HashMap
下标计算方法:hashCode & (length-1) ,&按位与操作,二进制相同位都是1,该位才为1
JDK1.7与JDK1.8中HashMap区别: JDK1.8在put元素时,若计算得到的下标下的链表长度达到8时(算上当前要加到链表尾部的元素),链表会转换成红黑树提高查找效率
通过调整hashmap初始大小避免rehash的实例:要转移1000个数据到hashmap,那么假定初始大小1024,在转移到1024*0.75=768个时会触发rehash,将1024扩容到2048,所以如果在设置初始大小时指定2048就可以避免一次rehash
https://www.cnblogs.com/williamjie/p/9358291.html
hashMap是线程不安全的,hashtable利用synchronized加在put和get方法上实现线程安全
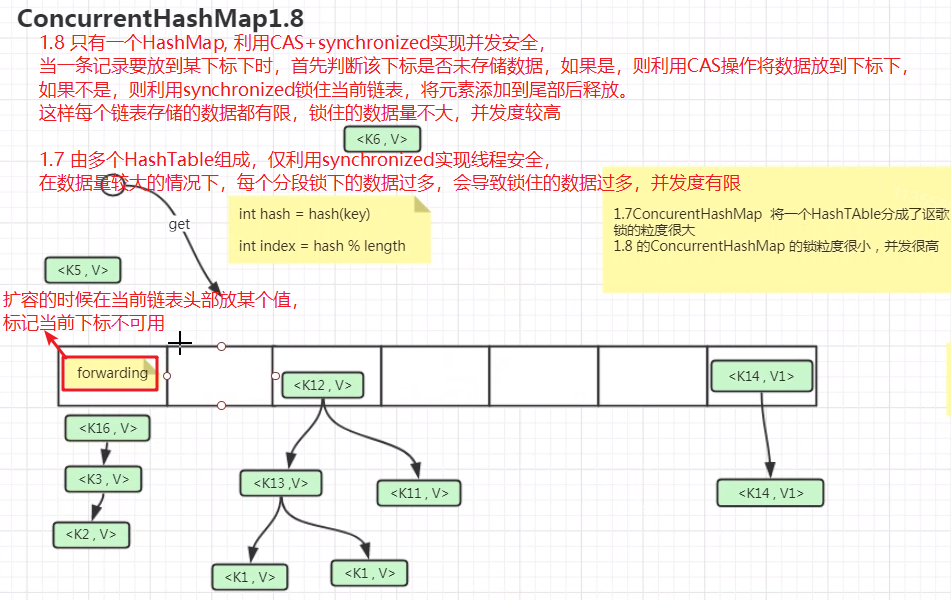
ConcurrentHashMap
线程安全的HashMap
JDK1.7 ConcurrentHashMap有多个HashTable组成,有几个HashTable并发级别concurrencyLevel就是几,默认16,这就叫分段锁,



ConcurrentSkipListMap/TreeMap
TreeMap与HashMap不同之处在于,TreeMap按照key的字典顺序来排序(升序),也可通过Comparator实现排序逻辑
TreeMap线程不安全,使用ConcurrentSkipListMap保证线程安全


ArrayList
非线程安全
CopyOnWriteArrayList
线程安全,通过ReentrantLock实现,add()方法加锁
但会对数组进行拷贝,在某段时间数据量翻倍造成内存溢出,不适用数据量过大的情况
读取新写入的数据会有延迟,因为数组的引用需要从旧数组转到新数组
1 /** 2 * Appends the specified element to the end of this list. 3 * 4 * @param e element to be appended to this list 5 * @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add}) 6 */ 7 public boolean add(E e) { 8 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 9 lock.lock(); 10 try { 11 Object[] elements = getArray(); 12 int len = elements.length; 13 Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); 14 newElements[len] = e; 15 setArray(newElements); 16 return true; 17 } finally { 18 lock.unlock(); 19 } 20 }
HashSet
HashMap如果遇到相同的Key会对Value值进行覆盖,保证HashMap的Key是不重复的。
HashSet<T> 即利用HashMap这一特性保证Set集合中元素(KEY)不重复,其并不关心Value的值。
CopyOnWriteArraySet
写的时候会判断数组中是否已经存在,若存在就不再写入,其他特性与CopyOnWriteArrayList相同
ConcurrentSkipListSet
跳表实现原理同ConcurrentSkipListMap,KEY不重复且有序
队列QUEUE
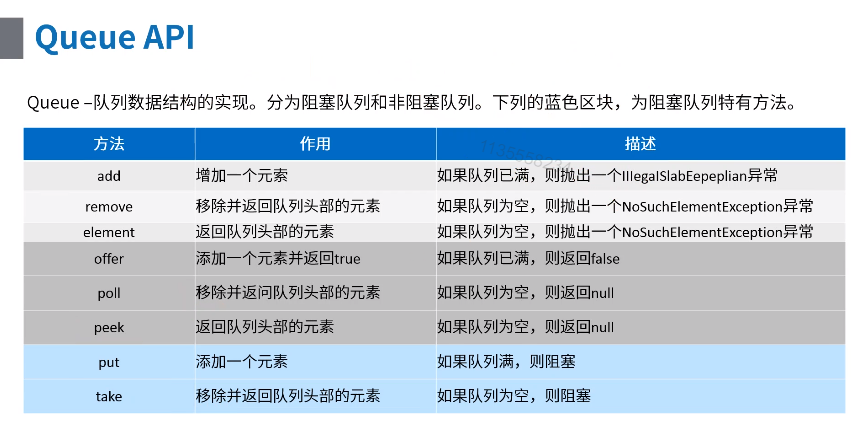
ArrayBlockingQueue
线程安全,数组实现,ReentrantLock锁,只有一把锁,take() 和 put() 互斥,加的是同一把锁;
take()和put()方法是阻塞的,offer()和poll()方法是非阻塞的
构造函数制定队列长度capacity,利用参数count记录队列中元素数量,count=capacity时put操作阻塞(poll()方法直接返回null),count=0时take操作阻塞(offer()方法直接返回false),底层唤醒其实是利用condition的2个队列实现,参照1.3.1 Lock利用condition实现的阻塞队列;
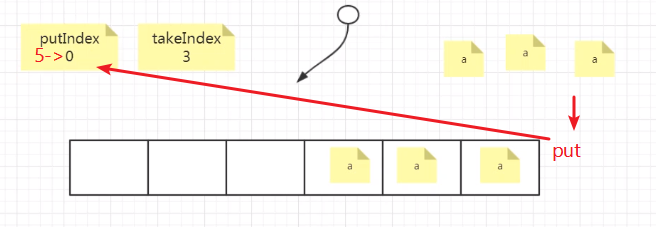
put和take时利用takeIndex和putIndex记录下一个操作应该放到那个位置或从哪个位置取;
循环数组实现:当putIndex达到capacity时,takeIndex并不是+1,而是变成0,即下一个put操作会将元素放到队列头部;takeIndex原理相同

1 public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException { 2 checkNotNull(e); 3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 4 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 5 try { 6 while (count == items.length) 7 notFull.await(); 8 enqueue(e); 9 } finally { 10 lock.unlock(); 11 } 12 } 13 14 public E take() throws InterruptedException { 15 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 16 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 17 try { 18 while (count == 0) 19 notEmpty.await(); 20 return dequeue(); 21 } finally { 22 lock.unlock(); 23 } 24 } 25 26 public boolean offer(E e) { 27 checkNotNull(e); 28 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 29 lock.lock(); 30 try { 31 if (count == items.length) 32 return false; 33 else { 34 enqueue(e); 35 return true; 36 } 37 } finally { 38 lock.unlock(); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public E poll() { 43 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 44 lock.lock(); 45 try { 46 return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue(); 47 } finally { 48 lock.unlock(); 49 } 50 }
LinkedBlockingQueue
线程安全,链表实现,put和take各一把ReentrantLock锁,读和写操作加的是不同的锁,互不干扰,提高了读写性能
take()操作利用takeLock操作链表头部,put()利用putLock操作链表尾部,互不干扰,读和取不会互斥,并发度比ArrayBlockingQueue高一些
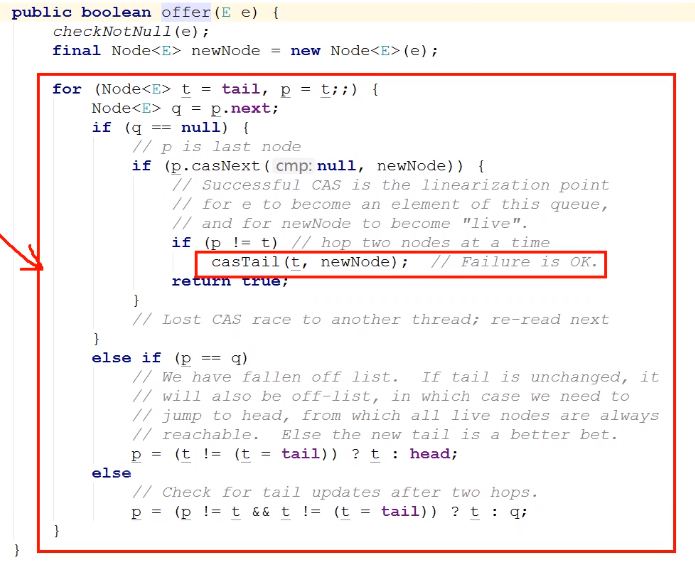
ConcurrentLinkedQueue
线程安全,并发度高,非阻塞队列,无锁,没有take() 和 put()这2个阻塞方法
利用CAS操作,采用自旋的方式将元素添加到链表尾部 或 将链表头部替换为null

SynchronousQueue
不常用
package com.study.list_set_queue.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
/*
1、take会阻塞,直到取到元素
2、put时会阻塞,直到被get
3、若没有take方法阻塞等待,offer的元素可能会丢失
4、poll取不到元素,就返回null,如果正好有put被阻塞,可以取到
5、peek 永远只能取到null,不能让take结束阻塞
*/
public class Demo2_SyncQueueTest {
static SynchronousQueue<String> syncQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
//put时会阻塞,直到被get
public static void test01() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000L);
System.out.println(syncQueue.poll());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
System.out.println("begain to put...");
syncQueue.put("put_element");
System.out.println("put done...");
}
//3、若没有take方法阻塞等待,offer的元素可能会丢失
public static void test02() throws InterruptedException {
syncQueue.offer("offered_element");
System.out.println(syncQueue.poll());
}
//4、poll取不到元素,就返回null,如果正好有put被阻塞,可以取到
public static void test03() throws InterruptedException {
/* new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
syncQueue.put("put_element");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();*/
Thread.sleep(200L);
Object obj = syncQueue.poll();
System.out.println(obj);
}
//peek 永远只能取到null,不能让take结束阻塞
public static void test04() throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
syncQueue.put("put_element");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}.start();
Thread.sleep(200L);
Object obj = syncQueue.peek();
System.out.println(obj);
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws InterruptedException {
test02();
}
}
PriorityBlockingQueue
优先级队列,可以通过比较器对入队列的元素进行排序存储,进而改变出队列顺序
package com.study.list_set_queue.queue;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.concurrent.PriorityBlockingQueue;
public class Demo4_PriorityBlockingQueue3 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
PriorityBlockingQueue<Student> queue = new PriorityBlockingQueue<>(5, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
int num1 = o1.age;
int num2 = o2.age;
if (num1 > num2)
return 1;
else if (num1 == num2)
return 0;
else
return -1;
}
});
queue.put(new Student(10, "enmily"));
queue.put(new Student(20, "Tony"));
queue.put(new Student(5, "baby"));
for (; queue.size() > 0;) {
try {
System.out.println(queue.take().name);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Student {
public int age;
public String name;
public Student(int age, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
}
}


