参数校验放置位置:一般推荐与业务无关的放在Controller层中进行校验,而与业务有关的放在Service层中进行校验。如果项目中都在Controller层中进行的校验,则按照项目的规范要求参照进行校验即可。
1.1.常用的校验工具类
使用Hiberbate Validate
引入依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>4.3.1.Final</version> </dependency>
常用注解说明
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Length(min=,max=) | 检查所属的字段的长度是否在min和max之间,只能用于字符串 |
| @Range(min=,max=,message=) | 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
| @Max | 该字段的值只能小于或等于该值 |
| @Min | 该字段的值只能大于或等于该值 |
| @NotNull | 不能为null |
| @NotBlank | 不能为空,检查时会将空格忽略 |
| @NotEmpty | 不能为空,这里的空是指空字符串 |
| @Pattern(regex=,flag=) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
使用姿势
需要搭配在Controller中搭配@Validated或@Valid注解一起使用,@Validated和@Valid注解区别不是很大,一般情况下任选一个即可,区别如下:
| 注解 | @Validated | @Valid |
|---|---|---|
| 所属的包 | 属于org.springframework.validation.annotation包下的,是spring提供的 | 属于javax.validation包下,是jdk给提供的 |
| 是否支持分组和排序 | 是 | 否 |
虽然@Validated比@Valid更加强大,在@Valid之上提供了分组功能和验证排序功能,不过在实际项目中一直没有用到过 Hibernate-validate框架中的注解是需要加在实体中一起使用的
- 定义一个实体
public class DataSetSaveVO { //唯一标识符为空 @NotBlank(message = "user uuid is empty") //用户名称只能是字母和数字 @Pattern(regexp = "^[a-z0-9]+$", message = "user names can only be alphabetic and numeric") @Length(max = 48, message = "user uuid length over 48 byte") private String userUuid; //数据集名称只能是字母和数字 @Pattern(regexp = "^[A-Za-z0-9]+$", message = "data set names can only be letters and Numbers") //文件名称过长 @Length(max = 48, message = "file name too long") //文件名称为空 @NotBlank(message = "file name is empty") private String name; //数据集描述最多为256字节 @Length(max = 256, message = "data set description length over 256 byte") //数据集描述为空 @NotBlank(message = "data set description is null") private String description; }
说明:message字段为不符合校验规则时抛出的异常信息
- Controller层中的方法
@PostMapping public ResponseVO createDataSet(@Valid @RequestBody DataSetSaveVO dataSetVO) { return ResponseUtil.success(dataSetService.saveDataSet(dataSetVO)); }
说明:在校验的实体DataSetSaveVO旁边添加@Valid或@Validated注解
1.2.使用commons-lang3
引入依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId> <artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId> <version>3.4</version> </dependency>
常用方法说明
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| CollectionUtils.isEmpty | 判断集合是否为空,为null或者size==0,返回true |
| CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty | 判断集合是否为非空 |
| StringUtils.isEmpty | 判断字符串是否为空 |
| StringUtils.isNotEmpty | 判断字符串是否非空 |
| StringUtils.isBlank | 判断字符串是否为空,为null或者size==0或者只存在空白字符(如" "),则返回true |
| StringUtils.isNotBlank | 判断字符串是否为非空 |
测试代码
//StringUtils.isEmpty System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty("")); //true System.out.println(StringUtils.isEmpty(" ")); //false //StringUtils.isNotEmpty System.out.println(StringUtils.isNotEmpty("")); //false //StringUtils.isBlank System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank("")); //true System.out.println(StringUtils.isBlank(" ")); //true //StringUtils.isNotBlank System.out.println(StringUtils.isNotBlank(" ")); //false List<Integer> emptyList = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> nullList = null; List<Integer> notEmptyList = new ArrayList<>(); notEmptyList.add(1); //CollectionUtils.isEmpty System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(emptyList)); //true System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(nullList)); //true System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(notEmptyList)); //false //CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(emptyList)); //false System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(nullList)); //false System.out.println(CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(notEmptyList)); //true
