每篇一句
大师都是偏执的,偏执才能产生力量,妥协是没有力量的。你对全世界妥协了你就是空气。所以若没有偏见,哪来的大师呢
相关阅读
【小家Spring】详解PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer、PropertyOverrideConfigurer等对属性配置文件Properties的加载和使用
【小家Spring】Spring中@PropertySource和@ImportResource的区别,以及各自的实现原理解析
【小家Spring】Spring中@Value注解有多强大?从原理层面去剖析为何它有如此大的“能耐“
前言
写这篇文章的原动力是由于昨晚深夜一个小伙伴咨询我的一个问题(这位小伙伴这么晚了还在折腾,也是给个大大的赞),涉及到了如题方面的知识。
当然促使我书写本文最重要原因的是:这种从传统Spring项目向SpringBoot迁移进阶的case,我个人认为在现阶段的环境下还是有较大概率出现的,因此推荐收藏本文,对你后续或许有所帮助~
情景描述
为了更直观的说明问题所在,截图部分聊天记录如下:
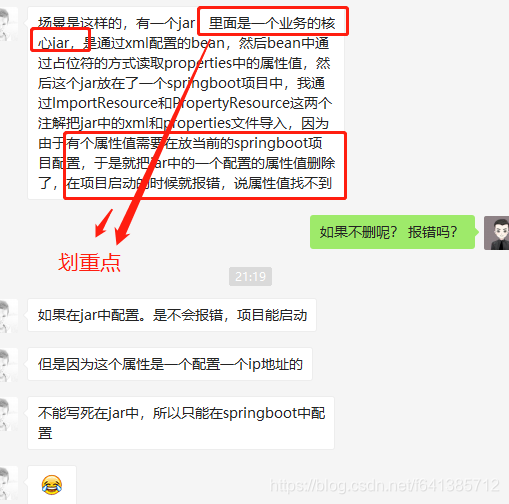
这位小伙伴描述的问题还是蛮清晰,所以我还是很愿意跟他一起探讨的~
勾起兴趣还有一个原因:Spring对占位符提供了非常强大的支持,但基本上新手都还不能好好利用它和利用好它,更区分不清使用的规范和区别,本文也希望做点努力,能够起到稍微一点的作用~
对此部分内容若需要热场,推荐可以先浏览一下这篇文章:【小家Spring】Spring中@PropertySource和@ImportResource的区别,以及各自的实现原理解析 可以看到,早在我这篇文章里我就说了这么一句话:

而刚好这个小伙伴的场景(其实我自己还并没有遇到过此场景),就类属于老项目到SpringBoot新项目的一个迁移case,这时不结合分析,更待何时呢。
看到聊天记录,部分小伙伴可能会想:把Bean拿出来配置不就行了吗?或者key就写在原来的属性文件里呗?
其实对于职场老兵都能对此种现象给与理解和接受,毕竟有种叫理想化,有种叫是叫实际化~
因为我不可能贴出该小伙伴的源码(毕竟人家是生产环境的代码,咋可能贴出给大伙看呢?)so,接下来旨在说明这个问题,我就只好采用我的模拟大法喽:
传统Spring工程下使用
本处以一个传统的Spring工程为例,模拟这种使用case。classpath下有如下两个文件:
spring-beans.xml:
<bean id="myPerson" class="com.fsx.bean.Person">
<property name="name" value="${diy.name}"/>
<property name="age" value="18"/>
</bean>
可以看到此xml配置Bean中使用了占位符:${diy.name}来引用下面属性文件的属性值~
my.properties:
diy.name = fsx-fsx
使用@ImportResource和@PropertySource分别把它哥俩导入:
@ImportResource(locations = "classpath:spring-beans.xml")
@PropertySource("classpath:my.properties")
@Configuration
public class RootConfig {
}
运行如下测试用例:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {RootConfig.class})
public class TestSpringBean {
@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Test
public void test1() {
Person bean = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("myPerson");
System.out.println(bean);
System.out.println(environment.getProperty("diy.name"));
}
}
打印结果为:
Person{name='${diy.name}', age=18}
fsx-fsx
从结果中可以至少知道如下两点:
- 环境变量里是存在
diy.name这个属性k-v的。并且此处我附上截图如下:
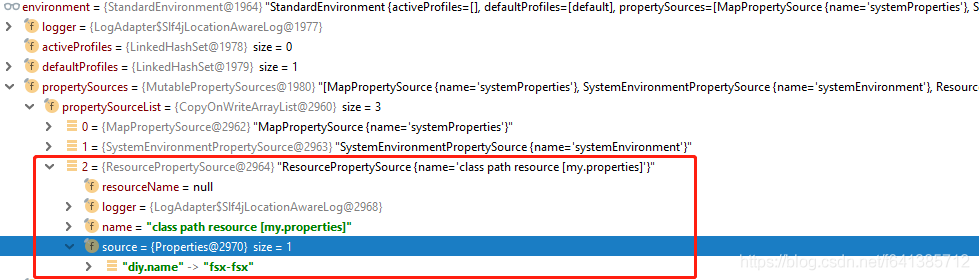
- xml中的占位符并没有被解析
若你对技术有敏感性的话,你会疑问为何占位符没被解析但并没有报错呢?
