Linux的命令总结
1、 man:在线请求系统帮助
例:man mkdir
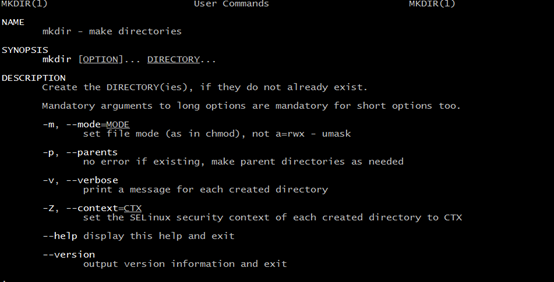
NAME:这个命令的完整全名 mk(make directories)
SYNOPSIS:这个命令的基本语法
mkdir [OPTION]... DIRECTORY...
OPTION:参数
DERECTORY:目录或者行为
DESCRIPTION:具体描述命令的使用方法
-m, --mode=MODE
set file mode (as in chmod), not a=rwx – umask
左边的-m为短参数,右边的--mode为完整参数名称
设置目录的状态(这里可以理解为权限),和chmod这个命令一样,并不是默认权限
用法:
mkdir 777 test.c 使用短参数
等价于
mkdir --mode 777 test1 使用长参数
AUTHOR:作者
REPORTING BUGS:如果出现问题,请发邮件或者登录说明的网址
COPYRIGHT:受到了著作权的法律保护,是GPL
SEE ALSO:还可以在哪里查询这个命令的使用方法,例如:info mkdir
按键:
[Page Dowm]: 向下翻页
[空格键]: 向下翻页
[page Up]:向上翻页
[Home]:回到首页
[End]:回到末页
/String:向下查询字符串,如果要向下查询vbird,使用输入/vbird
?String:向上查询字符串,
n/N:利用/或者?来查询字符串时,可以使用n来继续下一个查询(不论是还是?),可以利用N来向下查询。举例来说,我以/vbird查询vbird字符串,那么我可以使用n来往下查询,使用N来
q:结束这次的man page
touch
touch:chage file timestamps
update the access and modification times of each FILE to current time .
A FILE argument that does not exsit is created empty unless -c or -h is suppiled
参数:
-a:change only the access time
-c:do not create any files
-d –date=STRING:parse STRING and use it instead of use current time
-f:ignore
-m:change only the modification time
-t STAMP:use [YYMMDDhhmm] instead of current time
--time=WORD:change specified time :WORD is access,atime,or use:equivalent to -a WORD is modify or mtime:equivalent to -m
atime:access time :file is executed or read
ctime:creat time :file is change including content,owner,authority and so on
mtime:modify time:file is written
so if a file is written all time will change
If you want know more ,please click:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_67178440010101gr.html
LS
ls – list directory contents
List information about the FILES (the curren directory by default),sort entries alphabetically if none of -cftuzSUX nor
-–sort
-a,--all list
do not ignore entries starting with .
-A –almost-all
Do not list imply . and ..
--author
With l print the author of each file
-d –-directory
list directory entries instead of conents,and do not dereference symblolic links
-f
Do not sort,enable -aU
-F –- classify
append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries
-h --human-readable
With -l,print sizes human readable format(e.g.,234M,2G)
-l
Use long list format
-S
sort by file size
-t
sort by modification time
-i
print the index number of each file
for example, use i l and h .
-F --classify
append indicator(one of */=>@|) to entries
usually use -F will add / at the end of the directory, so you can use it and grep to easily get directories.
for example:
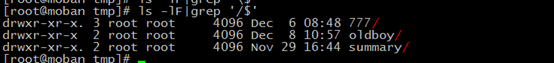
-p --indicator--style=slash
append / indicator to directories
we also think it: -F contain -p
-r --reverse
reverse order while sorting
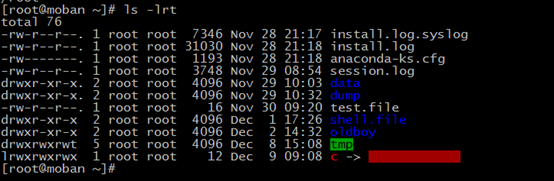
if you want find the latest file you create of many files,you can use: ls -lrt
mkdir
mkdir -- make directory
Create the DIRECTOTY(ies) if the they do not already exsit
args:
-m,--mode=MODE
set file mode (as in chomd),not a=rwx -umask
umask:default authority
-p --parents
no error if existing ,make parent directories as needed
-v --verbose
-v, --verbose
print a message for each created directory
-Z, --context=CTX
set the SELinux security context of each created directory to CTX
cp(copy)
copy -- copy files and directories
args
-a --archive
same as -dR --preserve=all
-d:若为连接文件,则复制文件本身
-i --interactive
prompt before overwrite(overrides a previous -n position)
-p
same as -preserve=mode,ownership,timestamps,using 备份
-r --recursive
copy directories recursively
rm
rm --remove directories or files
args:
-f --force
ignore nonexistent files,never prompt
-i
prompt before every removal
-r --recursive
remove directories and their contents recursiveable
mv
mv --move(rename) files
args:
-f --force
do not prompt before overwriting
-i --interactive
prompt before overwriting
-u --update
move only when the SOURCE is newer than destination file or destination file is missing
echo
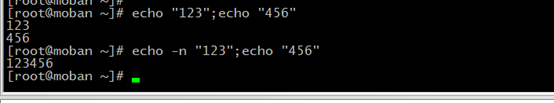
echo --display a line of a text
-n do not output the trailing newline
for example:
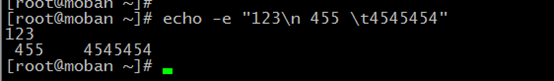
-e enable interpretation of backslash escapes
If e in effect the following sequences are recognized
new line
vertical tab
for example:
Example:
create a file and write a line content:
echo "This is a test file" > test.file
if you execute the command secondly,it will overwrite the file and if you want to add not to overwrite,you could use the command:
echo "This is a test file" >> test.file
1、 if PATH is a variable param is system,you use echo $PATH to input its value
2、 echo 123 --> 123
cat&tac
cat -- concatenate files and print on the standard output
-a --show-all
equivalent to -vET
-b --number-noneblank
number nonempty output lines
-e
equvilent to -vE
-E --show-ends
display $ at the end of each line
-n --number
number all output lines
-T --show-tabs
display TAB characters as ^I
-v show-nonprinting
use ^ and M- natation except for LFD and TAB
Example:
if you want use cat to create file,you can use follow
cat > test.file <<EOF
> ds
> dssdwew
> weew
> EOF
the content between EOE will be writtern the file and if the file is not exsit,will create or overwrite
tac: concatenate and print files in inverse
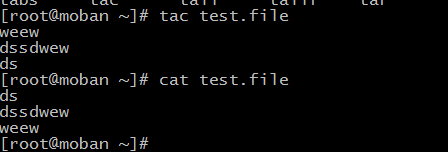
pwd
pwd --print name of current/working directory
Print full name of current working directory
-L --logcial
use PWD from envirment,even if contains symlinks
-P --physical
avoid all symlinks
alias
alias --set a name or var of a long command or character
Example:
1、alias:show all alias in you system or user
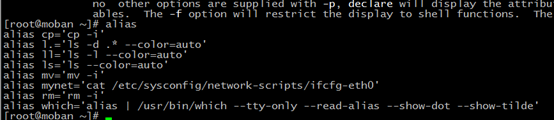
“cp = ‘cp -i’” mean that if you cp a file to destination directory and exsiting a same name file in the directory,The system will ask you whether overwrite
2、 if want to set some alias,you can do follow:
alias cat='cat -n',use cat to represent cat -n
in ‘ ’ ,you should use command
3、 if wan cancel some alias,you can use follow:
unalias cat
But we suggest don’t modify system alias which can help we avoid some bad execution. If some command or path too long ,you could use alias. such as, I will use this command “mynet” to respresent my network information:
alias mynet='cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0'
but if do above, this alias is temporary,if you want to use the alias forever, you shoud add the command in ~/.bashrc

head && tail
head --output the first part of files
Print the first 10 lines of each FILE to standard output. With more than one FILE, precede each with a header
giving the file name. With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input.
Example:
head -3 test.file.
print the first 3 line of test.file
head test.file default 10 line
in contrast
tail -- tail - output the last part of files
Ways to use is same as head
Question: print 20~30 line of file
head -30 test.txt|tail -11
or
tail -81 test.txt|head -11
-f : listen a file tail
Open two terminal, one to write to test.txt
for example:
for n in `seq 1000`; do echo $n >> /tmp/test.txt;sleep 1; done
the other to use tail to listen test.txt
for example: tail -f /tmp/test.txt
This command is used to listen log file of web ,you can view some information or exception from the tail of files
-F the same as -f, but if the file is deleted, it will try too.
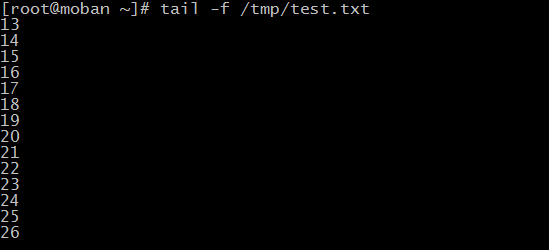
“|” means pipe
rmdir
rmdir --remove empty directory
if want more, reference man rmdir.
seq
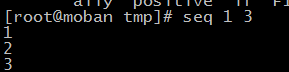
seq --print a sequence of numbers
seq 1 3
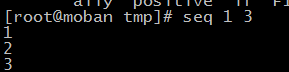
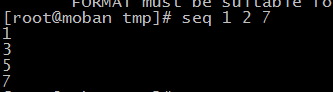
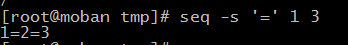
use “ ” as the separator. you also can use ‘-s’ to change it

vi/vim
they are the notepad of linux, if want more, reference book.
find
This is a vital command, we explain it by examples.
1、find by type and name
find --search for files in a directories
find / -type f -name "att.txt"
/:the directory you think the file searched in
-type: the file’s type
f:regular file
d:directory
...
-name :the file name you want to search
-maxdepth +number choose how depth the directory you would search
-pruen: True,if the file is a directory ,do not descend into it. If -depth is given ,not effective
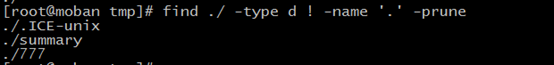
! :not
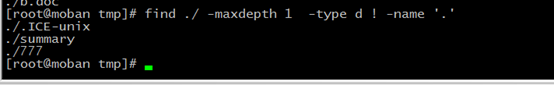

-o || -or:OR
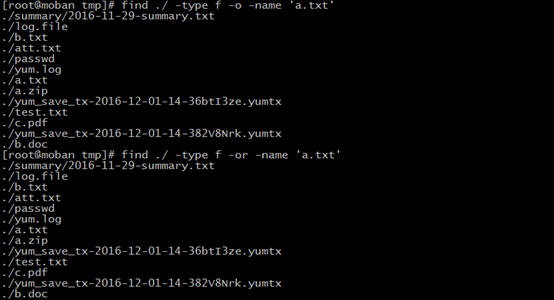
-a or -and :and
you have fond some files, but you want to view or execute them?
how do to? Following
2、find and execute
find / -type f -name "att.txt" -exec ls -l {} ;
you could comprehension as follow:
-exec COMMAND
“;” is the bash
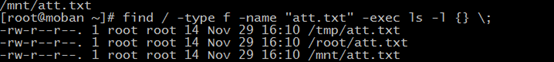
But above command also can be replaced by “xargs”, please reference “xargs”
3、find by time
find / -type f -mtime -4
-4:the last 4 days
4 :the fourth day
+4 the fourth day ago
xagrs
xargs --built and execute command lines from standard input
some command may not support pipe,but we can use xargs to standard input.we use example to explain the command:
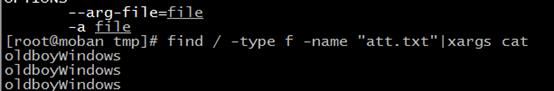
find / -type f -name "att.txt"|xargs cat
use xargs to cat file
grep/egrep
grep --print lines matching a pattern
args
-a --text
process a binary file as if it were text this is equivalent to the --binary-files=text option
-c --calculate the matching pattern counts.
-i --ignore-case
ignore case distinctions in both PATTERN and input files
-E : for example: grep -E “A|B|C” means to show A or B C
-n, --line-number
Prefix each line of output with the 1-based line number within its input file. (-n is specified by
POSIX.)
-v --invert-match
Invert the sense of matching, to select non-matching lines. (-v is specified by POSIX.)
-A means after N, except for current line we needs ,it will show after N lines
-B means before N expect for current lines we need, it will show before N lines.
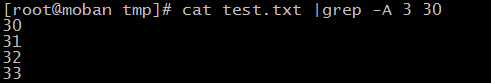
for example, if want to list current and its after 3 lines, you can use:
cat test.txt |grep -A 3 30
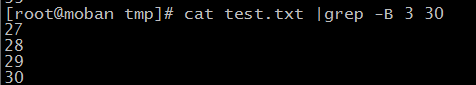
similarly,
cat test.txt |grep -B 3 30
--color=auto the characters which is PATTERN will be show by color, for example
dmesg | grep -n --color=auto 'eth0'
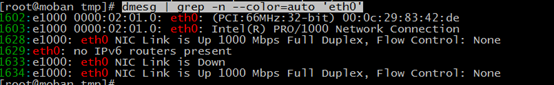
the result is colorful!
so we can use alias to use it forever
alias grep = ‘grep --color=auto’
add it in your ~/.bashrc
sed
sed -- sed - stream editor for filtering and transforming text
we will examples to use this command
-n:use silent mode, only deal with date will be show screen
-i:means insert
Examples:
1、search 20-30 line a file

2、search all file named att.txt and replace their content “oldboyWindows” to ”oldboyLinux” how to do ?
Firstly, find those files
find / -type f -name att.txt
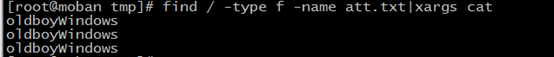
Secondly, change them in screen,but source files don’t update
find / -type f -name att.txt|xargs sed #oldboyWindows#oldboyLinux#g
sed s#P1#P2#g
P1:the content if source files
P2:the content you want to replace

Thirdly: replace in source files, we only need add “-i” after sed, successful!

/^S/:begin with S

//$/:/$ is the end of /,because of //,nend to uer to change it

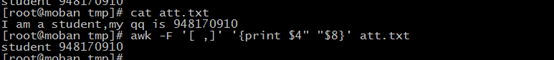
what to do to use ‘sed’ to get you ip address;
use the regex to match, (.*) is the content we need,we can use
“1” to get it at the behind of the second “#”.if you use more one ”()”,you can user “1” to the get first one, use “2” to get the second. if you get nothing, express you regex is not match the character. Be careful of “-n” and ‘p’

if you want to insert some content to some files, you can use find and sed
sed -i '1 i http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com/2561410/'
-i insert ‘1(line number) i(insert) http://oldboy.blog.51cto.com/2561410/ (the content you want to insert)’
some hacker may use it to attract you web

you can use following ways to solve it.
1、 delete it(recommend because it will not anything including blank line)
sed -i ‘/the content you want delete/d(delete)’

2、 replace it(don’t recommend ,because if will keep blank line)
find /tmp/ -type f|xargs sed -i ‘s#the content you want to replace#(keep blank)#g’
awk
awk -- pattern scanning and processing language
-F --field-separator FS
Use FS for the input field separator and if want use more one, user’[]’
example:
for example:
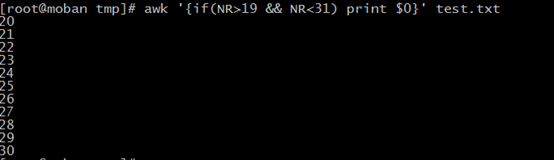
1、search 20-30 line a file
awk '{if(NR>19 && NR<31) print $0}' test.txt
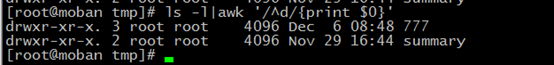
NR meas line numbers $0 meas all characters
/^d/: begin with d
$0:all characters
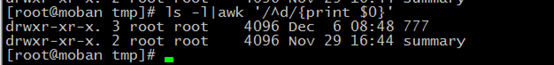
//$/:/$ is the end of /,because of //,nend to uer to change it
if want to use more separator, you can use “-F”, for example:
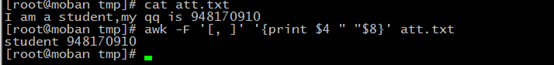
Above we use “ ” and “,” two separators, so we can get result we want.
but if the characters have one more “ ” or “,”, what we to do it. We can use “+” end the ‘]’,it express that if has many separators, we will see it as one.

histioy
view your history command
history -c :clean all history command
histoty -d +number :delete the number of the history command
!+numer: execute corresponding command
!!: execute the latest command
!+”CHARACTER”: exrcute latest start with “CHARACTER”
yum series
yum install pagename (-y) :install package name not need interactive
-y: allow all operate
yum groupinstall “Devolopment Tools” : install page groups, and pagegroup name must use “”
yum grouplist : view how many package your system has installed and available

yum update or yum upgrade: update you system to the newest version
SELinux
SELinux has three status :
1、 enforce(default) must to do some operation
2、 permissive permit to do some operation but give warning
3、 disabled : don’t manage operation
But we don’t use it in server, so we will close it.
update the /etc/selinux/config can change its setting,but this operation need to reboot
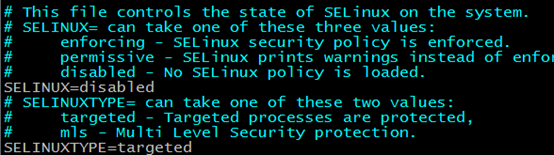
getenforce :view current SELinux status
setenforce set the status of SELinux and not neeed reboot

In this situation: Your server is running ,but you can’t reboot it and you want
to close SELiux, how to do it?
1、 update the /etc/seliunx/config SELINUX=disabled
2、 enforence 0 :change current SELinux status to permissive
So when the next time your system reboot, your SELinux will change to disabled
This is perfect ways!
runlevel & init
runlevel:view you system run level
init +number : switch you system level
If your want more, reference Homework: Linux seven pattern of start
chkconfig
chkconfig:update and queries runlevel information for system service
chkconfig --list:list all system levels service
chkconfig --del +name delete the system service
chkconfig --add +name add service on system
chkconfig --level RUN_LEVEN SERVICE_NAME ON/OFF :set service on RUN_LEVEL that you set
chkconfig SERVICE_NAME ON/OFF :set SERVICE_NAME ON/OFF on all run_level except for 0 and 6;
You also can User setup--system-servide or User the command “ntsysv” to open system_service windows
reload or restart
SSH SERVICE:if you update the /etc/ssh/sshd_config, and want it available, you can user this command to reload the file “/etc/init.d/sshd reload”.And use this command “/etc/init.d/sshd restart” to restart sshd service
Open/Close the firewall:
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
/etc/init.d/iptables stop
netstat & lsof
netstat:Print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, multicast memberships
-l --listen
-n --numeric
-t --tcp
-u --udp
-p --program
So we always to use the five params together

-a -all
We also user -an together
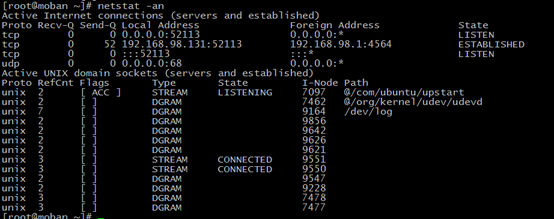
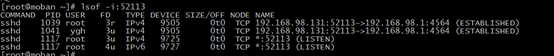
losf --list open file
-i: This option selects the listing of files any of whose Internet address matches the address specified in i. If no address is specified, this option selects the listing of all Internet and x.25 (HP-UX) net-
work files.
we also use the command “lsof -i:52113” to view the port:52113 status
which
which: show the full path of (shell) commands
for example:
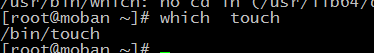
PATH
we use the command or shell ,but what does the system to search the command and execute it. This is PATH, is a environmental parameter

