- /* * public static Object getValue(String expression, Map context, Object root){...} * 书写OGNL Ognl.getValue(expression, context, root); * expression:表明这次OGNL操作要"做什么" * context:规定OGNL的操作"在哪里进行" * root:规定"对谁操作" */ // 取出Root中user对象的name属性 String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name); System.out.println(age); // ----------------------------------------------------------------- // 取出Context中键为user1对象的name属性 String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); Integer age1 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user1.age", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1);// jack System.out.println(name2);// rose System.out.println(age1);// 20 }
Ognl在解析表达式的时候如果发现表达式开头带有"#",会去context对象中寻找;如果没有"#",则会默认去根对象中去寻找,由于根对象只有一个,所以只需要属性名字。
- 赋值
public void demo2() throws Exception { // 准备OGNLContext // 准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom", 18); // 准备Context Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<>(); context.put("user1", new User("jack", 20)); context.put("user2", new User("rose", 24)); OgnlContext ognlContext = new OgnlContext(); // 将rootUser作为Root部分 ognlContext.setRoot(rootUser); // 将Context这个Map作为Context部分 ognlContext.setValues(context); //---------------------------------------------- // 为root中的user对象的name属性赋值 Ognl.getValue("name='mike'", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name); //mike // 为context中的user1对象的name属性赋值 /*Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='jerry'", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot());*/ // 上述表达式可以合并为: String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='jerry',#user1.name", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1); }
- 调用方法
public void demo3() throws Exception { // 准备OGNLContext // 准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom", 18); // 准备Context Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<>(); context.put("user1", new User("jack", 20)); context.put("user2", new User("rose", 24)); OgnlContext ognlContext = new OgnlContext(); // 将rootUser作为Root部分 ognlContext.setRoot(rootUser); // 将Context这个Map作为Context部分 ognlContext.setValues(context); //------------------------------------------- // 调用root中user对象的setName方法 Ognl.getValue("setName('lucy')", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name); //lucy // 调用context中user1对象的setName方法 String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('kobe'),#user1.getName()", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1); }
- 调用静态方法
public void demo4() throws Exception { OgnlContext context = new OgnlContext(); // @类的全路径名@方法名称(参数列表) Object value = Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@random()", context, context.getRoot()); // @类的全路径名@属性名称 Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@PI", context, context.getRoot()); System.out.println(value); System.out.println(pi); }
- 创建对象(list,map)
public void demo5() throws Exception { // 准备OGNLContext // 准备Root User rootUser = new User("tom", 18); // 准备Context Map<String, User> context = new HashMap<>(); context.put("user1", new User("jack", 20)); context.put("user2", new User("rose", 24)); OgnlContext ognlContext = new OgnlContext(); // 将rootUser作为Root部分 ognlContext.setRoot(rootUser); // 将Context这个Map作为Context部分 ognlContext.setValues(context); // ------------------------------------------- // 创建list对象 Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack'}.size()", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(size);//3 String name1 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack'}[0]", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name1);//tom String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack'}.get(1)", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name2);//jerry //---------------------------------------------------- // 创建map对象 // 这里的#号表示创建的是map对象,不是从context中取值的# Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(size2);//2 String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(name3);//tom Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", ognlContext, ognlContext.getRoot()); System.out.println(age); }
三、OGNL与Struts2的结合
3.1 结合原理
OGNL表达式不管是自己单独拿来用,还是与struts2结合来用,一定要给它提供一个OgnlContext对象(root+context)。我们学习struts2与ognl结合,其实学的就是struts2分别给root部分和context部分准备了什么东西。struts2为OGNL准备的OgnlContext对象是一个ValueStack(值栈),可以简单的理解为OgnlContext在struts2中改名为ValueStack了。ValueStack由两部分组成,一部分叫做Root,放置的是一个栈;一部分是Context,放置的是ActionContext数据中心。
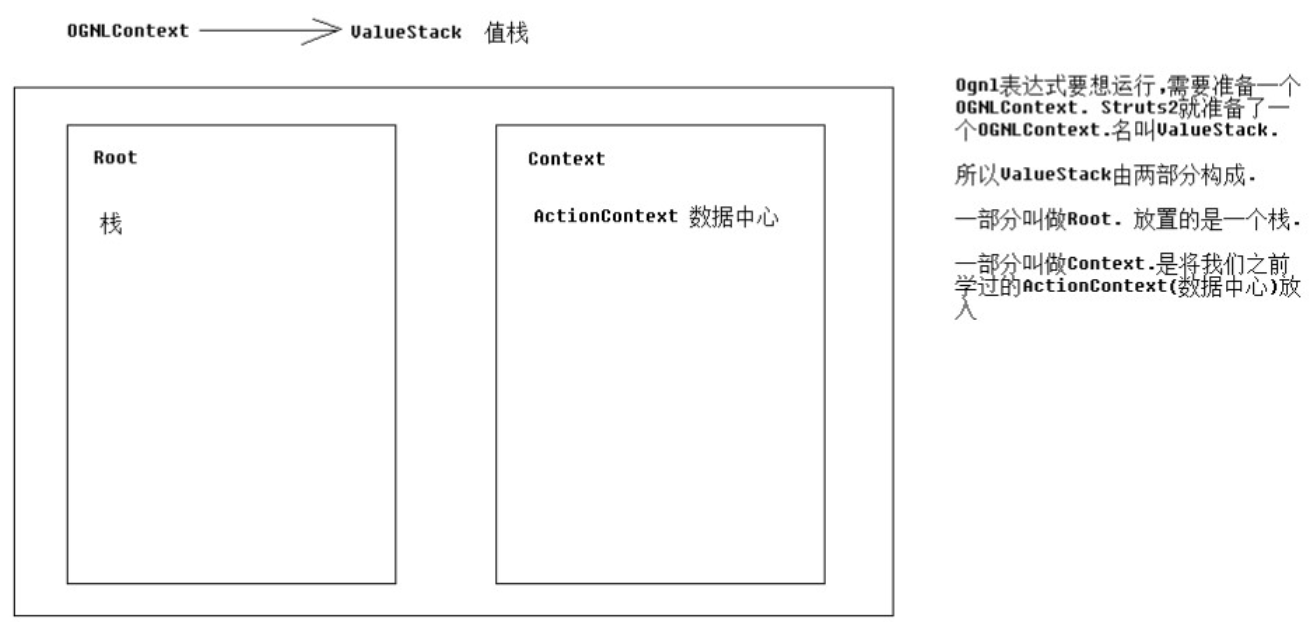
3.2 ValueStack
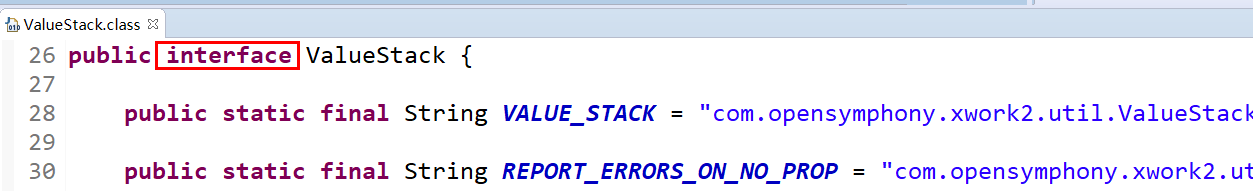
ValueStack是Struts2的一个接口,字面意义为值栈,而OgnlValueStack是它的唯一实现类

在这个类中,有两个属性CompoundRoot root;和Map<String, Object> context;分别与上图对应
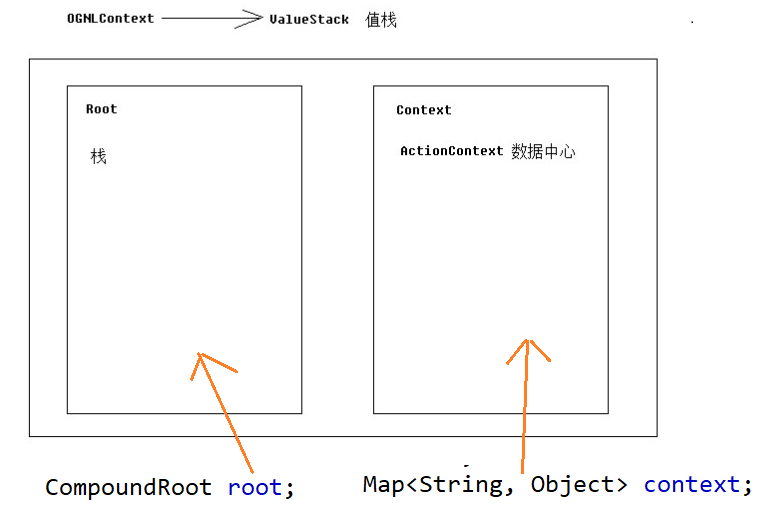
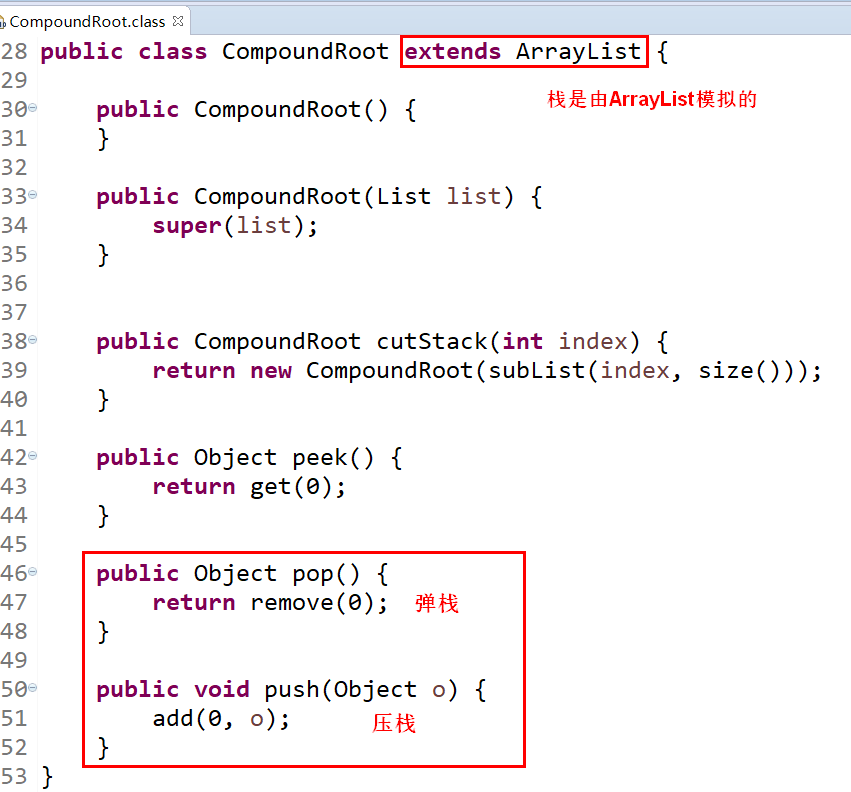
CompoundRoot其实就是一个栈:
context部分就是ActionContext数据中心(request、response、ServletContext、requestScope、sessionScope、applicationScope、params、attrs)

客户端发起一个请求时,Struts2框架会创建一个Action实例,同时创建一个OgnlValueStack值栈实例,OgnlValueStack贯穿整个Action的生命周期,Struts2中使用OGNL将请求Action的参数封装为对象存储到值栈中,并通过OGNL表达式读取值栈中的对象属性值。 取栈的属性值时,会从栈顶开始寻找,如果栈顶对象不存在该属性,就会从第二个对象寻找,如果没有找到就从第三个对象寻找,依次往下访问,直到找到为止。
值栈的作用:在我们访问一个action时,会将action加入到栈顶,也就是action会在CompoundRoot的栈顶,而我们提交的各种表单参数(充当了ognl表达式)会在valueStack从顶向下查找对应的属性进行赋值。
3.2.1 使用<debug>查看值栈中两部分内容
(1)创建一个Action类——ValueStackAction
public class ValueStackAction extends ActionSupport{ @Override public String execute() throws Exception { return SUCCESS; } }
(2)在struts.xml中配置该Action类
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"> <struts> <!-- 配置一个包:package --> <package name="demo" namespace="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="ValueStackDemo" class="cn.itcast.action.ValueStackAction"> <result name="success">valueStack.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
(3)创建valueStack.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s" %> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 使用这个标签可以看到值栈内部结构 --> <s:debug></s:debug> </body> </html>
(4)访问http://localhost:8080/struts2-02/ValueStackDemo.action后,看到如下界面
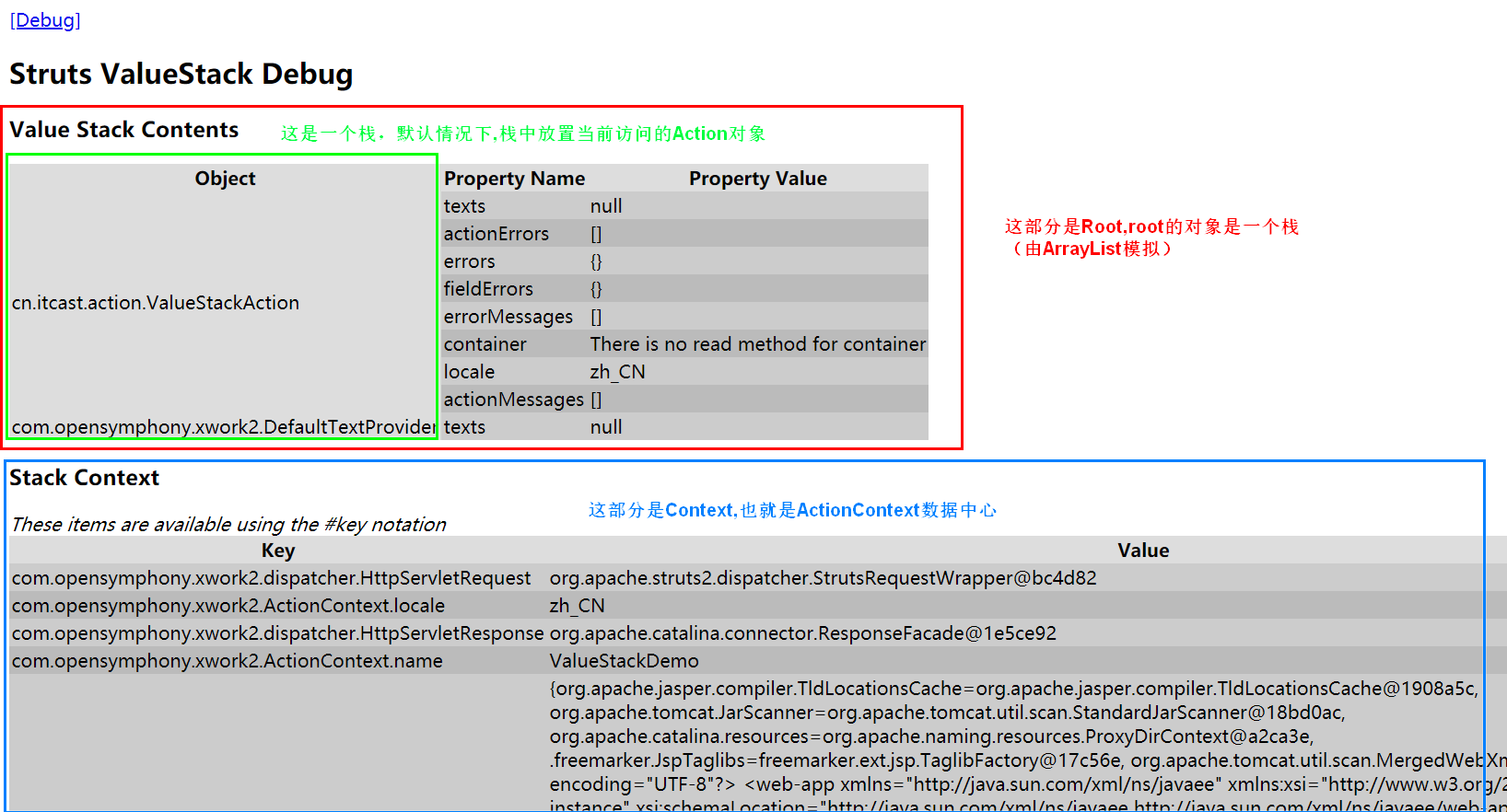
(5)点击这个[Debug]即可看到值栈的结构
3.2.2 向值栈中存取数据
【方式一:获取值栈对象,调用值栈对象里面的set方法】
- 使用set方法存数据
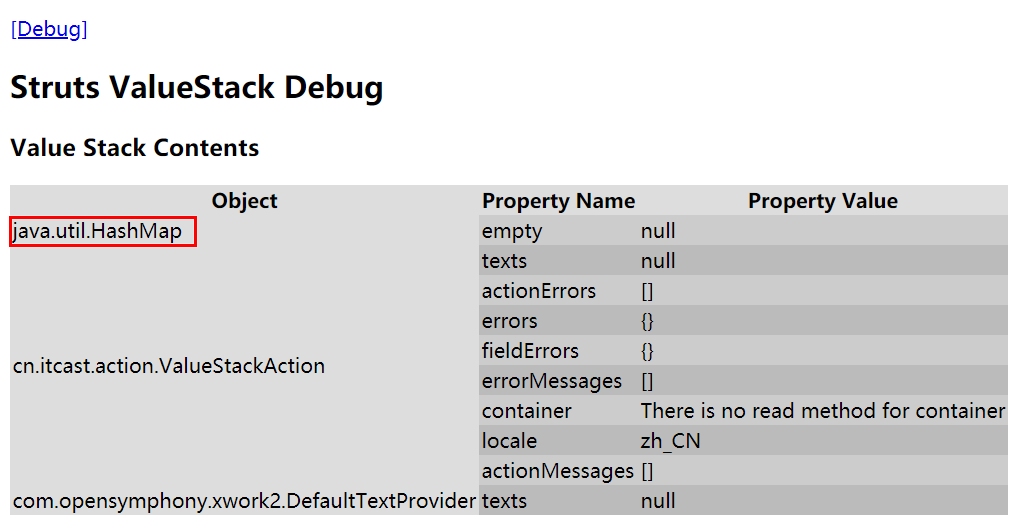
public class ValueStackAction extends ActionSupport { @Override public String execute() throws Exception { // 获取ActionContext对象 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext(); // 获取ValueStack对象 ValueStack stack = context.getValueStack(); /* * 使用set方法存数据 * set方法的第一个值:保存的数据的名字,在页面中取数据时使用该名字来取数据 * set方法的第二个值:要在页面中展示的值 */ stack.set("name", "张三"); return SUCCESS; } }
-
在页面取set方法存的数据
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 使用这个标签可以看到值栈内部结构 --> <s:debug></s:debug> <!-- 1、ognl表达式必须要在struts2标签中使用 2、在ognl表达式中可以直接调用Java的方法 3、value的值就是ognl表达式,就是在set方法中保存数据时的第一个参数的值 name: --> <s:property value="name" /> </body> </html>
