https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV184411Q7Ng?p=73

数据集介绍:


1.设计占位符:
注解:
- [None, 784] 样本数据量未知。[None, 10] 每个样本都有10个类别的概率。
2.设计网络结构:




注解:
- 最后一层全连接层,[7,7,64]要变成一个二维的矩阵,[7*7*64],就是说用这么多的特征数量和10个神经元进行全连接。再经过sigmoid函数的作用,变成10个概率值。
""" 用单层神经网络实现手写数字识别 def conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=True, data_format="NHWC", dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None): Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors. 参数说明: Given an input tensor of shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]` and a filter / kernel tensor of shape `[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`, this op performs the following: 1. Flattens the filter to a 2-D matrix with shape `[filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels]`. 2. Extracts image patches from the input tensor to form a *virtual* tensor of shape `[batch, out_height, out_width, filter_height * filter_width * in_channels]`. 3. For each patch, right-multiplies the filter matrix and the image patch vector. """ import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #FLAGS=tf.app.flags.FlAGS #tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("is_train",1,"指定程序是预测还是训练") #is_train=1 #is_train的值设为1,代表是训练 is_train=0 #is_train的值设为0,代表是训练之后的预测 def full_connected(): mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("./data/mnist/input_data/",one_hot=True) #建立数据的占位符, x [None,784] y_true [None,10] with tf.variable_scope("data"): x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784]) y_true=tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[None,10]) #2、建立一个全连接层的神经网络w [784,10] b [10] with tf.variable_scope("fc_model"): # 随机初始化权重和偏置 weight=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784,10],mean=0.0,stddev=1.0,name='w')) bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[10])) #预测None个样本的输出结果[None, 784]*[784,10]+[10]=[None,10] y_predict=tf.matmul(x,weight)+bias #3、求出所有样本的损失 with tf.variable_scope("soft_cross"): #求平均的交叉熵损失 loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict)) #4、梯度下降求损失 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): train_op=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #5、计算准确率 with tf.variable_scope("acc"): equal_list=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_true,1),tf.argmax(y_predict,1)) #equal_list is None个样本 [1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0...] accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32)) # 收集变量,单个数字值的收集 tf.summary.scalar("losses",loss)#收集损失 tf.summary.scalar("acc",accuracy)#收集准确率 # 高维度变量收集 tf.summary.histogram("weightes",weight) tf.summary.histogram("biases",bias) # 定义一个初始化的变量op init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer() # 定义一个合并变量的op merged=tf.summary.merge_all() # 创建一个saver saver=tf.train.Saver() #开启会话去训练 with tf.Session() as sess: #初始化变量 sess.run(init_op) #建立events文件,然后写入 filewriter=tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary/test/",graph=sess.graph) if is_train==1: #迭代步数去训练,更新参数进行预测 for i in range(2000): #取出样本的特征值和目标值 mnist_x,mnist_y=mnist.train.next_batch(50) #运行train_op训练 sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}) # 写入每步训练的值 summary=sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}) filewriter.add_summary(summary,i) print("训练第%d步,准确率为:%f"%(i,sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}))) #保存模型 saver.save(sess,"./tmp/ckpt/fc_model") else: # 加载模型,主要是加载训练之后保存在模型中的weight和bias saver.restore(sess,"./tmp/ckpt/fc_model") # 如果是0,做预测 for i in range(100): # 每次测试一张图片 x_test,y_test=mnist.test.next_batch(1) print("第%d张图片,手写数字图片目标是:%d,预测结果是:%d"%( i, tf.argmax(y_test,1).eval(), tf.argmax(sess.run(y_predict,feed_dict={x:x_test,y_true:y_test}),1).eval() )) return None def weight_variables(shape): """ 自定义一个随机初始化权重的函数 因为w是要迭代更新的,所以它要定义成一个tf的变量 """ w=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=shape,mean=0.0,stddev=1.0)) return w def bias_variables(shape): """ 自定义一个随机初始化偏置的函数 """ b=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=shape)) return b def model(): """ 自定义一个卷积模型 :return: """ """ 1、准备数据的占位符 """ # 1、准备数据的占位符, x [None,784] y_true [None,10] with tf.variable_scope("data"): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, 10]) """ 2、卷积层1,卷积:核->5*5*1,strides=1,padding="SAME" 激活,tf.nn.relu、池化 """ with tf.variable_scope("conv1"): #要有一些随机初始化的权重w和偏置bias # 随机初始化权重 w_conv1=weight_variables([5,5,1,32]) # 随机初始化bias,有多少个filter,就有多少个bias b_conv1=bias_variables([32]) #因为tf.nn.conv2d()的第一个参数是:[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels] #所以需要把输入数据改成张量 [None,784]->[None,28,28,1] x_reshape=tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) #当不知道有多少样本的时候,此处不能填写None,要填写-1 # 卷积:[None,28,28,1]->[None,28,28,32] conv1=tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape,w_conv1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv1 x_relu1=tf.nn.relu(conv1)# 卷积后使之经过激活函数 # 池化 pooling,2*2,strides=2 [None,28,28,32]->[None,14,14,32] x_pool1=tf.nn.max_pool(x_relu1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME") """ 2、卷积层2,卷积核->5*5*32,filter=64,strides=1,padding="SAME" 激活,tf.nn.relu、池化 注意:每一张图像的通道数此时变成了32 卷积核此时应是:5*5*32,因为一个人要观察32张图,共有64个人观察 """ with tf.variable_scope("conv2"): # 要有一些随机初始化的权重w和偏置bias # 随机初始化权重 w_conv2 = weight_variables([5, 5, 32, 64]) # 随机初始化bias,有多少个filter,就有多少个bias b_conv2 = bias_variables([64]) # 卷积,激活,池化计算:[None,14,14,32]->[None,14,14,64] conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(x_pool1, w_conv2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b_conv2 x_relu2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2) # 卷积后使之经过激活函数 # 池化 pooling,2*2,strides=2 [None,14,14,64]->[None,7,7,64] x_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(x_relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding="SAME") """ 4、全连接层 [None,7,7,64]->[None,7*7*64]*[7*7*64(权重数),10]+[10]=[None,10] """ with tf.variable_scope("full_connected"): #随机初始化权重和偏置 w_fc=weight_variables([7*7*64,10]) b_fc=bias_variables([10]) #进行矩阵运算得出每个样本的10个结果 # 进行矩阵运算之前,修改形状:4维张量到2维矩阵 # [None,7,7,64]->[None,7*7*64] x_pool2_reshape = tf.reshape(x_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) #-1代表不知道多少个样本,每个样本都是7*7*64个特征 y_predict=tf.matmul(x_pool2_reshape,w_fc)+b_fc return x,y_true,y_predict def conv_fc(): # 获取真实的数据 mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("./data/mnist/input_data/",one_hot=True) x,y_true,y_predict=model() #进行交叉熵损失的计算 #求出所有样本的损失,然后求平均值 #3、求出所有样本的损失 with tf.variable_scope("soft_cross"): #求平均的交叉熵损失 loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict)) #4、梯度下降求损失 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): train_op=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #5、计算准确率 with tf.variable_scope("acc"): equal_list=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_true,1),tf.argmax(y_predict,1)) #equal_list is None个样本 [1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0...] accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32)) # 定义一个初始化的变量op init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer() #开启会话运行程序 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) #进行变量初始化 #循环去训练 # 迭代步数去训练,更新参数进行预测 for i in range(1000): # 取出样本的特征值和目标值 mnist_x, mnist_y = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # 运行train_op训练 sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={ x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}) print("训练第%d步,准确率为:%f"%(i,sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}))) if __name__ == '__main__': conv_fc()
运行结果:
训练第0步,准确率为:0.200000
训练第1步,准确率为:0.200000
训练第2步,准确率为:0.160000
训练第3步,准确率为:0.060000
训练第4步,准确率为:0.120000
训练第5步,准确率为:0.100000
训练第6步,准确率为:0.200000
训练第7步,准确率为:0.140000
.
.
.
训练第995步,准确率为:0.100000
训练第996步,准确率为:0.100000
训练第997步,准确率为:0.080000
训练第998步,准确率为:0.140000
训练第999步,准确率为:0.120000
这样收敛过慢的结果,原因考虑学习率太大。
""" 用单层神经网络实现手写数字识别 def conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=True, data_format="NHWC", dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None): Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors. 参数说明: Given an input tensor of shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]` and a filter / kernel tensor of shape `[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`, this op performs the following: 1. Flattens the filter to a 2-D matrix with shape `[filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels]`. 2. Extracts image patches from the input tensor to form a *virtual* tensor of shape `[batch, out_height, out_width, filter_height * filter_width * in_channels]`. 3. For each patch, right-multiplies the filter matrix and the image patch vector. """ import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data #FLAGS=tf.app.flags.FlAGS #tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer("is_train",1,"指定程序是预测还是训练") #is_train=1 #is_train的值设为1,代表是训练 is_train=0 #is_train的值设为0,代表是训练之后的预测 def full_connected(): mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("./data/mnist/input_data/",one_hot=True) #建立数据的占位符, x [None,784] y_true [None,10] with tf.variable_scope("data"): x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784]) y_true=tf.placeholder(tf.int32,[None,10]) #2、建立一个全连接层的神经网络w [784,10] b [10] with tf.variable_scope("fc_model"): # 随机初始化权重和偏置 weight=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([784,10],mean=0.0,stddev=1.0,name='w')) bias=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=[10])) #预测None个样本的输出结果[None, 784]*[784,10]+[10]=[None,10] y_predict=tf.matmul(x,weight)+bias #3、求出所有样本的损失 with tf.variable_scope("soft_cross"): #求平均的交叉熵损失 loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict)) #4、梯度下降求损失 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): train_op=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss) #5、计算准确率 with tf.variable_scope("acc"): equal_list=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_true,1),tf.argmax(y_predict,1)) #equal_list is None个样本 [1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0...] accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32)) # 收集变量,单个数字值的收集 tf.summary.scalar("losses",loss)#收集损失 tf.summary.scalar("acc",accuracy)#收集准确率 # 高维度变量收集 tf.summary.histogram("weightes",weight) tf.summary.histogram("biases",bias) # 定义一个初始化的变量op init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer() # 定义一个合并变量的op merged=tf.summary.merge_all() # 创建一个saver saver=tf.train.Saver() #开启会话去训练 with tf.Session() as sess: #初始化变量 sess.run(init_op) #建立events文件,然后写入 filewriter=tf.summary.FileWriter("./tmp/summary/test/",graph=sess.graph) if is_train==1: #迭代步数去训练,更新参数进行预测 for i in range(2000): #取出样本的特征值和目标值 mnist_x,mnist_y=mnist.train.next_batch(50) #运行train_op训练 sess.run(train_op,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}) # 写入每步训练的值 summary=sess.run(merged,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}) filewriter.add_summary(summary,i) print("训练第%d步,准确率为:%f"%(i,sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}))) #保存模型 saver.save(sess,"./tmp/ckpt/fc_model") else: # 加载模型,主要是加载训练之后保存在模型中的weight和bias saver.restore(sess,"./tmp/ckpt/fc_model") # 如果是0,做预测 for i in range(100): # 每次测试一张图片 x_test,y_test=mnist.test.next_batch(1) print("第%d张图片,手写数字图片目标是:%d,预测结果是:%d"%( i, tf.argmax(y_test,1).eval(), tf.argmax(sess.run(y_predict,feed_dict={x:x_test,y_true:y_test}),1).eval() )) return None def weight_variables(shape): """ 自定义一个随机初始化权重的函数 因为w是要迭代更新的,所以它要定义成一个tf的变量 """ w=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=shape,mean=0.0,stddev=1.0)) return w def bias_variables(shape): """ 自定义一个随机初始化偏置的函数 """ b=tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0,shape=shape)) return b def model(): """ 自定义一个卷积模型 :return: """ """ 1、准备数据的占位符 """ # 1、准备数据的占位符, x [None,784] y_true [None,10] with tf.variable_scope("data"): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) y_true = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, 10]) """ 2、卷积层1,卷积:核->5*5*1,strides=1,padding="SAME" 激活,tf.nn.relu、池化 """ with tf.variable_scope("conv1"): #要有一些随机初始化的权重w和偏置bias # 随机初始化权重 w_conv1=weight_variables([5,5,1,32]) # 随机初始化bias,有多少个filter,就有多少个bias b_conv1=bias_variables([32]) #因为tf.nn.conv2d()的第一个参数是:[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels] #所以需要把输入数据改成张量 [None,784]->[None,28,28,1] x_reshape=tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) #当不知道有多少样本的时候,此处不能填写None,要填写-1 # 卷积:[None,28,28,1]->[None,28,28,32] conv1=tf.nn.conv2d(x_reshape,w_conv1,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding="SAME")+b_conv1 x_relu1=tf.nn.relu(conv1)# 卷积后使之经过激活函数 # 池化 pooling,2*2,strides=2 [None,28,28,32]->[None,14,14,32] x_pool1=tf.nn.max_pool(x_relu1,ksize=[1,2,2,1],strides=[1,2,2,1],padding="SAME") """ 2、卷积层2,卷积核->5*5*32,filter=64,strides=1,padding="SAME" 激活,tf.nn.relu、池化 注意:每一张图像的通道数此时变成了32 卷积核此时应是:5*5*32,因为一个人要观察32张图,共有64个人观察 """ with tf.variable_scope("conv2"): # 要有一些随机初始化的权重w和偏置bias # 随机初始化权重 w_conv2 = weight_variables([5, 5, 32, 64]) # 随机初始化bias,有多少个filter,就有多少个bias b_conv2 = bias_variables([64]) # 卷积,激活,池化计算:[None,14,14,32]->[None,14,14,64] conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(x_pool1, w_conv2, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding="SAME") + b_conv2 x_relu2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2) # 卷积后使之经过激活函数 # 池化 pooling,2*2,strides=2 [None,14,14,64]->[None,7,7,64] x_pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(x_relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1,2,2,1], padding="SAME") """ 4、全连接层 [None,7,7,64]->[None,7*7*64]*[7*7*64(权重数),10]+[10]=[None,10] """ with tf.variable_scope("full_connected"): #随机初始化权重和偏置 w_fc=weight_variables([7*7*64,10]) b_fc=bias_variables([10]) #进行矩阵运算得出每个样本的10个结果 # 进行矩阵运算之前,修改形状:4维张量到2维矩阵 # [None,7,7,64]->[None,7*7*64] x_pool2_reshape = tf.reshape(x_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64]) #-1代表不知道多少个样本,每个样本都是7*7*64个特征 y_predict=tf.matmul(x_pool2_reshape,w_fc)+b_fc return x,y_true,y_predict def conv_fc(): # 获取真实的数据 mnist=input_data.read_data_sets("./data/mnist/input_data/",one_hot=True) x,y_true,y_predict=model() #进行交叉熵损失的计算 #求出所有样本的损失,然后求平均值 #3、求出所有样本的损失 with tf.variable_scope("soft_cross"): #求平均的交叉熵损失 loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_true,logits=y_predict)) #4、梯度下降求损失 with tf.variable_scope("optimizer"): train_op=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.0001).minimize(loss) #5、计算准确率 with tf.variable_scope("acc"): equal_list=tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_true,1),tf.argmax(y_predict,1)) #equal_list is None个样本 [1,0,1,1,0,0,0,1,1,0...] accuracy=tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(equal_list,tf.float32)) # 定义一个初始化的变量op init_op=tf.global_variables_initializer() #开启会话运行程序 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) #进行变量初始化 #循环去训练 # 迭代步数去训练,更新参数进行预测 for i in range(2000): # 取出样本的特征值和目标值 mnist_x, mnist_y = mnist.train.next_batch(50) # 运行train_op训练 sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={ x: mnist_x, y_true: mnist_y}) print("训练第%d步,准确率为:%f"%(i,sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist_x,y_true:mnist_y}))) if __name__ == '__main__': conv_fc()
学习率改成了0.0001,循环步数改成了2000次的运行结果是:
训练第0步,准确率为:0.080000
训练第1步,准确率为:0.160000
训练第2步,准确率为:0.100000
训练第3步,准确率为:0.180000
训练第4步,准确率为:0.180000
训练第5步,准确率为:0.120000
.
.
.
训练第1995步,准确率为:0.780000
训练第1996步,准确率为:0.800000
训练第1997步,准确率为:0.820000
训练第1998步,准确率为:0.780000
训练第1999步,准确率为:0.820000
注解:
- 准确率得到了明显的提升。
- 最后的一个全连接层的激活函数是softmax.
