传送门:
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1885
Key Task
Time Limit: 3000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 2654 Accepted Submission(s): 1143
Problem Description
The Czech Technical University is rather old — you already know that it celebrates 300 years of its existence in 2007. Some of the university buildings are old as well. And the navigation in old buildings can sometimes be a little bit tricky, because of strange long corridors that fork and join at absolutely unexpected places.
The result is that some first-graders have often di?culties finding the right way to their classes. Therefore, the Student Union has developed a computer game to help the students to practice their orientation skills. The goal of the game is to find the way out of a labyrinth. Your task is to write a verification software that solves this game.
The labyrinth is a 2-dimensional grid of squares, each square is either free or filled with a wall. Some of the free squares may contain doors or keys. There are four di?erent types of keys and doors: blue, yellow, red, and green. Each key can open only doors of the same color.
You can move between adjacent free squares vertically or horizontally, diagonal movement is not allowed. You may not go across walls and you cannot leave the labyrinth area. If a square contains a door, you may go there only if you have stepped on a square with an appropriate key before.
The result is that some first-graders have often di?culties finding the right way to their classes. Therefore, the Student Union has developed a computer game to help the students to practice their orientation skills. The goal of the game is to find the way out of a labyrinth. Your task is to write a verification software that solves this game.
The labyrinth is a 2-dimensional grid of squares, each square is either free or filled with a wall. Some of the free squares may contain doors or keys. There are four di?erent types of keys and doors: blue, yellow, red, and green. Each key can open only doors of the same color.
You can move between adjacent free squares vertically or horizontally, diagonal movement is not allowed. You may not go across walls and you cannot leave the labyrinth area. If a square contains a door, you may go there only if you have stepped on a square with an appropriate key before.
Input
The input consists of several maps. Each map begins with a line containing two integer numbers R and C (1 ≤ R, C ≤ 100) specifying the map size. Then there are R lines each containing C characters. Each character is one of the following:
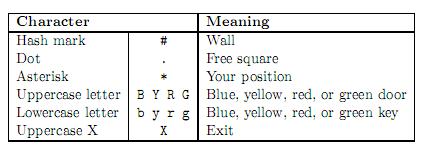
Note that it is allowed to have
You may assume that the marker of your position (“*”) will appear exactly once in every map.
There is one blank line after each map. The input is terminated by two zeros in place of the map size.

Note that it is allowed to have
- more than one exit,
- no exit at all,
- more doors and/or keys of the same color, and
- keys without corresponding doors and vice versa.
You may assume that the marker of your position (“*”) will appear exactly once in every map.
There is one blank line after each map. The input is terminated by two zeros in place of the map size.
Output
For each map, print one line containing the sentence “Escape possible in S steps.”, where S is the smallest possible number of step to reach any of the exits. If no exit can be reached, output the string “The poor student is trapped!” instead.
One step is defined as a movement between two adjacent cells. Grabbing a key or unlocking a door does not count as a step.
One step is defined as a movement between two adjacent cells. Grabbing a key or unlocking a door does not count as a step.
Sample Input
1 10
*........X
1 3
*#X
3 20
####################
#XY.gBr.*.Rb.G.GG.y#
####################
0 0
Sample Output
Escape possible in 9 steps.
The poor student is trapped!
Escape possible in 45 steps.
Source
Recommend
分析:
这道题和HDU1429是胜利大逃亡(续)是同一类型的题目,属于模板题,
但是这题需要注意的地方是*代表起点,X代表终点,可能有多个终点,还有就是X终点最好改为其他字符,不然会与门弄混淆,可以改为^
还有就是只有4把钥匙,所以三维数组开(1<<4)+10大小就可以了
太大了不行,会超内存所以我们改一下模板就可以了
具体的做法请参考这篇博客:
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define max_v 105 char G[max_v][max_v];//图 int dis[max_v][max_v][(1<<4)+10];//步数 int dir[4][2]= {{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0},{0,1}}; //方向数组 int n,m;//行,列,限定时间 int sx,sy;//起点 struct node { int x,y; int key; node(int a,int b,int c) { x=a; y=b; key=c; } }; inline int get_key(int key,int num)//返回新的钥匙集合 { //参数:元素的钥匙集合 活动钥匙的编号 return key|(1<<num); } inline bool has_key(int key,int num)//返回是否存在门的钥匙 { //参数:钥匙集合 门的编号 return (key&(1<<num))>0; } int bfs() { //初始化 queue<node> q; int step=-1; memset(dis,-1,sizeof(dis)); q.push(node(sx,sy,0)); dis[sx][sy][0]=0; while(!q.empty()) { int x=q.front().x; int y=q.front().y; int key=q.front().key; q.pop(); if(G[x][y]=='^') { step =dis[x][y][key]; return key; } for(int i=0; i<4; i++) { int xx=x+dir[i][0]; int yy=y+dir[i][1]; int kk=key; if(xx<0||xx>=n||yy<0||yy>=m||G[xx][yy]=='#')//越界和墙 continue; if(G[xx][yy]>='a'&&G[xx][yy]<='j')//遇到了钥匙 { kk=get_key(kk,G[xx][yy]-'a');//返回新的钥匙集合 } if(G[xx][yy]>='A'&&G[xx][yy]<='J')//遇到了门 { if(!has_key(kk,G[xx][yy]-'A'))//没有对应的钥匙 { continue; } } if(dis[xx][yy][kk]==-1) { dis[xx][yy][kk]=dis[x][y][key]+1;//步数加1 if(G[xx][yy]=='^')//放这里是因为路上有门的特殊性 { step = dis[xx][yy][kk]; return step; } q.push(node(xx,yy,kk)); } } } return step; } int main() { while(~scanf("%d %d",&n,&m)) { if(n==0&&m==0) break; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { for(int j=0; j<m; j++) { scanf(" %c",&G[i][j]); if(G[i][j]=='*') { sx=i;//起点 sy=j; } if(G[i][j]=='X') { G[i][j]='^'; } if(G[i][j]=='Y') { G[i][j]='A'; } if(G[i][j]=='R') { G[i][j]='C'; } if(G[i][j]=='G') { G[i][j]='D'; } if(G[i][j]=='y') { G[i][j]='a'; } if(G[i][j]=='r') { G[i][j]='c'; } if(G[i][j]=='g') { G[i][j]='d'; } } } int ans=bfs(); if(ans==-1) { printf("The poor student is trapped! "); } else { printf("Escape possible in %d steps. ",ans); } } return 0; }