前面几节学习到的CDI内容,基本上都是hard-code,以硬编码的方式在代码里指定注入类型,这并非依赖注入的本意,依赖注入的优势之一在于“解耦”,这一节我们将学习如何利用配置来动态注入的类型及属性初始化。
一、@Alternative/@Default/@Any
当一个服务接口(也称契约)有多个实现时,可以在代码里指定一个缺省的实现类型(即:标注成@Default或@Any),其它实现类标注成@Alternative,以后如果需要动态切换实现类,只要在webapp/WEB-INF/beans.xml中配置即可。
1.1 新建二个示例接口

1 package contract; 2 3 public interface Connection { 4 5 String connect(); 6 7 }
该接口模拟db连接,里面有一个connect方法,用来连接db.

1 package contract; 2 3 public interface DriveService { 4 5 String drive(); 6 7 }
该接口模拟游戏应用中,有些人物具有驾驶技能。
1.2 提供接口实现
假设Connection有二个实现,一个用来连接到Oracle Database,另一个用来连接Microsoft Sql Server

1 package contract.impl; 2 3 import javax.enterprise.inject.Default; 4 5 import contract.Connection; 6 7 @Default 8 public class OracleConnection implements Connection { 9 10 @Override 11 public String connect() { 12 13 return "Oracle Database is connecting..."; 14 } 15 16 }

1 package contract.impl; 2 3 import javax.enterprise.inject.Alternative; 4 5 import contract.Connection; 6 7 @Alternative 8 public class SqlServerConnection implements Connection { 9 10 @Override 11 public String connect() { 12 13 return "Microsoft SqlServer is connecting..."; 14 } 15 16 }
注:OracleConnection上应用了注解@Default,表示这是接口Connection的默认实现类(@Default实质上是系统的默认注解,其实也可以省略,系统会自动默认为@Default);SqlServerConnection上应用了注解@Alternative,表示它是候选项,俗称:备胎:),所有非@Default的实现类,都必须标识@Alternative,否则注入时,会提示“不明确的类型”
再来看DriveService的实现,我们提供三种实现:驾驶汽车、摩托车、拖拉机

1 package contract.impl; 2 3 import contract.DriveService; 4 5 public class CarDriveImpl implements DriveService { 6 7 @Override 8 public String drive() { 9 String msg = "Drive a car..."; 10 System.out.println(msg); 11 return msg; 12 } 13 14 }

1 package contract.impl; 2 3 import javax.enterprise.inject.Alternative; 4 5 import contract.DriveService; 6 7 @Alternative 8 public class MotorcycleDriveImpl implements DriveService { 9 10 @Override 11 public String drive() { 12 String msg = "Drive a motocycle..."; 13 System.out.println(msg); 14 return msg; 15 } 16 17 }

1 package contract.impl; 2 3 import javax.enterprise.inject.Alternative; 4 5 import contract.DriveService; 6 7 @Alternative 8 public class TractorDriveImpl implements DriveService { 9 10 @Override 11 public String drive() { 12 String msg = "Drive a tractor..."; 13 System.out.println(msg); 14 return msg; 15 } 16 17 }
注:MotocycleDriveImpl、TractorDriveImpl这二个类使用了@Alternative,即它们俩是候选,剩下的CarDriveImpl上未使用任何注解,即默认的@Default
1.3 编写Controller类

1 package controller; 2 3 import javax.inject.Inject; 4 import javax.inject.Named; 5 6 import contract.Connection; 7 8 @Named("Conn") 9 public class ConnectionController { 10 11 @Inject 12 private Connection conn; 13 14 public Connection getConn() { 15 return conn; 16 } 17 18 }

1 package controller; 2 3 import javax.enterprise.inject.*; 4 import javax.inject.Inject; 5 import javax.inject.Named; 6 7 import contract.DriveService; 8 9 @Named("Drive") 10 public class DriveController { 11 12 @Inject 13 private DriveService driveService; 14 15 public DriveService getDriveService() { 16 return driveService; 17 } 18 19 @Inject 20 @Any 21 private Instance<DriveService> anySerInstance; 22 23 public DriveService getAnySerInstance() { 24 return anySerInstance.get(); 25 } 26 27 }
注:DriveController中anySerInstance成员上使用了@Any,从本例最终使用的效果上看,它跟@Default一样,只不过细节要留意一下,需要使用Instance<T>接口,这点跟@Default有点不同。
1.4 UI层

1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" 3 xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" 4 xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" 5 xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"> 6 7 <h:head> 8 <title>CDI - Alternative/Default/Any</title> 9 </h:head> 10 <body> 11 #{Drive.driveService.drive()} 12 <br /> 13 <br />#{Drive.anySerInstance.drive()} 14 <br /> 15 <br /> #{Conn.conn.connect()} 16 </body> 17 </html>
运行结果:
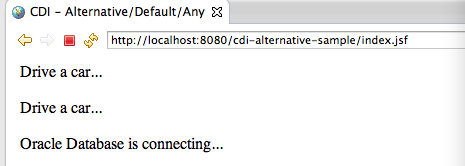
修改beans.xml的内容如下:

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 3 <beans xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xsi:schemaLocation=" http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/beans_1_0.xsd"> 5 <alternatives> 6 <class>contract.impl.SqlServerConnection</class> 7 <class>contract.impl.TractorDriveImpl</class> 8 </alternatives> 9 </beans>
重新在Jboss里部署、运行,结果如下:

在不修改java源代码的前提下,仅通过配置文件beans.xml的修改,就动态切换了接口的实现类。
二、Extension
不仅注入的类型可以由配置文件来动态切换,也可以由配置文件来直接初始化注入对象的属性值(虽然我个人认为这种场景在实际开发中其实并不多见)
2.1 先来定义几个类:
BaseDto.java

1 package dto; 2 3 import java.io.Serializable; 4 5 public class BaseDto implements Serializable { 6 7 private static final long serialVersionUID = 804047416541420712L; 8 9 public BaseDto() { 10 System.out.println("BaseDto's constructor is called..."); 11 12 } 13 14 }

1 package dto; 2 3 @DtoType(ProductType.Product) 4 public class Product extends BaseDto { 5 6 public Product() { 7 System.out.println("Product's constructor is called..."); 8 9 } 10 11 private static final long serialVersionUID = 7364741422914624828L; 12 private String productNo; 13 private String productName; 14 15 public String getProductName() { 16 return productName; 17 } 18 19 public void setProductName(String productName) { 20 this.productName = productName; 21 } 22 23 public String getProductNo() { 24 return productNo; 25 } 26 27 public void setProductNo(String productNo) { 28 this.productNo = productNo; 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public String toString() { 33 return "productNo:" + productNo + " , productName: " + productName 34 + " , serialVersionUID:" + serialVersionUID; 35 } 36 }

1 package dto; 2 3 //@DtoType(ProductType.Computer) 4 public class Computer extends Product { 5 6 public Computer() { 7 System.out.println("Computer's constructor is called..."); 8 } 9 10 private static final long serialVersionUID = -5323881568748028893L; 11 12 private String cpuType; 13 14 private int hardDiskCapacity; 15 16 public String getCpuType() { 17 return cpuType; 18 } 19 20 public void setCpuType(String cpuType) { 21 this.cpuType = cpuType; 22 } 23 24 public int getHardDiskCapacity() { 25 return hardDiskCapacity; 26 } 27 28 public void setHardDiskCapacity(int hardDiskCapacity) { 29 this.hardDiskCapacity = hardDiskCapacity; 30 } 31 32 @Override 33 public String toString() { 34 return "productNo:" + getProductNo() + " , productName: " 35 + getProductName() + " , cpuType:" + getCpuType() 36 + " , hardDiskCapacity: " + getHardDiskCapacity() 37 + " , serialVersionUID:" + serialVersionUID; 38 } 39 }

1 package dto; 2 3 //@DtoType(ProductType.Cloth) 4 public class Cloth extends Product { 5 6 private static final long serialVersionUID = -8799705022666106476L; 7 private String brand; 8 9 public String getBrand() { 10 return brand; 11 } 12 13 public void setBrand(String brand) { 14 this.brand = brand; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public String toString() { 19 return "productNo:" + getProductNo() + " , productName: " 20 + getProductName() + " , brand:" + getBrand() 21 + " , serialVersionUID:" + serialVersionUID; 22 } 23 24 }
Product上使用了一个自定义的注解:@DtoType

1 package dto; 2 3 import javax.inject.Qualifier; 4 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 5 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 6 7 @Qualifier 8 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 9 public @interface DtoType { 10 11 public ProductType value(); 12 13 }
以及枚举:

1 package dto; 2 3 public enum ProductType { 4 Product,Computer,Cloth 5 }
2.2 BaseDtoExtension
为了实现注入配置化,我们还需要对BaseDto写一个扩展类:

1 package dto.extension; 2 3 import java.io.IOException; 4 import java.io.InputStream; 5 import java.util.logging.Logger; 6 7 import javax.enterprise.event.Observes; 8 9 import javax.enterprise.inject.spi.*; 10 import javax.xml.parsers.*; 11 12 import dto.*; 13 import org.w3c.dom.*; 14 15 import org.xml.sax.SAXException; 16 17 18 public class BaseDtoExtension implements Extension { 19 private final Document document; 20 private final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(BaseDtoExtension.class 21 .getName()); 22 23 public BaseDtoExtension() { 24 try { 25 InputStream creatureDefs = BaseDtoExtension.class.getClassLoader() 26 .getResourceAsStream("inject-beans.xml"); 27 DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory 28 .newInstance(); 29 DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); 30 document = builder.parse(creatureDefs); 31 } catch (ParserConfigurationException e) { 32 throw new RuntimeException("Error building xml parser, aborting", e); 33 } catch (SAXException e) { 34 throw new RuntimeException("SAX exception while parsing xml file", 35 e); 36 } catch (IOException e) { 37 throw new RuntimeException("Error reading or parsing xml file", e); 38 } 39 } 40 41 42 <X extends BaseDto> void processInjectionTarget( 43 @Observes ProcessInjectionTarget<X> pit) { 44 Class<? extends BaseDto> klass = pit.getAnnotatedType().getJavaClass(); 45 log.info("Setting up injection target for " + klass); 46 final Element entry = (Element) document.getElementsByTagName( 47 klass.getSimpleName().toLowerCase()).item(0); 48 pit.setInjectionTarget(new XmlWrappedInjection<X>(pit 49 .getInjectionTarget(), entry)); 50 } 51 }
该扩展,将读取resources/inject-beans.xml文件的内容,并完成BaseDto以及所有子类的加载,包括Inject,该类还使用了另一个辅助类:

1 package dto.extension; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 import javax.enterprise.context.spi.CreationalContext; 7 import javax.enterprise.inject.InjectionException; 8 import javax.enterprise.inject.spi.*; 9 10 import dto.*; 11 import org.w3c.dom.Element; 12 13 public class XmlWrappedInjection<X extends BaseDto> implements 14 InjectionTarget<X> { 15 private final InjectionTarget<X> wrapped; 16 private final Element xmlBacking; 17 18 public XmlWrappedInjection(InjectionTarget<X> it, Element xmlElement) { 19 wrapped = it; 20 xmlBacking = xmlElement; 21 } 22 23 @Override 24 public void inject(X instance, CreationalContext<X> ctx) { 25 wrapped.inject(instance, ctx); 26 27 final Class<? extends BaseDto> klass = instance.getClass(); 28 //yjm注:出于演示目的,这里仅反射了本类中声明的field,所以注入时,父类中的field会被忽略,大家可以自行修改,逐层向上反射,直到BaseDto类为止 29 for (Field field : klass.getDeclaredFields()) { 30 field.setAccessible(true); 31 final String fieldValueFromXml = xmlBacking.getAttribute(field 32 .getName()); 33 try { 34 //System.out.println("the filed name is :" + field.getName()); 35 if (field.getName().toLowerCase().equals("serialversionuid")) { 36 continue; 37 } 38 //注:出于演示目的,这里只处理了int、long、String这三种类型,其它类型大家可自行扩展 39 if (field.getType().isAssignableFrom(Integer.TYPE)) { 40 field.set(instance, Integer.parseInt(fieldValueFromXml)); 41 } else if (field.getType().isAssignableFrom(Long.TYPE)) { 42 field.set(instance, Long.parseLong(fieldValueFromXml)); 43 } else if (field.getType().isAssignableFrom(String.class)) { 44 field.set(instance, fieldValueFromXml); 45 } else { 46 throw new InjectionException("Cannot convert to type " 47 + field.getType()); 48 } 49 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 50 throw new InjectionException("Cannot access field " + field); 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 55 @Override 56 public void postConstruct(X instance) { 57 wrapped.postConstruct(instance); 58 } 59 60 @Override 61 public void preDestroy(X instance) { 62 wrapped.preDestroy(instance); 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public X produce(CreationalContext<X> ctx) { 67 return wrapped.produce(ctx); 68 } 69 70 @Override 71 public void dispose(X instance) { 72 wrapped.dispose(instance); 73 } 74 75 @Override 76 public Set<InjectionPoint> getInjectionPoints() { 77 return wrapped.getInjectionPoints(); 78 } 79 }
注:这里仅只是演示,所以处理得相对比较简单,如果一个类继承自父类,Inject时,上面的代码,只反射了子类本身声明的field,对于父类的属性,未逐层向上反射,大家可以自行改进。
2.3 控制器

1 package controller; 2 3 import javax.inject.Inject; 4 import javax.inject.Named; 5 6 import dto.Cloth; 7 import dto.Computer; 8 import dto.DtoType; 9 import dto.Product; 10 import dto.ProductType; 11 12 @Named("Ext") 13 public class ExtensionController { 14 15 @Inject 16 //@DtoType(ProductType.Computer) 17 private Computer computer; 18 19 @Inject 20 //@DtoType(ProductType.Cloth) 21 private Cloth cloth; 22 23 @Inject 24 @DtoType(ProductType.Product) 25 private Product product; 26 27 public Computer getComputer() { 28 return computer; 29 } 30 31 public Cloth getCloth() { 32 return cloth; 33 } 34 35 public Product getProduct() { 36 return product; 37 } 38 39 }
注:这里思考一下,为什么Product上必须使用注解@DtoType(ProductType.Product),而其它二个Inject的field不需要?如果暂时没想明白的朋友,建议回到第一节 ,看下1.7节的内容,因为Computer、Cloth都继承自Product类,所以在实例Product类时,系统有3个选择:Computer、Cloth、Product,它不知道该选哪一个?所以运行时,系统会罢工,so,需要额外的注释给它一点提示。
2.4 ext.xhtml

1 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd"> 2 <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" 3 xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html" 4 xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core" 5 xmlns:ui="http://java.sun.com/jsf/facelets"> 6 7 <h:head> 8 <title>Extension Test</title> 9 </h:head> 10 <body> 11 #{Ext.product.toString()} 12 <br /> #{Ext.computer.toString()} 13 <br /> #{Ext.cloth.toString()} 14 15 </body> 16 </html>
2.5 inject-beans.xml

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <basedtos> 3 <product productNo="001" productName="A Unknown New Product" /> 4 <computer productNo="T60" productName="ThinkPad" cpuType="2-cores" 5 hardDiskCapacity="320" /> 6 <cloth productNo="XX" productName="Underware" brand="JackJohns" /> 7 </basedtos>
该文件设计时,要放在main/java/resources/目录下,部署时,会自动复制到webapp/resources/
2.6 javax.enterprise.inject.spi.Extension
/main/java/resources/META-INF/services目录下,新建一个文件:javax.enterprise.inject.spi.Extension,内容如下:
dto.extension.BaseDtoExtension
该文件的作用是在运行时,告诉系统根据BaseDtoExtension类的定义去找inject-beans.xml,它相当于入口。
2.7 运行效果:浏览地址 http://localhost:8080/cdi-alternative-sample/ext.jsf

跟预期结果完全一样,不过正如文中指出的一样,父类的属性被忽略了,如果父类成员也需要初始化,需要大家自行修改XmlWrappedInjection类
最后附示例源代码:cdi-alternative-sample.zip