【方式二:获取值栈对象,调用值栈对象里面的push方法】
- 使用push方法存数据
public class ValueStackAction extends ActionSupport { @Override public String execute() throws Exception { // 获取ActionContext对象 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext(); // 获取ValueStack对象 ValueStack stack = context.getValueStack(); /* * 使用push方法存数据 * push方法的值:保存的数据. */ stack.push("李四"); return SUCCESS; } }

-
在页面取push方法存的数据
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 使用这个标签可以看到值栈内部结构 --> <s:debug></s:debug> <!-- 1、ognl表达式必须要在struts2标签中使用 2、在ognl表达式中可以直接调用Java的方法 3、value的值就是ognl表达式. 4、push存的数据在值栈中是以数组的方式来存放的 5、数组的名字是固定的。就是top 6、在Java中数组的第一个值是top[0],但是在ognl表达式中为[0].top --> name:<s:property value="[0].top"/> </body> </html>
【方式三:在action成员变量位置定义变量,生成这个变量的get方法】(重点)
- 存取字符串:
(1)往值栈存字符串
public class ValueStackAction extends ActionSupport { // 存放字符串数据 // 创建一个字符串对象 private String name; // 创建该对象的getter方法 public String getName() { return name; } public String execute() { // 对字符串对象赋值 name = "王五"; return SUCCESS; } }
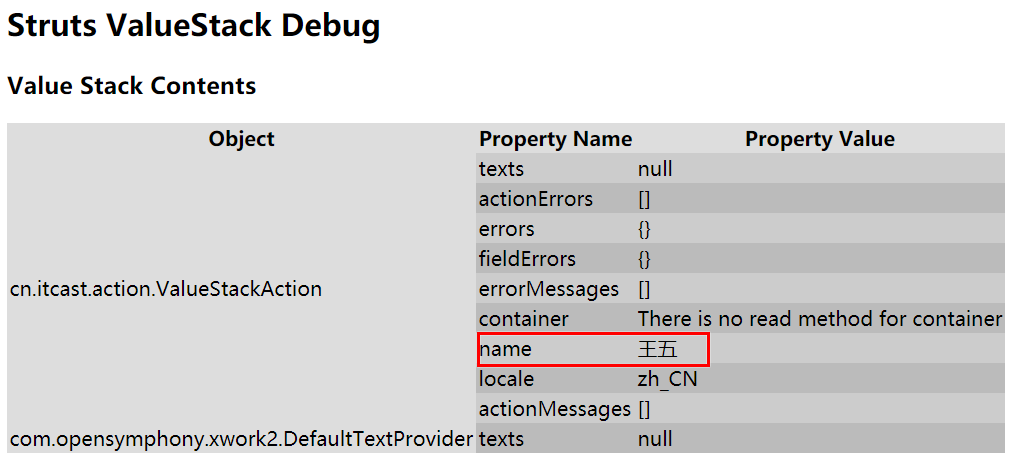
(2)从值栈中读取字符串
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!--要使用struts2标签,必须要引入struts2标签库 --> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 1、ognl表达式必须要在struts2标签中使用 2、在ognl表达式中可以直接调用Java的方法 3、value的值就是ognl表达式.是Action中字符串对象的名字 --> name:<s:property value="name"/> </body> </html>
- 存取对象
(1)往值栈中存入对象
public class ValueStackAction extends ActionSupport { // 保存对象到值栈中 // 创建实体对象 private User user = new User(); public User getUser() { return user; } @Override public String execute() throws Exception { // 给对象的属性赋值 user.setName("刘备"); user.setAge(20); return SUCCESS; } }
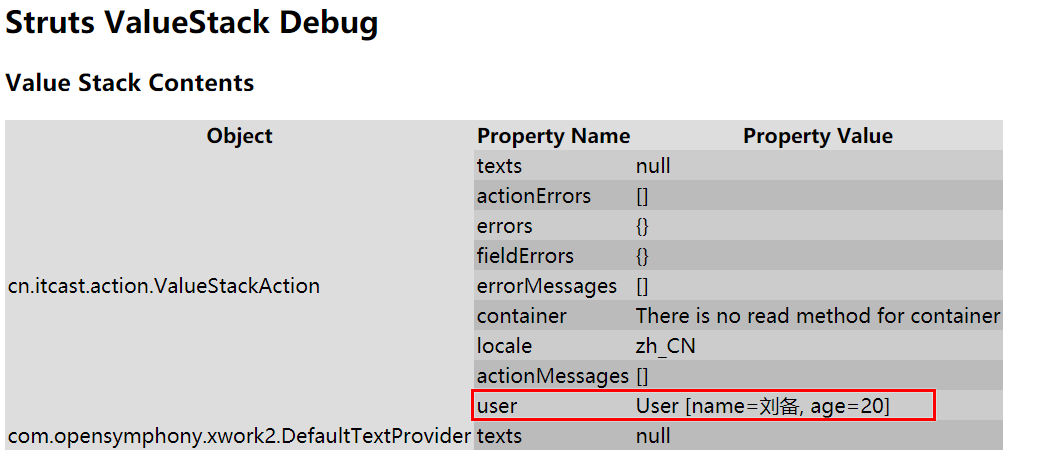
(2)从值栈中读取对象
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 使用这个标签可以看到值栈内部结构 --> <s:debug></s:debug> <!-- 1、ognl表达式必须要在struts2标签中使用 2、在ognl表达式中可以直接调用Java的方法 3、value的值就是ognl表达式. 4、表达式的值为:对象实例名称.对象属性名称 --> name:<s:property value="user.name"/> age:<s:property value="user.age"/> </body> </html>
- 存取list集合
(1)往值栈存list集合
public class ValueStackAction extends ActionSupport { // 往值栈中存放list集合数据 // 声明一个list对象 private List<User> list = new ArrayList<>(); public List<User> getList() { return list; } @Override public String execute() throws Exception { // 创建对象,并设置属性值 User user1 = new User("关羽", 18); User user2 = new User("张飞", 21); // 将对象放入list中 list.add(user1); list.add(user2); return SUCCESS; } }

(2)从值栈中读取list集合(四种方式)
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%--要使用struts2标签,必须要引入struts2标签库 --%> <%@ taglib uri="/struts-tags" prefix="s"%> <%--要使用jstl标签,必须要引入jstl标签库 --%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <!-- 使用这个标签可以看到值栈内部结构 --> <s:debug></s:debug> <!-- 第一种读取方式 value的值:list[0]表示集合中的第一个对象 表达式:Action中的集合名称[第几个对象].对象的属性名称 缺点:要知道集合中对象的个数,如果个数太多,则代码太长 --> name:<s:property value="list[0].name" /> age:<s:property value="list[0].age" /> name:<s:property value="list[1].name" /> age:<s:property value="list[1].age" /> <br> <!-- 第二种读取方式 该方式使用struts2的<s:iterator>标签来读取 <iterator>标签中value的值:Action中的集合名称 <property>标签中value的值:对象的属性名称 --> <s:iterator value="list"> name:<s:property value="name" /> age:<s:property value="age" /> </s:iterator> <br> <!-- 第三种读取方式 该方式使用struts2的<s:iterator>标签来读取 <iterator>标签中value的值:Action中的集合名称 <iterator>标签中var的值:相当于遍历时的每一个对象的名称 <property>标签中value的值:#var属性的值.对象属性的值 机制:遍历list集合。得到list集合中的每一个对象,将对象以map的方式保存到context中 key就是var属性的值,值是每一个对象的引用。 在ognl表达式中要访问context中的数据时,要在表达式前面加上# --> <s:iterator value="list" var="user"> name:<s:property value="#user.name" /> age:<s:property value="#user.age" /> </s:iterator> <br> <!-- 第四种读取方式 该方式使用jstl的<c:foreach>标签来读取 <c:forEach>标签中value的值:Action中的集合名称 <c:forEach>标签中var的值:相当于遍历时的每一个对象的名称 el表达式能取到值栈数据的原因:struts2底层增强了request的setAttribute方法, 在增强中,首先去域对象中取值,如果在域对象中没有取到值,就去值栈中取值,将从值栈 中取到的值保存到域对象中返回。 缺点:需要先去域对象中取值,没有才去值栈中取值,取到后又要保存到域对象中返回,所有效率不高 一般不使用此方法 --> <c:forEach items="${list }" var="user"> name:${user.name } age:${user.age } </c:forEach> </body> </html>
四、struts2标签库
Struts2中OGNL表达式必须配合Struts2标签使用,不然没什么效果。
对于一个MVC框架而言,重点是实现两部分:业务逻辑控制器部分和视图页面部分。Struts2作为一个优秀的MVC框架,也把重点放在了这两部分上。控制器主要由Action来提供支持,而视图则是由大量的标签来提供支持。
4.1 Struts2标签库概述
在JavaWeb中,Struts2标签库是一个比较完善,而且功能强大的标签库,它将所有标签都统一到一个标签库中,从而简化了标签的使用,它还提供主题和模板的支持,极大地简化了视图页面代码的编写,同时它还提供对ajax的支持,大大的丰富了视图的表现效果。与JSTL(JSP Standard Library,JSP 标准标签库)相比,Struts2标签库更加易用和强大。
4.2 Struts2标签库的分类
早期的JSP页面需要嵌入大量的Java脚本来进行输出,这样使得一个简单的JSP页面加入了大量的代码,不利于代码的可维护性和可读性。随着技术的发展,逐渐的采用标签库来进行JSP页面的开发,这使得JDP页面能够在很短的时间内开发完成,而且代码通俗易懂,大大的方便了开发者,Struts2的标签库就是这样发展起来的。
Struts2框架对整个标签库进行了分类,按其功能大致可分为两类,如图所示。

由图中可以看出, Struts2标签库主要分为两类:普通标签和UI标签。普通标签主要是在页面生成时,控制执行的流程。UI标签则是以丰富而可复用的HTML文件来显示数据。
普通标签又分为控制标签( Control Tags)和数据标签( Data Tags)。控制标签用来完成条件逻辑、循环逻辑的控制,也可用来做集合的操作。数据标签用来输出后台的数据和完成其他数据访问功能。
UI标签又分为表单标签( Form Tags)、非表单标签( non-form Tags)和Ajax标签。表单标签主要用来生成HTML页面中的表单元素,非表单标签主要用来生成HTML的<div>标签及输出 Action中封装的信息等。Ajax标签主要用来提供Ajax技术支持。
4.3 Struts2标签的使用
Struts2标签库被定义在 struts-tags tld文件中,我们可以在 struts-core-2.3.24jar中的META-INF目录下找到它。要使用 struts2的标签库,一般只需在JsP文件使用 taglib指令导入 Struts2标签库,具体代码如下:
<%@taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
在上述代码中, taglib指令的uri属性用于指定引入标签库描述符文件的URI, prefix属性用于指定引入标签库描述符文件的前缀。需要注意的是,在JSP文件中,所有的 Struts2标签库的使用“s”前缀。
4.4 控制标签
<!-- 遍历标签 iterator --> <!-- ------------------------------------- --> <s:iterator value="#list" > <s:property /><br> </s:iterator> <!-- ------------------------------------- --><hr> <s:iterator value="#list" var="name" > <s:property value="#name" /><br> </s:iterator> <!-- ------------------------------------- --><hr> <s:iterator begin="1" end="100" step="1" > <s:property />| </s:iterator> <!-- ------------------if else elseif------------------- --><hr> <s:if test="#list.size()==4"> list长度为4! </s:if> <s:elseif test="#list.size()==3"> list长度为3! </s:elseif> <s:else> list不3不4! </s:else>
4.5 数据标签
<!-- ------------------property 配合ognl表达式页面取值 ------------------- --> <s:property value="#list.size()" /> <s:property value="#session.user.name" />
4.6 表单标签
<!-- struts2表单标签 --> <!-- 好处1: 内置了一套样式. --> <!-- 好处2: 自动回显,根据栈中的属性 --> <!-- theme:指定表单的主题 xhtml:默认 simple:没有主题 --> <s:form action="Demo3Action" namespace="/" theme="xhtml" > <s:textfield name="name" label="用户名" ></s:textfield> <s:password name="password" label="密码" ></s:password> <s:radio list="{'男','女'}" name="gender" label="性别" ></s:radio> <s:radio list="#{1:'男',0:'女'}" name="gender" label="性别" ></s:radio> <s:checkboxlist list="#{2:'抽烟',1:'喝酒',0:'烫头'}" name="habits" label="爱好" ></s:checkboxlist> <s:select list="#{2:'大专',1:'本科',0:'硕士'}" headerKey="" headerValue="---请选择---" name="edu" label="学历" > </s:select> <s:file name="photo" label="近照" ></s:file> <s:textarea name="desc" label="个人简介" ></s:textarea> <s:submit value="提交" ></s:submit> </s:form>
4.7 非表单标签
<s:actionerror/>