you command directory in PATH, you can use it in Terminal or shell.
you can use “PATH=$PATH:/root/oldboy” to add your path,but is temporary ,if you want to save it forever, to add it in /etc/profile. and,
if you want user the command on you own, you can add it at ~/.bashrc or /home/.bash_profile
il8n
if you want to change you character coding ,you change it in /etc/sysconfig/i18n
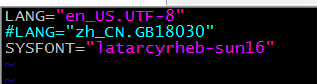
you need to use the command “souce /etc/sysconfig/i18n” ,it will change in you system now,or it will change an next reboot
you also can user LANG=CH to change it temporary.
you can user “locale” to view the character coding specific information.

chattr && lsattr
chattr +i +filename can give a file a limits that don’t do any operate to it
lsattr +filename view the special limits about a file
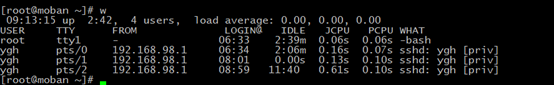
whomi && w
whoami: print effective userid

w - Show who is logged on and what are they doing
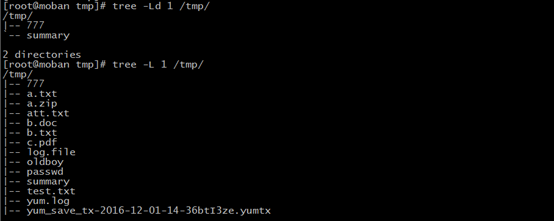
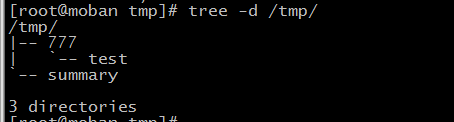
tree
tree: list contents of directories in a tree-like format
-L:--level +number show the depth of directories
-d: list directories only
examples:
file
file:determin file type
1、 view file type
file +filenamePath
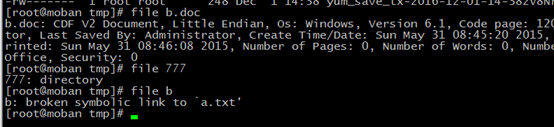
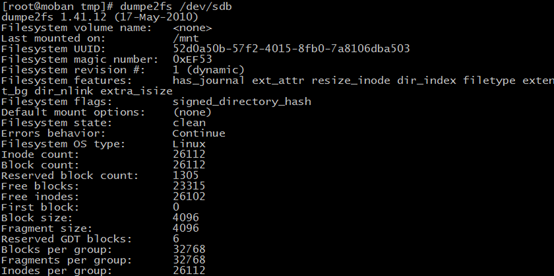
dumpe2fs
dumpe2fs:dump ext2/ext3/ext4 filesystem information
for example:
tar
-c --create
create a new archive
-x --extract,--get
extract files from a archive
-t --list
list the contents of an archive
-v --verbose
verbosely list files processed
-f --file=ARCHIVE
user archive file or device file
-C --directory=DIR
change directory to DIR
-z --gzip
filter the archive through gzip.
-j --bgzip2
filter the archive through bgzip2
so we also use those commands
zip:
tar -zcvf ARCHIVE.tar.gz SOURCE
create archive from files foo and bar through zip
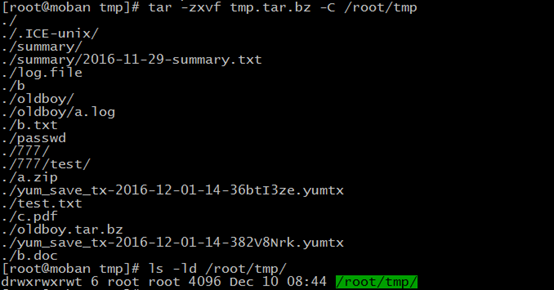
tar -zxvf ARCHIVE.tar.bz (-C DIRECTORY)
extract all files from archive.tar through zip
tar -ztvf ARCHIVE.tar
list all files in ARCHIVE.tar verbosely through zip
bgzip2
tar -jcvf ARCHIVE.tar.gz SOURCE
create an archive from files foo and bar through bgzip2
tar -jxvf ARCHIVE.tar (-C DIRECTORY)
extract all files from archive.tar through bgzip2
tar -ztvf ARCHIVE.tar
list all files in ARCHIVE.tar verbosely through bgzip2
examples:
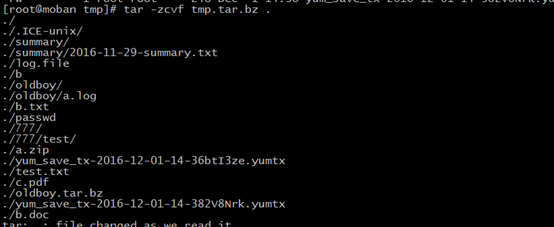
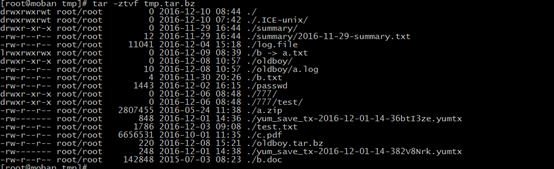
cut
cut remove sections from each line of files, default “ ”
-c --character=LIST
select only these characters
-d --delimiter=DELIM
use DELIM instead of TAB for field delimiter
-f --field
select only these field; also print any line that contains no delimiter character, unless the -s option is specified
-s, --only-delimited
do not print lines not containing delimiters
for example:
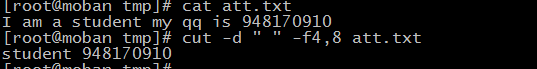
what to do get your ip address by using “cut”

wc
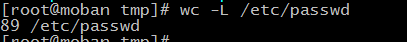
wc print newline, word, and byte counts for each files
-L --max-line-length
print the length of the longest line
ln
ln make links between files
-s --symbolic
make symbolic instead of hard links
hard link:
ln SOURCE_FILE HARD_FILE_LINK
symbolic link
ln -s SOURCE_FILE SYMBOLIC_LINK_FILE
mkfs
mkfs: build a Linux file system
for example:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb
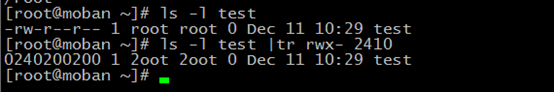
tr
tr --translate or delete characters
for example:
date
date --print or set system date or time
-s --set=STRING
set time described by STRING
%F --full-date; same as %Y-%m-%d
%Y year
%y last two digits of year
%m month (01..12)
%d day of month
%H hour(00..23)
%M minute(00..59)
%S second(00..60)
%w day of week(0..6) 0 is Sunday
%u day of week(1..7) 1 is Monday
%T time same as %H:%M:%S
special characters
.: current directory
.. : parent directory
- cd - : back the directory you open latest
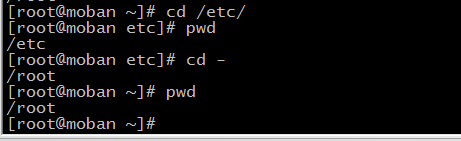
>> && > && << && <
standard (stdin) input: code: 0 <<(0) or <(0)
standard output (stdout) code 1 (1)>> or (1)>
standard error (stderr) code 2 2>> or 2>
2>&1:let let stderr redirect to stdout
for example
`command`: let the command to execute
~:cd ~ redirect home directory
{}:
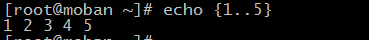
; the separator about many commands
/:root or path deperator
^: startwith character
$: endwith character
^$:blank line
Hotkeys:
Tab: complement command
Ctrl+C stop current process in the front
在CRT中
Ctrl+Shift+C copy
Ctrl+Shift+V paste
Ctrl+d: exit or quit
Ctrl+a: move to the first of current line
Ctrl+e: move to the end of current line
Ctrl+u :delete current line
Cthr+r search command in your history
Ctrl+l clean screen