实验内容 1. 某计算机硬件系统,为了实现特定的功能,在某个子模块设计了 ABC 三款芯片用于 数字计算。各个芯片的计算功能如下: A 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的减法(m-n) B 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的乘法(m*n) C 芯片:计算两位整数的加法(m+n)、计算两位整数的除法(m/n) 为 ABC 三个芯片分别定义类,描述上述芯片的功能,并在 main 函数中测试这三个类。 (提示:利用类的继承和派生,抽象出共有属性和操作作为基类。)
解答:

下面给出该题目的一个cpp文件
代码:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Z{ 4 public: 5 void createZ(int x0,int y0); 6 void jia(); 7 private: 8 int m; 9 int n; 10 }; 11 void Z::createZ(int x0,int y0){ 12 m=x0; 13 n=y0; 14 } 15 void Z::jia(){ 16 cout<<"相加的结果:"<<m+n<<endl; 17 } 18 19 20 21 class A:public Z{ 22 public: 23 void createA(int x0,int y0); 24 void jian(); 25 private: 26 int m1; 27 int n1; 28 }; 29 void A::createA(int x0,int y0){ 30 createZ(x0,y0); 31 m1=x0; 32 n1=y0; 33 } 34 void A::jian(){ 35 cout<<"相减之后的答案:"<<m1-n1 <<endl; 36 } 37 class B:public Z{ 38 public: 39 void createB(int x0,int y0); 40 void cheng(); 41 private: 42 int m2; 43 int n2; 44 }; 45 void B::createB(int x0,int y0){ 46 createZ(x0,y0); 47 m2=x0; 48 n2=y0; 49 } 50 void B::cheng(){ 51 cout<<"相乘的结果:"<<m2*n2<<endl; //从A继承到B呢 52 } 53 class C:public Z{ 54 public: 55 void createC(int x0,int y0); 56 void chu(); 57 private: 58 int m3; 59 int n3; 60 }; 61 void C::createC(int x0,int y0){ 62 createZ(x0,y0); 63 m3=x0; 64 n3=y0; 65 } 66 void C::chu(){ 67 cout<<"相除的结果:"<<m3/n3<<endl; //从A继承到B呢 68 } 69 70 71 72 73 int main(){ 74 75 A a; 76 B b; 77 C c; 78 a.createA(3,2); 79 a.jia(); 80 a.jian(); 81 cout<<endl; 82 c.createC(8,9); 83 c.chu(); 84 c.jia(); 85 cout<<endl; 86 b.createB(10,2); 87 b.cheng(); 88 b.jia(); 89 90 91 return 0; 92 }
运行截图:

该题总结:
2. 定义一个车(vehicle)基类,具有数据成员 maxspeed, weight(均为 int 型), 函数 成员 run(), stop(),由此派生出自行车(bicycle)类、汽车(motorcar)类。其中, bicycle 类 新增数据成员高度(height), motorcar 类新增数据成员座位数(seatnum)属性。再从 bicycle
第 2 页/共 4 页
和 motorcar 派生出摩托车(motorcycle)类,并在主程序中测试这个类。(每个类都要求定 义构造函数和析构函数) (提示: ① 注意把 vehicle 设置为虚基类; ② run(), stop()函数体,通过输出字符串 run, stop 简单模拟。 )
解答:
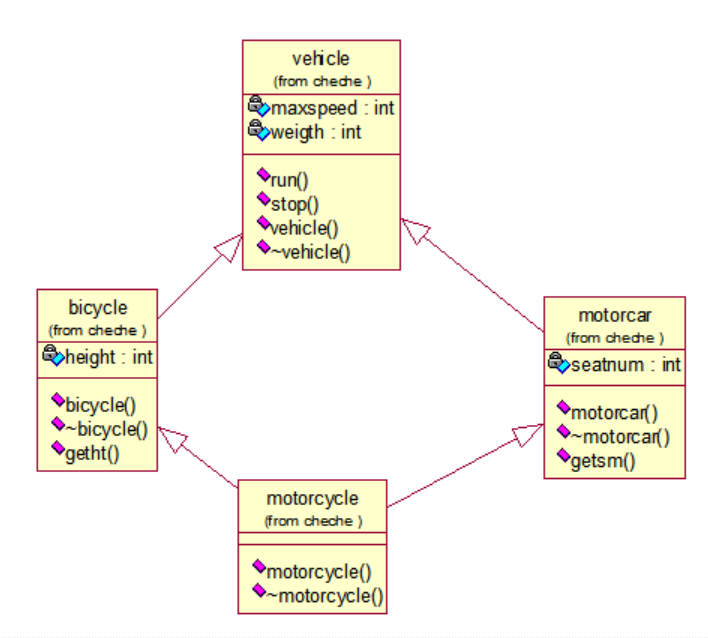
代码是一个cpp文件:
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class vehicle{ 4 public: 5 vehicle(int m,int w):maxspeed(m),weight(w){ 6 } 7 ~vehicle(){ 8 } 9 void run(){ 10 cout<<"正在启动中。"<<endl; 11 } 12 void stop(){ 13 cout<<"停下汽车!"<<endl; 14 } 15 16 private: 17 int maxspeed; 18 int weight ; 19 20 }; 21 class bicycle:virtual public vehicle{ 22 public: 23 bicycle(int w,int m,int h):vehicle(w,m),height(h){ 24 } 25 26 ~bicycle(){ 27 } 28 void getht(){ 29 cout<<"高度:"<<height<<endl; 30 } 31 private: 32 int height; 33 }; 34 class motorcar:virtual public vehicle{ 35 public: 36 motorcar(int w,int m,int s):vehicle(w,m),seatnum(s){ 37 } 38 ~motorcar(){ 39 } 40 void getsm(){ 41 cout<<"座位数量:"<<seatnum<<endl; 42 } 43 private: 44 int seatnum; 45 }; 46 class motorcycle:public bicycle,public motorcar{ 47 public: 48 motorcycle(int w,int m,int h,int s):vehicle(w,m),bicycle(w,m,h),motorcar(w,m,s){ 49 50 } 51 ~motorcycle(){ 52 } 53 }; 54 55 56 int main(){ 57 motorcycle m(30,20,2,7); 58 m.getht(); 59 m.getsm(); 60 m.run(); 61 m.stop(); 62 return 0; 63 } 64 //构造函数的写法是这个程序带给我的最大收获。 65 //派生类的构造函数需要写出基类的构造函数,并可以根据参数的不同来进行修改fuzhi
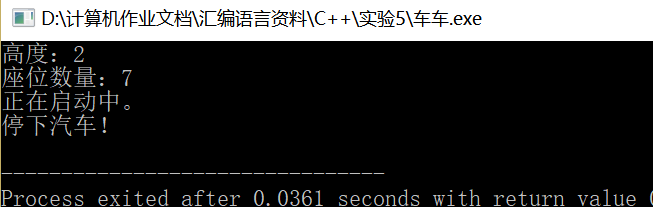
运行截图:
3. 基于「实验 4 类和对象-2」中设计并实现的类 Fraction,创建派生类 iFraction,用以 描述如下形式的分数:
要求: (1) 更新 Fraction 类 为 Fraction 类编写运算符+、-、*、/重载函数,实现在 main 函数中直接用+、-、 *、/进行 Fraction 类运算。 (2)设计并实现派生 iFraction 类 ① 为派生类 iFraction 定义构造函数,实现 iFraction 对象的初始化 ② 为派生类 iFraction 增加一个成员函数,用于在屏幕上显示 iFraction 对象 (3)设计一个普通函数 convertF()用于对 iFraction 类对象进行规范化处理。(*选做*)
(提示:把 convertF()设计为 Fraction 类和 iFraction 类的友元函数) 例如:(更多情形请自行考虑)
5/3
→ 1
2 /3
(4)以多文件结构方式编写(fraction.h, fraction.cpp, ifraction.h, ifraction.cpp, main.cpp)
解答:
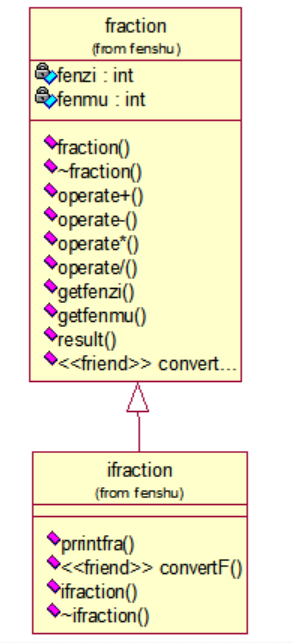
代码如下:
1.fraction.h
1 #ifndef FRACTION_H 2 #define FRACTION_H 3 class fraction{ 4 public: 5 fraction(int a=0,int b=1); 6 // fraction(fraction &f); 7 ~fraction(); 8 fraction operator+(const fraction &f2) const; 9 fraction operator-(const fraction &f2) const; 10 fraction operator*(const fraction &f2) const; 11 fraction operator/(const fraction &f2) const; 12 int getfenzi(); 13 int getfenmu(); 14 void result(); 15 friend void convertF(fraction &f); 16 private: 17 int fenzi; 18 int fenmu; 19 }; 20 21 #endif
2.fraction.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include"fraction.h" 3 using namespace std; 4 //构造函数 5 fraction::fraction(int a,int b):fenzi(a),fenmu(b){ 6 } 7 //fraction::fraction(fraction &f):fenzi(f.fenzi),fenmu(f.fenmu){ 8 //}为啥这里用复制构造函数反而使函数报错 9 10 // 析构函数 11 fraction::~fraction(){ 12 } 13 fraction fraction::operator+(const fraction &f2) const{ 14 if(fenmu==f2.fenmu) 15 { 16 return fraction(fenzi+f2.fenzi,fenmu); 17 } 18 else{ 19 return fraction(fenzi*f2.fenmu+fenmu*f2.fenzi,fenmu*f2.fenmu); 20 } 21 } 22 //运算符重载 23 fraction fraction::operator-(const fraction &f2) const{ 24 if(fenmu==f2.fenmu) 25 { 26 return fraction(fenzi-f2.fenzi,fenmu); 27 } 28 else{ 29 return fraction(fenzi*f2.fenmu-fenmu*f2.fenzi,fenmu*f2.fenmu); 30 } 31 } 32 fraction fraction::operator*(const fraction &f2) const{ 33 return fraction(fenzi*f2.fenzi,fenmu*f2.fenmu); 34 } 35 fraction fraction::operator/(const fraction &f2) const{ 36 return fraction(fenzi*f2.fenmu,fenmu*f2.fenzi); 37 } 38 //访问私有成员 39 int fraction::getfenmu(){ 40 return fenmu; 41 } 42 43 int fraction::getfenzi(){ 44 return fenzi; 45 } 46 //输出最后结果 47 void fraction::result(){ 48 cout<<fenzi<<"/"<<fenmu<<endl; 49 } 50 //友元函数规范化 51 //第一次出错因为在实现函数时也加进了友元标识 52 void convertF(fraction &f){ 53 54 int a,b,t; 55 a=f.getfenzi(); 56 b= f.getfenmu(); 57 if(a>=b){ 58 t=a/b; 59 while(a>b){ 60 a=a-b; 61 } 62 cout<<"分数应该化为:"<<t<<"+"<<a<<"/"<<b<<endl; 63 } 64 else cout<<"分数就是:"<<a<<"/"<<b<<endl; 65 66 }
3.ifraction.h
1 #ifndef ifraction_h 2 #define ifraction_h 3 #include"fraction.h" 4 class ifraction:public fraction { 5 public: 6 ifraction(int a=0,int b=1); 7 void printfra(); 8 ~ifraction(); 9 friend void convertF(ifraction &f); 10 }; 11 12 13 14 #endif
4.ifraction.cpp
1 #include"ifraction.h" 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void ifraction::printfra(){ 6 cout<<getfenzi()<<"/"<<getfenmu()<<endl; 7 } 8 9 ifraction::ifraction(int a,int b):fraction(a,b){ 10 } 11 12 ifraction::~ifraction(){ 13 } 14 15 void convertF(ifraction &f){ 16 17 int a,b,t; 18 a=f.getfenzi(); 19 b= f.getfenmu(); 20 if(a>=b){ 21 t=a/b; 22 while(a>b){ 23 a=a-b; 24 } 25 26 cout<<"分数应该化为:"<<t<<"+"<<a<<"/"<<b<<endl; 27 } 28 else cout<<"分数就是:"<<a<<"/"<<b<<endl; 29 30 }
5.main.cpp
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include"fraction.h" 4 #include"ifraction.h" 5 6 int main(){ 7 ifraction a(1,4),b(2,4),c(8,3); 8 //c=a+b;//测试了运算符重载,发现这里报错,为什么?是运算符重载不能继承吗? 9 //检查之后发现是虽然能重载,返回值的类型却是fraction类类型,比如一个函数原本是int 类型,继承之后也不会变成double吧 10 11 fraction d,e(1,3); 12 13 d=a+b; 14 cout<<"输出a+b="; 15 d.result(); 16 cout<<"输出a-b="; 17 d=a-b; 18 d.result(); 19 cout<<"输出a*b="; 20 d=a*b; 21 d.result(); 22 cout<<"输出a/b="; 23 d=a/b; 24 d.result(); 25 cout<<"输出ifraction的对象c:"; 26 c.printfra(); 27 convertF(e); 28 convertF(c); 29 return 0; 30 }
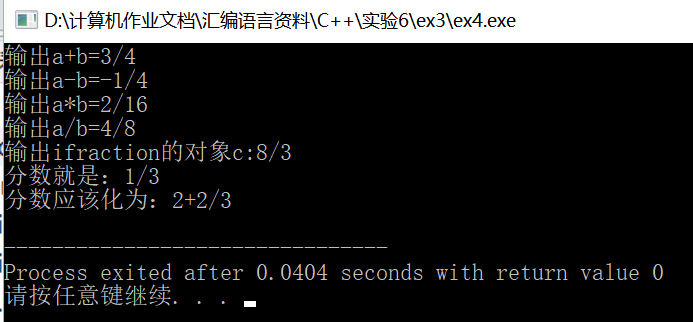
运行截图:
该实验总结:
运算符重载能不能被继承?修改过后的代码显示当然可以。是不是所有的运算符重载都能被继承?
查到赋值操作符的特殊,如下解释:
class widget
{
① widget& operator=( const widget& rhs ){} // 这个叫做赋值操作符
② widget& operator=( const int ) {} // 这个叫做赋值操作符重载
} ;
①. 赋值操作符属于类的复制控制的一部分(默构,复构,赋值,析构), 自己不定义,编译器会自动合成.它的正式叫法是(copy assignment operator),强调的是属于复制控制的一部分.
②. 赋值操作符重载和赋值操作符不一样,你不定义,编译器不会自动合成.
所以你要是问子类赋值操作符会不会继承父类,那肯定是不会的.
1. 如果 子类没定义赋值操作符, 那么 子类会自动合成赋值操作符, 子类在赋值的时候会自动调用父类的赋值操作符来完成基类部分的复制拷贝.
2. 如果 子类自己定义了赋值操作符, 那么 子类就不会继续自动合成, 仍然子类必须手动调用父类的赋值操作符来完成基类部分的赋值拷贝,否则会造成部分复制( partial copy assignment )
4. (***选做***) 基于提供的程序文件,补足并扩充程序,实现一个多类型玩家角色扮演游戏。 在本次实验附件包 ex4 中有如下文件: container.h, container.cpp, player.h, player.cpp, swordsman.h, swordsman.cpp, main.cpp (1)阅读源码,理解并补足程序,让程序运行生效。 其中,程序中出现有????????之处,是需要补足的部分。 (2)画出这个角色扮演游戏 UML 类图,尤其是类和类之间的关系 (3)设计并实现 archer 类和 mage 类。在 UML 类图中也加进这两个新类。 (4)修改 main 函数,随机生成不同角色的敌人,并保证程序正常运行。 (5)为游戏增加其它元素,完善游戏的可玩性、趣味性,等。 (说明:这道涉及虚函数、运行时多态。你可以在第 8 章学完后尝试编写,或者, 在尝试编写这道题的过程中,学习第 8 章虚函数和运行时多态的知识。 )
这道题待我计算完毕之后再行更新。。。