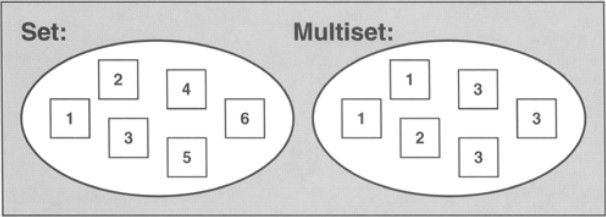
set和multiset会根据特定的排序准则,自动将元素进行排序。不同的是后者允许元素重复而前者不允许。
需要包含头文件:
#include <set>
set和multiset都是定义在std空间里的类模板:
template<class _Kty, class _Pr = less<_Kty>, class _Alloc = allocator<_Kty> > class multiset
template<class _Kty, class _Pr = less<_Kty>, class _Alloc = allocator<_Kty> > class multiset
只要是可复赋值、可拷贝、可以根据某个排序准则进行比较的型别都可以成为它们的元素。第二个参数用来定义排序准则。缺省准则less是一个仿函数,以operator<对元素进行比较。
所谓排序准则,必须定义strict weak ordering,其意义如下:
1、必须使反对称的。
对operator<而言,如果x<y为真,则y<x为假。
2、必须使可传递的。
对operator<而言,如果x<y为真,且y<z为真,则x<z为真。
3、必须是非自反的。
对operator<而言,x<x永远为假。
因为上面的这些特性,排序准则可以用于相等性检验,就是说,如果两个元素都不小于对方,则它们相等。
set和multiset的功能
和所有关联式容器类似,通常使用平衡二叉树完成。事实上,set和multiset通常以红黑树实作而成。
自动排序的优点是使得搜寻元素时具有良好的性能,具有对数时间复杂度。但是造成的一个缺点就是:
不能直接改变元素值。因为这样会打乱原有的顺序。
改变元素值的方法是:先删除旧元素,再插入新元素。
存取元素只能通过迭代器,从迭代器的角度看,元素值是常数。
操作函数

set的形式可以是:

set的程序练习:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<set> #include<string> //1.集合 元素唯一 自动排序(默认情况是从小到大) 不能按照数组的方式插入元素 //2.红黑树 void main91() { set<int> set1; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int temp = rand(); set1.insert(temp); } //插入元素 set1.insert(100); set1.insert(100); set1.insert(100); for (set<int>::iterator it = set1.begin(); it != set1.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; //删除集合 while (!set1.empty()) { set<int>::iterator it = set1.begin(); cout << *it << " "; set1.erase(set1.begin()); } } //对基本的数据类型能够自动排序 void main92() { set<int> set1; set<int, less<int> > set2;//从小到大 set1的完整形式(默认情况下) set<int, greater<int> > set3;//从大到小的完整形式 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { int temp = rand(); set3.insert(temp); } //插入元素 set3.insert(100); set3.insert(100); set3.insert(100); // 遍历 顺序应是从大到小 for (set<int, greater<int>> ::iterator it = set3.begin(); it != set3.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } //对于复杂的数据类型 Teacher Student class Student { public: Student(const char *name, int age) { strcpy_s(this->name, name); this->age = age; } public: char name[64]; int age; }; //仿函数 struct FuncStudent { bool operator()(const Student& left, const Student& right) const //不加const报错 { if (left.age < right.age) //如果左边的小 就返回真 从小到大按照年龄进行排序 { return true; } else { return false; } } }; //仿函数的用法 void main93() { set<Student,FuncStudent> set1; Student s1("s1", 31); Student s2("s2", 22); Student s3("s3", 17); Student s4("s4", 35); Student s5("s5", 31); pair<set<Student,FuncStudent>::iterator, bool> it1 = set1.insert(s1); if (it1.second == true) { cout << "插入s1成功" << endl; } else { cout << "插入s1失败" << endl; } set1.insert(s2); /*set1.insert(s3); set1.insert(s4);*/ pair<set<Student, FuncStudent>::iterator, bool> it5 = set1.insert(s5); if (it5.second == true) { cout << "插入s5成功" << endl; } else { cout << "插入s5失败" << endl; } //如何知道插入的结果? // pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& _Val) //如何判断set1.insert函数的返回值 //遍历 for (set<Student, FuncStudent>::iterator it = set1.begin(); it != set1.end(); it++) { cout << it->age << " " << it->name << endl; } cout << endl; } void main95() { set<int> set1; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { set1.insert(i + 1); } for (set<int>::iterator it = set1.begin(); it != set1.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; set<int>::iterator it0 =set1.find(5); cout << "it0: " << *it0 << endl; int num = set1.count(5);//找值为5的个数 cout << "mum: " << num << endl; set<int>::iterator it3 = set1.upper_bound(3);//大于3的元素迭代器位置 cout << "大于3的迭代器位置 " << *it3 << endl; set<int>::iterator it4 = set1.lower_bound(3);//大于等于3的元素迭代器位置 cout << "大于等于3的迭代器位置 " << *it4 << endl; pair<set<int>::iterator, set<int>::iterator> mypair = set1.equal_range(3);//找大于等于3和大于三的迭代器位置 set<int>::iterator it5 = mypair.first;//3 cout << "it5 " << *it5 << endl; set<int>::iterator it6 = mypair.second;//4 cout << "it6 " << *it6 << endl; } int main() { //main91(); //main92(); //main93(); main95(); system("pause"); return 0; }
multiset用法:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<set> void main1001() { multiset<int> set1; int temp = 0; printf("请输入multiset集合的值:"); scanf_s("%d", &temp); while (temp != 0) { set1.insert(temp); printf("请输入multiset集合的值:"); scanf_s("%d", &temp); } //遍历 for (multiset<int>::iterator it = set1.begin(); it != set1.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; while (!set1.empty()) { multiset<int>::iterator it = set1.begin(); cout << *it << " "; set1.erase(it); } } int main() { main1001(); system("pause"); return 0; }