
【SpringBoot DB 系列】Mybatis 基于 AbstractRoutingDataSource 与 AOP 实现多数据源切换
前面一篇博文介绍了 Mybatis 多数据源的配置,简单来讲就是一个数据源一个配置指定,不同数据源的 Mapper 分开指定;本文将介绍另外一种方式,借助AbstractRoutingDataSource来实现动态切换数据源,并通过自定义注解方式 + AOP 来实现数据源的指定
I. 环境准备
1. 数据库相关
以 mysql 为例进行演示说明,因为需要多数据源,一个最简单的 case 就是一个物理库上多个逻辑库,本文是基于本机的 mysql 进行操作
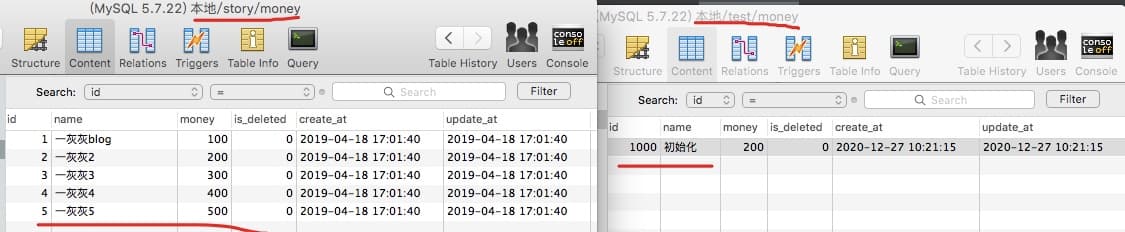
创建数据库test 与 story,两个库下都存在一个表money (同名同结构表,但是数据不同哦)
CREATE TABLE `money` (
`id` int(11) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户名',
`money` int(26) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '钱',
`is_deleted` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
`create_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_at` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
2. 项目环境
本项目借助SpringBoot 2.2.1.RELEASE + maven 3.5.3 + IDEA进行开发
下面是核心的pom.xml(源码可以再文末获取)
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置文件信息application.yml
# 数据库相关配置,请注意这个配置和之前一篇博文的不一致,后面会给出原因
spring:
dynamic:
datasource:
story:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/story?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password:
test:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password:
# 日志相关
logging:
level:
root: info
org:
springframework:
jdbc:
core: debug
II. 多数据源配置
强烈建议没有看上一篇博文的小伙伴,先看一下上篇博文 【DB 系列】Mybatis 多数据源配置与使用
在开始之前,先有必要回顾一下之前 Mybatis 多数据源配置的主要问题在哪里
- 多加一个数据源,需要多一份配置
- Mapper 文件需要分包处理,对开发人员而言这是个潜在的坑
针对上面这个,那我们想实现的目的也很清晰了,解决上面两个问题
1. AbstractRoutingDataSource
实现多数据源的关键,从名字上就可以看出,它就是用来路由具体的数据源的,其核心代码如
// 返回选中的数据源
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
Object lookupKey = this.determineCurrentLookupKey();
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
}
if (dataSource == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
} else {
return dataSource;
}
}
@Nullable
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
其中determineCurrentLookupKey需要我们自己来实现,到底返回哪个数据源
2. 动态数据源实现
我们创建一个DynamicDataSource继承自上面的抽象类
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
String dataBaseType = DSTypeContainer.getDataBaseType();
return dataBaseType;
}
}
注意上面的实现方法,怎样决定具体的返回数据源呢?
一个可考虑的方法是,在 Mapper 文件上添加一个注解@DS,里面指定对应的数据源,然后再执行时,通过它来确定具体需要执行的数据源;
因为上面的实现没有传参,因此我们考虑借助线程上下文的方式来传递信息
public class DSTypeContainer {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> TYPE = new ThreadLocal<String>();
public static String defaultType;
/**
* 往当前线程里设置数据源类型
*
* @param dataBase
*/
public static void setDataBaseType(String dataBase) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(dataBase)) {
dataBase = defaultType;
}
TYPE.set(dataBase);
System.err.println("[将当前数据源改为]:" + dataBase);
}
/**
* 获取数据源类型
*
* @return
*/
public static String getDataBaseType() {
String database = TYPE.get();
System.err.println("[获取当前数据源的类型为]:" + database);
return database;
}
/**
* 清空数据类型
*/
public static void clearDataBaseType() {
TYPE.remove();
}
}
3. 注解实现
上面虽然给出了数据源选择的策略,从线程上下文中获取DataBaseType,但是应该怎样向线程上下文中塞这个数据呢?
我们需要支持的方案必然是在 Sql 执行之前,先拦截它,写入这个DataBaseType,因此我们可以考虑在xxxMapper接口上,定义一个注解,然后拦截它的访问执行,在执行之前获取注解中指定的数据源写入上下文,在执行之后清楚上下文
一个最基础的数据源注解@DS
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface DS {
String value() default "";
}
注解拦截
@Aspect
@Component
public class DsAspect {
// 拦截类上有DS注解的方法调用
@Around("@within(DS)")
public Object dsAround(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
DS ds = (DS) proceedingJoinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringType().getAnnotation(DS.class);
try {
// 写入线程上下文,应该用哪个DB
DSTypeContainer.setDataBaseType(ds == null ? null : ds.value());
return proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
} finally {
// 清空上下文信息
DSTypeContainer.clearDataBaseType();
}
}
}
4. 注册配置
接下来就是比较关键的数据源配置了,我们现在需要注册DynamicDataSource,然后将他提供给SqlSessionFactory,在这里,我们希望解决即便多加数据源也不需要修改配置,所以我们调整了一下数据源的配置结构
spring:
dynamic:
datasource:
story:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/story?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password:
test:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password:
然后给出一个加载上面配置的配置类DSProperties
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.dynamic")
public class DSProperties {
private Map<String, DataSourceProperties> datasource;
}
然后我们的AutoConfiguration类的实现方式就相对明确了(建议对比上一篇博文中的配置类)
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DSProperties.class)
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"com.git.hui.boot.multi.datasource.mapper"},
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "SqlSessionFactory")
public class DynamicDataSourceConfig {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Bean(name = "dynamicDataSource")
public DynamicDataSource DataSource(DSProperties dsProperties) {
Map targetDataSource = new HashMap<>(8);
dsProperties.getDatasource().forEach((k, v) -> {
targetDataSource.put(k, v.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build());
});
DynamicDataSource dataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
dataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSource);
// 设置默认的数据库,下面这个赋值方式写法不太推荐,这里只是为了方便而已
DSTypeContainer.defaultType = (String) targetDataSource.keySet().stream().findFirst().get();
dataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(targetDataSource.get(DSTypeContainer.defaultType));
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory test1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dynamicDataSource") DataSource dynamicDataSource)
throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dynamicDataSource);
bean.setMapperLocations(
new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath*:mapping/*/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
}
5. 数据库实体类
项目结构图
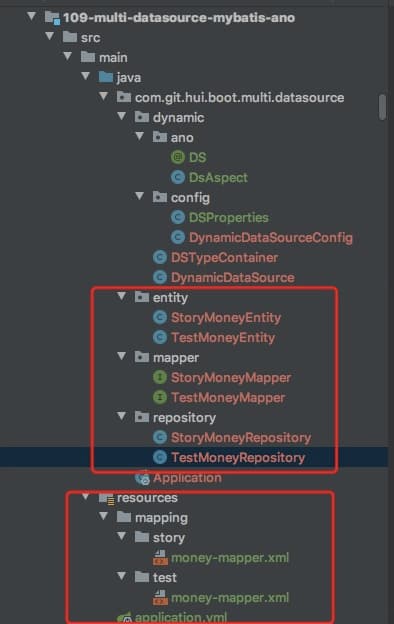
所有前面的东西属于通用配置相关,接下来给出具体的数据库操作相关实体类、Mapper 类
数据库实体类StoryMoneyEntity
@Data
public class StoryMoneyEntity {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Long money;
private Integer isDeleted;
private Timestamp createAt;
private Timestamp updateAt;
}
mapper 定义接口 StoryMoneyMapper + TestMoneyMapper
@DS(value = "story")
@Mapper
public interface StoryMoneyMapper {
List<StoryMoneyEntity> findByIds(List<Integer> ids);
}
@DS(value = "test")
@Mapper
public interface TestMoneyMapper {
List<TestMoneyEntity> findByIds(List<Integer> ids);
}
对应的 xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.git.hui.boot.multi.datasource.mapper.StoryMoneyMapper">
<resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.git.hui.boot.multi.datasource.entity.StoryMoneyEntity">
<id column="id" property="id" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="name" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="money" property="money" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="is_deleted" property="isDeleted" jdbcType="TINYINT"/>
<result column="create_at" property="createAt" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
<result column="update_at" property="updateAt" jdbcType="TIMESTAMP"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="money_po">
id, `name`, money, is_deleted, create_at, update_at
</sql>
<select id="findByIds" parameterType="list" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select
<include refid="money_po"/>
from money where id in
<foreach item="id" collection="list" separator="," open="(" close=")" index="">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
</mapper>
<!-- 省略第二个xml文件 内容基本一致-->
数据库操作封装类StoryMoneyRepository + TestMoneyRepository
@Repository
public class StoryMoneyRepository {
@Autowired
private StoryMoneyMapper storyMoneyMapper;
public void query() {
List<StoryMoneyEntity> list = storyMoneyMapper.findByIds(Arrays.asList(1, 1000));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
@Repository
public class TestMoneyRepository {
@Autowired
private TestMoneyMapper testMoneyMapper;
public void query() {
List<TestMoneyEntity> list = testMoneyMapper.findByIds(Arrays.asList(1, 1000));
System.out.println(list);
}
}
6. 测试
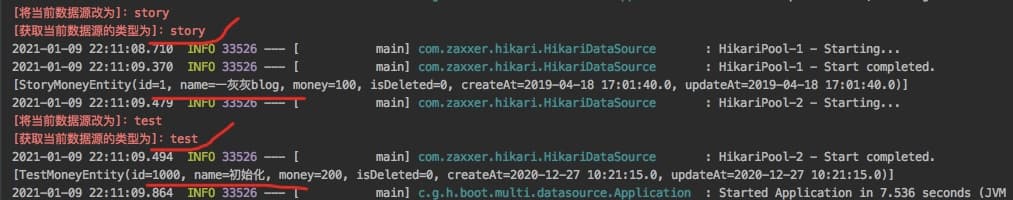
最后简单的测试下,动态数据源切换是否生效
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public Application(StoryMoneyRepository storyMoneyRepository, TestMoneyRepository testMoneyRepository) {
storyMoneyRepository.query();
testMoneyRepository.query();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}
输出日志如下
6.小结
本文主要给出了一种基于AbstractRoutingDataSource + AOP实现动态数据源切换的实现方式,使用了下面三个知识点
AbstractRoutingDataSource实现动态数据源切换- 自定义
@DS注解 + AOP 指定 Mapper 对应的数据源 ConfigurationProperties方式支持添加数据源无需修改配置
II. 其他
0. 项目
相关博文
- 【DB 系列】Mybatis 多数据源配置与使用
- 【DB 系列】JdbcTemplate 之多数据源配置与使用
- 【DB 系列】Mybatis-Plus 代码自动生成
- 【DB 系列】MybatisPlus 整合篇
- 【DB 系列】Mybatis+注解整合篇
- 【DB 系列】Mybatis+xml 整合篇
源码
- 工程:https://github.com/liuyueyi/spring-boot-demo
- 源码: https://github.com/liuyueyi/spring-boot-demo/tree/master/spring-boot/109-multi-datasource-mybatis
1. 一灰灰 Blog
尽信书则不如,以上内容,纯属一家之言,因个人能力有限,难免有疏漏和错误之处,如发现 bug 或者有更好的建议,欢迎批评指正,不吝感激
下面一灰灰的个人博客,记录所有学习和工作中的博文,欢迎大家前去逛逛
- 一灰灰 Blog 个人博客 https://blog.hhui.top
- 一灰灰 Blog-Spring 专题博客 http://spring.hhui.top
- 微信公众号: 一灰灰blog