1.3. Controller中统一异常拦截处理
以下是两个简单的在Controller中可以设置的异常捕获类,当代码在Service层中可以throw或者异常抛出的时候进行拦截处理:
@ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class) @ResponseBody public JsonResponse<Object> resloveConstraintViolationExcption(ConstraintViolationException ex, HttpServletResponse response){ Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> constraintViolations = ex.getConstraintViolations(); if(!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(constraintViolations)){ StringBuilder msgBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (ConstraintViolation<?> constraintViolation : constraintViolations) { msgBuilder.append(constraintViolation.getMessage()).append(","); } String errorMessage = msgBuilder.toString(); if(errorMessage.length() > 1){ errorMessage = errorMessage.substring(0, errorMessage.length()-1); } LOGGER.error("ConstranintViolationException:error{}", errorMessage); response.setStatus(JsonResponse.FAILED_STATUS); return new JsonResponse<>(JsonResponse.FAILED_STATUS, "请求参数有误:" + errorMessage); } LOGGER.error("ConstranintViolationException:error{}", ex.getMessage()); response.setStatus(JsonResponse.FAILED_STATUS); return new JsonResponse<>(JsonResponse.FAILED_STATUS, "请求参数有误:" + ex.getMessage()); } @ExceptionHandler(NumberFormatException.class) @ResponseBody public JsonResponse<Object> resolveNumberFormatException(NumberFormatException ex, HttpServletResponse response){ LOGGER.error("NumberFormatException:error{}", ex.getMessage()); response.setStatus(JsonResponse.FAILED_STATUS); return new JsonResponse<>(JsonResponse.FAILED_STATUS, "转换Number处理问题有误:" + ex.getMessage()); }
1.4.使用Validated与@Valid做参数校验
说明:java的JSR303声明了@Valid这类接口,而Hibernate-validator对其进行了实现。
注解位置:
@Validated:用在类、方法和方法参数上,但不能用于成员属性(fileld)上,会编译报错,嵌套校验必须使用@Valid一起加在成员属性上。
@Valid:可以用在方法、构造函数、方法参数和成员属性(field)上,用在类上面编译不报错,但是没用。
分组校验
@Validated:提供分组功能,可以在参数验证时,根据不同的分组采用不同的验证机制
@Valid:没有分组功能
@Getter @Setter public class RequestParam { @NotBlank(groups = {Insert.class}) private String paramInsert; @NotBlank(groups = {Update.class}) private String paramUpdate; private Order order; public interface Insert { } public interface Update { } }
请求Controller:
@RestController @RequestMapping("/param") @Validated public class ParamValidController { @PostMapping("/insert") public void insert(@RequestBody @Validated({RequestParam.Insert.class}) Order order){ } @PostMapping("/update") public void update(@RequestBody @Validated({RequestParam.Update.class}) Order order{} }
这样就可以实现对insert方法校验paramInsert,对update方法校验paramUpdate。
嵌套校验
@Getter @Setter public class RequestParam { @NotBlank(groups = {Insert.class}) private String paramInsert; @NotBlank(groups = {Update.class}) private String paramUpdate; @Valid @NotNull private Order order; public interface Insert { } public interface Update { } }
@Data public class Order { @NotBlank private String orderName; @Pattern(regexp = "[0-9A-Za-z]{5}", message = "设备编码必须符合数字与字母的规则") private Integer orderNo; }
一个待验证的pojo类,如果其中还包含了待验证的对象,需要在待验证对象上注解@Valid,才能验证待验证对象中的成员属性。
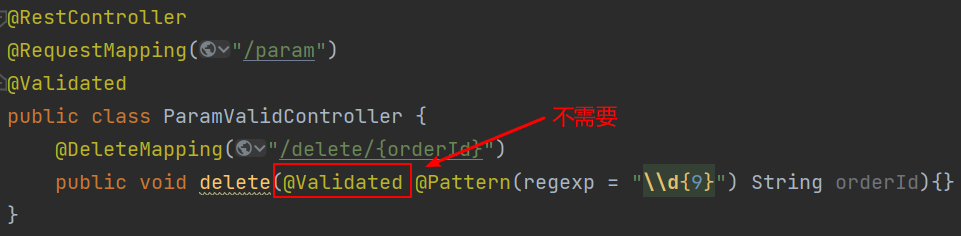
另外推荐两篇写的比较好的SpringBoot项目做参数校验的博文:
博文参考: