java.lang包下有二个非常有用的东西:Runnable接口与Thread类,Thread实现了Runnable接口(可以认为Thread是Runnable的子类),利用它们可以实现最基本的多线程开发。
一、Runnable入门示例

1 public class RunnableDemo1 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new Runnable() { 5 public void run() { 6 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 7 try { 8 Thread.sleep(100); 9 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 System.out.println("r1 -> i=" + i); 13 } 14 15 } 16 }.run(); 17 18 new Runnable() { 19 public void run() { 20 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 21 try { 22 Thread.sleep(100); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 System.out.println("r2 -> i=" + i); 27 } 28 } 29 }.run(); 30 31 } 32 33 }
代码很简单,每个线程依次输出0-4这5个数字,运行结果:
r1 -> i=0
r1 -> i=1
r1 -> i=2
r1 -> i=3
r1 -> i=4
r2 -> i=0
r2 -> i=1
r2 -> i=2
r2 -> i=3
r2 -> i=4
二、向Runnable传递参数
实际应用中,线程开始处理前,通常会有一些初始参数,如果要传入参数,可以参考下面的方法,先定义一个Runnable的子类

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ 4 5 private String name; 6 private int max; 7 8 public MyRunnable(String name,int max){ 9 this.name = name; 10 this.max = max; 11 } 12 13 public void run() { 14 for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) { 15 try { 16 Thread.sleep(5); 17 System.out.println(name + ".i=" + i); 18 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 19 e.printStackTrace(); 20 } 21 } 22 } 23 24 }
然后这样使用:

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 public class RunnableDemo2 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 new MyRunnable("A", 5).run(); 8 9 new MyRunnable("B", 5).run(); 10 } 11 12 }
运行结果:
A.i=1
A.i=2
A.i=3
A.i=4
A.i=5
B.i=1
B.i=2
B.i=3
B.i=4
B.i=5
三、利用Thread并行处理
刚才的二个例子,相当大家也发现了问题,虽然是有二个线程,但是始终是按顺序执行的,上一个线程处理完成前,下一个线程无法开始,这其实跟同步处理没啥二样,可以通过Thread类改变这种局面:

1 public class RunnableDemo3 { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 Runnable r1 = new MyRunnable("A", 5); 6 Runnable r2 = new MyRunnable("B", 5); 7 8 Thread t1 = new Thread(r1); 9 Thread t2 = new Thread(r2); 10 11 t1.start(); 12 t2.start(); 13 14 } 15 16 }
Thread通过start方法,可以让多个线程并行处理,运行结果如下:
B.i=1
A.i=1
B.i=2
A.i=2
B.i=3
A.i=3
B.i=4
A.i=4
B.i=5
A.i=5
从输出结果上看,二个线程已经在并行处理了。
四、通过在线抢购示例理解资源共享
双十一刚过,每到这个时候,通常是狼多肉少,下面的OrderRunnable类模拟这种抢购情况,假设产品数只有10个,抢购的客户却有100个

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 public class OrderRunnable implements Runnable{ 4 5 String taskName; 6 7 public OrderRunnable(String taskName){ 8 this.taskName=taskName; 9 } 10 11 private int productNum = 10; 12 13 private int customerNum = 100; 14 15 public void run() { 16 17 for (int i = 0; i < customerNum; i++) { 18 if (productNum > 0) { 19 try { 20 Thread.sleep(50); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 System.out.println(taskName + " -> order success!"); 25 productNum -= 1; 26 } 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 }
现在想用二个线程来处理:

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 public class RunnableDemo4 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Runnable r1 = new OrderRunnable("A"); 8 Runnable r2 = new OrderRunnable("B"); 9 10 new Thread(r1).start(); 11 new Thread(r2).start(); 12 13 } 14 15 }
运行结果:
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
A -> order success!
B -> order success!
显然,这个结果不正确,只有10个产品,却生成了20个订单!
正确的做法,让多个Thread共同使用一个Runnable:

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 public class RunnableDemo5 { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 Runnable r1 = new OrderRunnable("A"); 8 9 new Thread(r1).start(); 10 new Thread(r1).start(); 11 12 } 13 14 }
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
A -> order success!
五、ThreadPoolExecutor
如果有大量线程,建议使用线程池管理,下面是ThreadPoolExecutor的示例用法:

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; 5 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 6 7 public class RunnableDemo7 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 11 ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 10, 1, 12 TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3)); 13 14 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { 15 threadPool.execute(new MyRunnable("R"+i, 5)); 16 } 17 18 } 19 20 }
运行结果:
R5.i=1
R0.i=1
R1.i=1
R5.i=2
R1.i=2
R0.i=2
R5.i=3
R1.i=3
R0.i=3
R5.i=4
R1.i=4
R0.i=4
R5.i=5
R0.i=5
R1.i=5
R2.i=1
R3.i=1
R4.i=1
R2.i=2
R3.i=2
R4.i=2
R2.i=3
R3.i=3
R4.i=3
R2.i=4
R4.i=4
R3.i=4
R2.i=5
R4.i=5
R3.i=5
agapple在ITeye上有一篇旧贴子,写得很好,推荐大家去看看,特别是下面这张图:
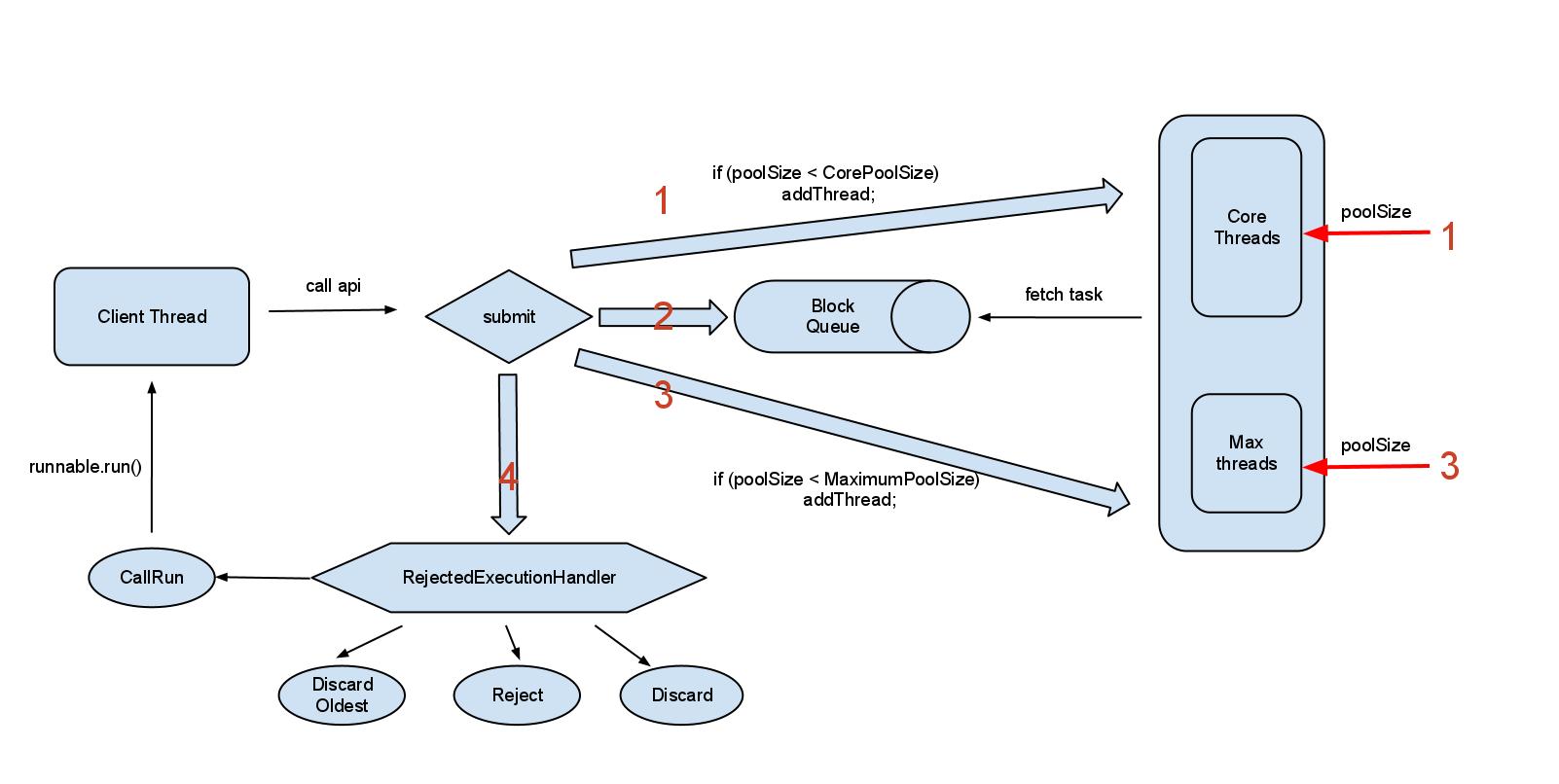
还有这篇 http://jiaguwen123.iteye.com/blog/1017636,也值得参考
六、ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
终于轮到我大Spring出场了,Spring框架提供了org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor类,可以用注入的形式生成线程池

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 4 xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc" 5 xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" 6 xsi:schemaLocation=" 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.0.xsd 11 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd" 12 default-autowire="byName"> 13 14 <bean id="threadPoolTaskExecutor" 15 class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor"> 16 <property name="corePoolSize" value="2" /> 17 <property name="maxPoolSize" value="10" /> 18 <property name="queueCapacity" value="1000" /> 19 <property name="keepAliveSeconds" value="15" /> 20 <property name="rejectedExecutionHandler"> 21 <bean class="java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$CallerRunsPolicy" /> 22 </property> 23 </bean> 24 25 </beans>
配置好以后,就可以直接使用了

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 4 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; 6 7 public class RunnableDemo8 { 8 9 @SuppressWarnings("resource") 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 12 ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 13 "spring.xml"); 14 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = applicationContext.getBean( 15 "threadPoolTaskExecutor", ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.class); 16 17 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) { 18 taskExecutor.execute(new MyRunnable("R" + i, 5)); 19 } 20 21 } 22 23 }
七、FutureTask<T>
如果某些线程的处理非常耗时,不希望它阻塞其它线程,可以考虑使用FutureTask,正如字面意义一样,该线程启用后,马上开始,但是处理结果将在"未来"某一时刻,才真正需要,在此之前,其它线程可以继续处理自己的事情

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.Callable; 4 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; 5 import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask; 6 7 public class RunnableDemo9 { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, 10 ExecutionException { 11 12 FutureTask<String> task = new FutureTask<String>( 13 new Callable<String>() { 14 public String call() throws InterruptedException { 15 System.out.println("FutureTask开始处理..."); 16 Thread.sleep(1000); 17 return "hello world"; 18 } 19 }); 20 System.out.println("FutureTask准备开始..."); 21 new Thread(task).start(); 22 System.out.println("其它处理开始..."); 23 Thread.sleep(1000); 24 System.out.println("其它处理完成..."); 25 System.out.println("FutureTask处理结果:" + task.get()); 26 System.out.println("全部处理完成"); 27 } 28 29 }
二个注意点:
a) FutureTask使用Callable接口取得返回值,因为结果可能并不需要立刻返回,而是等到未来真正需要的时候,而Runnable并不提供返回值
b) FutureTask通过Thread的start()调用后,马上就开始处理,但并不阻塞后面的线程,在真正需要处理结果的时候,调用get()方法,这时如果FutureTask本身的处理尚未完成,才会阻塞,等待处理完成
刚才的运行结果:
FutureTask准备开始...
FutureTask开始处理...
其它处理开始...
其它处理完成...
FutureTask处理结果:hello world
全部处理完成
可以看到,“其它处理”并未被FutureTask阻塞,但FutureTask其实已经在后台处理了。
