在上一篇jsf环境搭建的基础上 , 加入spring框架 , 先看下目录结构
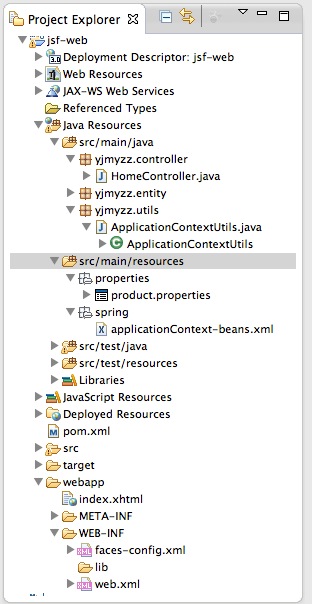
src/main/resources 这个source folder 放置web项目所需的主要配置,打包时,会自动打包到WEB-INF下
首先看下pom.xml,需要引入一些依赖项:

1 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 2 xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> 3 <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> 4 <groupId>yjmyzz</groupId> 5 <artifactId>jsf-web</artifactId> 6 <version>1.0</version> 7 <packaging>war</packaging> 8 9 10 <dependencies> 11 <!-- 单元测试 --> 12 <dependency> 13 <groupId>junit</groupId> 14 <artifactId>junit</artifactId> 15 <version>4.7</version> 16 <scope>test</scope> 17 </dependency> 18 19 <!-- jsf --> 20 <dependency> 21 <groupId>org.jboss.spec.javax.faces</groupId> 22 <artifactId>jboss-jsf-api_2.1_spec</artifactId> 23 <version>2.1.19.1.Final-redhat-1</version> 24 <scope>compile</scope> 25 </dependency> 26 27 28 <!-- spring --> 29 <dependency> 30 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 31 <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> 32 <version>4.0.2.RELEASE</version> 33 </dependency> 34 35 36 <dependency> 37 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 38 <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> 39 <version>4.0.2.RELEASE</version> 40 </dependency> 41 42 43 <!-- servlet支持 --> 44 <dependency> 45 <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> 46 <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> 47 <version>2.5</version> 48 </dependency> 49 50 </dependencies> 51 52 <build> 53 <plugins> 54 <plugin> 55 <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> 56 <version>3.1</version> 57 <configuration> 58 <source>1.7</source> 59 <target>1.7</target> 60 </configuration> 61 </plugin> 62 <plugin> 63 <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> 64 <version>2.3</version> 65 <configuration> 66 <warSourceDirectory>webapp</warSourceDirectory> 67 <failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml> 68 </configuration> 69 </plugin> 70 </plugins> 71 </build> 72 </project>
1. 自动加载配置文件
在web项目中,可以让spring自动加载配置文件(即上图中的src/main/resouces/spring下的xml文件),WEB-INF/web.xml中参考以下设置:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> 3 <display-name>jsf-web</display-name> 4 5 <welcome-file-list> 6 <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> 7 </welcome-file-list> 8 9 <listener> 10 <listener-class> 11 org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener 12 </listener-class> 13 </listener> 14 15 <context-param> 16 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 17 <param-value> 18 classpath*:spring/applicationContext-*.xml 19 </param-value> 20 </context-param> 21 22 </web-app>
解释一下: classpath*:spring/applicationContext-*.xml 这里表示将加载classpath路径下 spring目录下的所有以applicationContext-开头的xml文件 , 通常为了保持配置文件的清爽 , 我们会把配置分成多份 : 比如 applicationContext-db.xml 用来配置DataSource , applicationContext-cache.xml用来配置缓存...等等.
2.代码中如何取得ApplicationContext实例

1 package yjmyzz.utils; 2 3 import javax.faces.context.FacesContext; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 5 6 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 7 import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils; 8 9 public class ApplicationContextUtils { 10 11 public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() { 12 ServletContext context = (ServletContext) FacesContext 13 .getCurrentInstance().getExternalContext().getContext(); 14 ApplicationContext appctx = WebApplicationContextUtils 15 .getRequiredWebApplicationContext(context); 16 17 return appctx; 18 } 19 20 public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> t) { 21 return getApplicationContext().getBean(t); 22 } 23 }
有了这个工具类 , 就可以方便的取得注入的Bean
3. 使用properties文件注入
为了演示注入效果,先定义一个基本的Entity类

1 package yjmyzz.entity; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 public class ProductEntity implements Serializable { 6 7 private static final long serialVersionUID = -2055674628624266800L; 8 /* 9 * 产品编码 10 */ 11 private String productNo; 12 13 /** 14 * 产品名称 15 */ 16 private String productName; 17 18 /** 19 * 产品ID 20 */ 21 private Long productId; 22 23 public String getProductNo() { 24 return productNo; 25 } 26 27 public void setProductNo(String productNo) { 28 this.productNo = productNo; 29 } 30 31 public String getProductName() { 32 return productName; 33 } 34 35 public void setProductName(String productName) { 36 this.productName = productName; 37 } 38 39 public Long getProductId() { 40 return productId; 41 } 42 43 public void setProductId(Long productIdLong) { 44 this.productId = productIdLong; 45 } 46 47 @Override 48 public String toString() { 49 return productId + "/" + productNo + "/" + productName; 50 } 51 52 }
然后在applicationContext-beans.xml中配置以下内容:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 5 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> 6 7 <bean id="propertyConfigurer" 8 class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> 9 <property name="locations"> 10 <list> 11 <value>classpath:properties/*.properties</value> 12 </list> 13 </property> 14 </bean> 15 16 <bean id="productEntity" class="yjmyzz.entity.ProductEntity"> 17 <property name="productId" value="${product.id}" /> 18 <property name="productNo" value="${product.no}" /> 19 <property name="productName" value="${product.name}" /> 20 <!-- <property name="productId"> 21 <bean class="java.lang.Long"> 22 <constructor-arg index="0" value="${product.id}" /> 23 </bean> 24 </property> 25 --> 26 </bean> 27 </beans>
注:classpath:properties/*.properties表示运行时 , spring容器会自动加载classpathproperties目录下的所有以.properties后缀结尾的文件 , 我们在src/main/resources/properties/下放置一个product.properties属性文件 , 内容如下:

1 product.id=3 2 product.no=n95 3 product.name=phone
该文件被spring自动加载后 , 就可以用里面定义的属性值 , 为Bean做setter属性注入 , 即配置文件中的<property name="productId" value="${product.id}" />
4.验证注入是否成功
在HomeController里 , 向Spring容器要一个Bean , 显示下它的属性:

1 package yjmyzz.controller; 2 3 import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean; 4 5 import yjmyzz.entity.ProductEntity; 6 import yjmyzz.utils.ApplicationContextUtils; 7 8 @ManagedBean(name = "Home") 9 public class HomeController { 10 11 public String sayHello() { 12 13 ProductEntity product = ApplicationContextUtils 14 .getBean(ProductEntity.class); 15 16 return product.toString(); 17 } 18 19 }
index.xhtml里仍然跟上篇相同:

1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" 3 xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" 4 xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" 5 xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"> 6 7 <h:head> 8 <title>jsf-web</title> 9 </h:head> 10 <body> 11 <h1> 12 #{Home.sayHello()} 13 14 </h1> 15 </body> 16 </html>
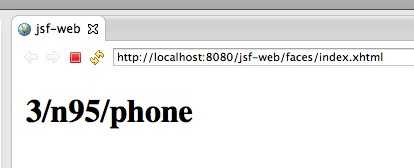
最后部署到jboss上 , 运行截图如下: