JDK和CGLib动态代理区别
JDK动态代理:利用拦截器(拦截器必须实现InvocationHanlder)加上反射机制生成一个实现代理接口的匿名类,
在调用具体方法前调用InvokeHandler来处理。
CGLib动态代理:利用ASM开源包,对代理对象类的class文件加载进来,通过修改其字节码生成子类来处理。
何时使用JDK和CGLib:
1)如果目标对象实现了接口,默认情况下会采用JDK的动态代理实现AOP。
2)如果目标对象实现了接口,可以强制使用CGLIB实现AOP。
3)如果目标对象没有实现了接口,必须采用CGLIB库,Spring会自动在JDK动态代理和CGLIB之间转换。
如何强制使用CGLib实现AOP:
1)添加CGLIB库(aspectjrt-xxx.jar、aspectjweaver-xxx.jar、cglib-nodep-xxx.jar)
2)在Spring配置文件中加入<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
JDK动态代理和CGLib字节码生成的区别:
1)JDK动态代理只能对实现了接口的类生成代理,而不能针对类。
2)CGLIB是针对类实现代理,主要是对指定的类生成一个子类,覆盖其中的方法,
并覆盖其中方法实现增强,但是因为采用的是继承,所以该类或方法最好不要声明成final,
对于final类或方法,是无法继承的。
)当Bean实现接口时,Spring就会用JDK的动态代理。
2)当Bean没有实现接口时,Spring使用CGlib是实现。
3)可以强制使用CGlib(在spring配置中加入<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>)
代码测试如下:
我们先创建一个接口及其类
//接口类 package com.zzj.math; public interface IMathService { int add(int a,int b); int div(int a,int b); } //及其类 package com.zzj.math; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class MathService implements IMathService{ @Override public int add(int a, int b) { return a+b; } @Override public int div(int a, int b) { return a/b; } }
再创建一个代理类:
package com.zzj.aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.Signature; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class MethodAop { @Before("execution(public int com.zzj.math.MathService.*(..))") public void before(JoinPoint jp){ Signature signature = jp.getSignature(); System.out.println("The "+signature.getName()+"method begins."); } }
spring中xml的配置:
<!--扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zzj"></context:component-scan> <!-- proxy-target-class为true时根据目标类来创建代理类,也就是CGlib代理,当不写或者为false时根据目标类接口来进行代理,也就是JDK代理 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="false"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
测试:
默认使用JDK代理,而且需要获取的bean必须是接口
package com.zzj.test; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import com.zzj.math.IMathService; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml"); IMathService mathService = applicationContext.getBean(IMathService.class); System.out.println(mathService.getClass()); applicationContext.close(); } }

当要强制使用CGLib时,我们将spring中xml的配置其对应标签属性改为true
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>)
测试类中获取的bean既可以是类也可以是接口,测试结果如下:

两种代理与目标类的关系
CGLib动态代理对象所产生的代理类是目标类的子类
System.out.println(mathService.getClass().getSuperclass());
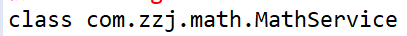
JDK动态代理产生而的代理类与目标类没有继承关系
Class clazz = mathService.getClass(); Class [] array = clazz.getInterfaces(); for(Class c: array){ System.out.println(c.getName()); }

<!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 启用事务注解 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> <!--AOP代理--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="false"></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
测试结果如下:
