Map Join实战案例
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.Map Join概述
使用场景 Map Join适用于一张表十分小、一张表很大的场景。 优点: 使用Map Join要比Reduce Join速度快的原因就是较少了Shuffle过程; 思考:在Reduce端处理过多的表,非常容易产生数据倾斜,怎么办? 在Map端缓存多张表,提前处理业务逻辑,这样增加Map端业务,减少Reduce端数据的压力,尽可能的减少数据倾斜。 具体办法:采用DistributedCache (1)在Mapper的setup阶段,将文件读取到缓存集合中。 (2)在驱动函数中加载缓存。
二.Map Join案例
1>.测试数据
参考连接: https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie2020/p/12783256.html
2>.实战案例代码

package cn.org.yinzhengjie.mapjoin; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import java.io.*; import java.net.URI; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class MapJoinMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable,Text,Text,NullWritable> { //定义字典用户缓存文件数据 private Map<String,String> pMap = new HashMap<>(); private Text k = new Text(); //在各个MapTask开始运行之前做的初始化操作,仅运行一次 @Override protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //获取到缓存文件列表 URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles(); //由于我们仅配置了一个缓存文件,因此默认取数组的第一个就可以拿到我们缓存的文件对象 String path = cacheFiles[0].getPath().toString(); //获取包装流 BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(path),"UTF-8")); String line; while (StringUtils.isNotEmpty((line = bufferedReader.readLine()))){ String[] fields = line.split(" "); pMap.put(fields[0],fields[1]); } //关闭流(释放资源) IOUtils.closeStream(bufferedReader); } @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] fields = value.toString().split(" "); //获取缓存数据 String pname = pMap.get(fields[1]); if (pname == null) { pname = "NULL"; } k.set(fields[0] + " " + pname + " " + fields[2]); context.write(k, NullWritable.get()); } }

package cn.org.yinzhengjie.mapjoin; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; public class MapJoinDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException, IOException { //获取一个Job实例 Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); //设置我们的当前Driver类路径(classpath) job.setJarByClass(MapJoinDriver.class); //设置自定义的Mapper类路径(classpath) job.setMapperClass(MapJoinMapper.class); //由于咱们使用的是Map Join,压根不需要使用Reduce,因此我们不设置Reducer的类路径(classpath),但需要显示设置Reduce Task的数量为0 job.setNumReduceTasks(0); //在驱动函数中加载缓存,缓存普通文件到Task运行节点。 job.addCacheFile(URI.create("file:///E:/yinzhengjie/MapJoin/cache/pd.txt")); //设置输入数据 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job,new Path(args[0])); //设置输出数据 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path(args[1])); //提交我们的Job,返回结果是一个布尔值 boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true); //如果程序运行成功就打印"Task executed successfully!!!" if(result){ System.out.println("Task executed successfully!!!"); }else { System.out.println("Task execution failed..."); } //如果程序是正常运行就返回0,否则就返回1 System.exit(result ? 0 : 1); } }
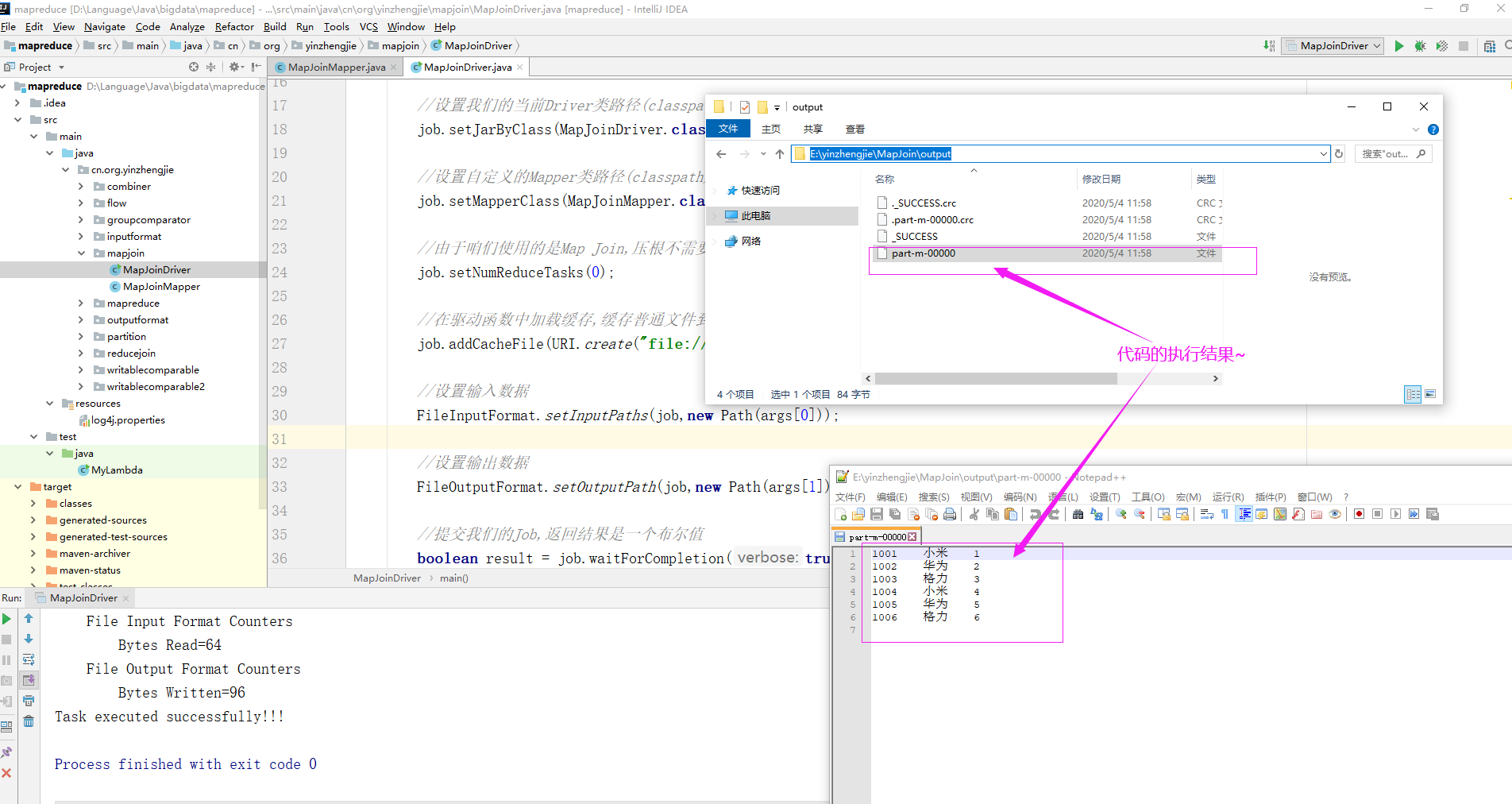
3>.运行MapJoinDriver.java代码
参数设置:E:yinzhengjieMapJoininput E:yinzhengjieMapJoinoutput