常见的网络结构:

注解:
- 杨乐昆写的。

注解:
- 参数数量6千万级别,一般的机器跑这个网络是跑不动的。
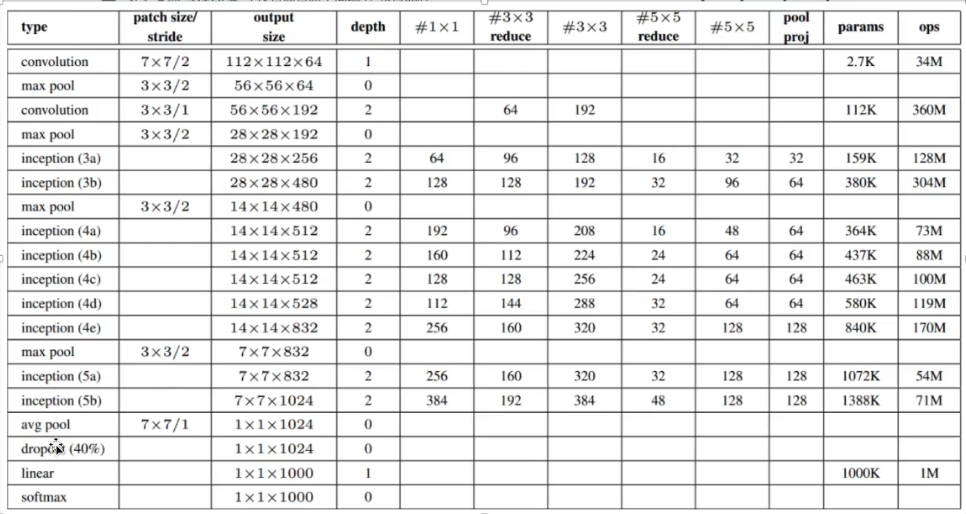
注解:
- 这个是googlenet网络。
- inception是特定的网络结构。
- 加入dropout是因为参数太多了,需要随机丢失一些,以减少计算量,最主要的目的还是降低过拟合。
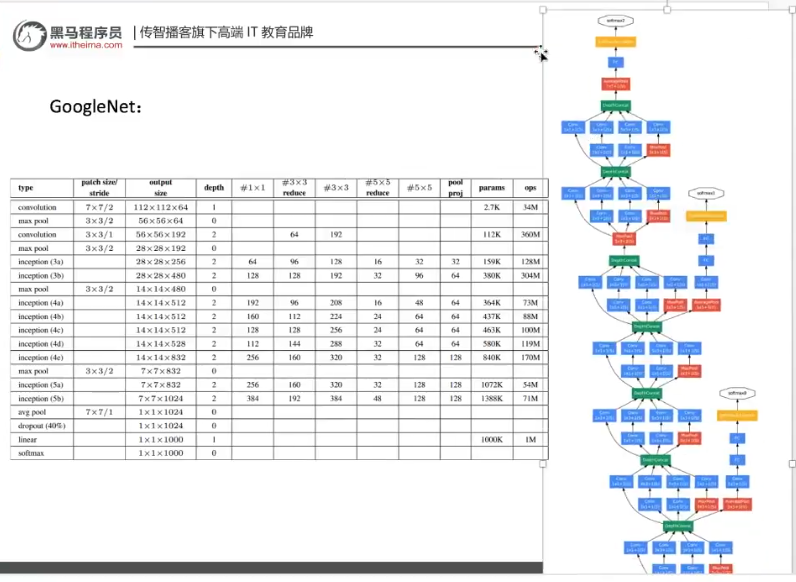
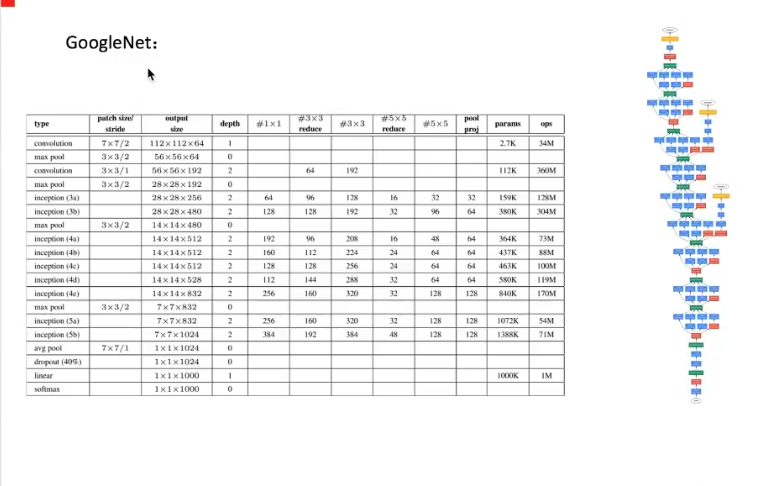

注解:
- tensorflow的库里面已经实现了googlenet的inception结构。
- 如果图片像素数量比较多,可以考虑使用inception结构。