这个问题我在这篇文章:【小家Spring】Spring中@Value注解有多强大?从原理层面去剖析为何它有如此大的“能耐“ 里有过解释,有兴趣的可以点开看看(没兴趣的可以略过)
存在但又没被解析,看似有点矛盾,难道Spring工程不支持这么用,作为职场老兵的你,答案肯定是否定的,那如何破呢?
其实解决起来非常简单,我们只需要配置上一个PropertyResourceConfigurer即可:
@Bean
public PropertyResourceConfigurer propertyResourceConfigurer() {
PropertyResourceConfigurer configurer = new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
// 使用的PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,不用自己再手动指定亦可处理占位符~~~
// configurer.setLocation(new ClassPathResource("my.properties")); // 加载指定的属性文件
return configurer;
}
再次运行,打印如下:
Person{name='fsx-fsx', age=18}
fsx-fsx
完美~
关于xml配置Bean处理占位符问题,为了加深理解,亦可参考:【小家Spring】Spring IoC是如何使用BeanWrapper和Java内省结合起来给Bean属性赋值的
我想说:此处介绍的是注解版怎么处理占位符问题,若你仍旧是传统的xml配置项目,至于具体使用哪个标签,小伙伴自行寻找咯~
我们知道PropertyResourceConfigurer它是个抽象类,它的三大实现子类除了上例使用的,还有其余两大实现类:PropertyOverrideConfigurer和PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,若注册它哥俩可行吗??? 行不行试试呗
使用PropertyOverrideConfigurer
PropertyOverrideConfigurer 利用属性文件的相关信息,覆盖XML 配置文件中Bean定义。它要求配置的属性文件第一个.前面是beanName来匹配,所以这个子类我看都不用看,它肯定不行(因为它改变了k-v的结构)。
其实上面说配置
PropertyResourceConfigurer的实现类来处理是不太准确的。
准确的说应该是配置PlaceholderConfigurerSupport的实现子类来处理Placeholder占位符更精确,特此纠正哈~
使用PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
其实大多数小伙伴对PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer比对PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer熟悉多了,毕竟前者的年纪可大多了~
它哥俩都是PlaceholderConfigurerSupport的实现子类有能力能够处理占位符
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer是Spring 3.1后提供的,希望用来取代PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer
@Bean
public PropertyResourceConfigurer propertyResourceConfigurer() {
PropertyResourceConfigurer configurer = new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer();
//configurer.setLocation(new ClassPathResource("my.properties")); // 加载指定的属性文件
return configurer;
}
运行上面用例就报错了:
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Could not resolve placeholder 'diy.name' in value "${diy.name}"
at org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper.parseStringValue(PropertyPlaceholderHelper.java:172)
at org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper.replacePlaceholders(PropertyPlaceholderHelper.java:124)
what?看打印结果,明明environment.getProperty("diy.name")从环境里能拿到这个key呀,怎么会报错呢???
这就是为何Spring3.1要提供一个PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer旨在想代替掉此类的原因了。
但是,但是,但是把上配置中注掉的那行代码放开(也就是说自己设置location从而把属性文件加载进来),就能正常work了。
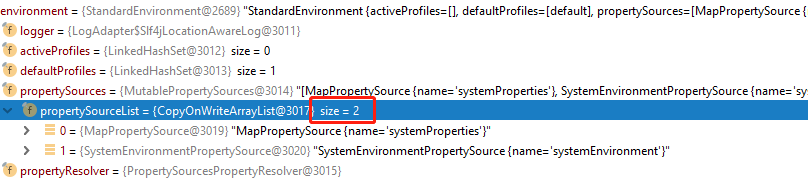
关于使用这种方式我还有必要再说明一点:若自己设置了location加载属性文件,@PropertySource("classpath:my.properties")这句代码对此种场景就没有必要了,xml配置的占位符也是能够读取到的。但是但是但是,若注掉这句@PropertySource...,此时运行输出如下:
Person{name='fsx-fsx', age=18}
null
会发现environment.getProperty("diy.name")为null,也就是说该属性值并不会存在应用的环境内了(但是xml的占位符已被成功解析)。从我的这个截图中也能看出来环境里已经没它了:
至于这深处到底是什么原因,有兴趣的可以轻点这里:【小家Spring】详解PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer、PropertyOverrideConfigurer等对属性配置文件Properties的加载和使用
只new一个PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer报错原因分析:
其实从源代码处一眼就能看出来原因:
public class PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer extends PlaceholderConfigurerSupport {
...
// 是否能被解析到值,重点在于入参的这个Properties props是否有这个key,而这个参数需要追溯它的父类~
@Override
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props) throws BeansException {
StringValueResolver valueResolver = new PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver(props);
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}
...
}
// 从父类中看看props的传值是啥~~~
public abstract class PropertyResourceConfigurer extends PropertiesLoaderSupport implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered {
...
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// Convert the merged properties, if necessary.
convertProperties(mergedProps);
// Let the subclass process the properties.
// 抽象方法,交给子类~~~这里传入的mergedProps,全部来自location~~~
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
protected Properties mergeProperties() throws IOException {
...
loadProperties(result);
...
}
// 从配置里的location里把属性值都读出来~~~~~
protected void loadProperties(Properties props) throws IOException {
if (this.locations != null) {
for (Resource location : this.locations) {
...
PropertiesLoaderUtils.fillProperties(props, new EncodedResource(location, this.fileEncoding), this.propertiesPersister);
...
}
}
}
...
}
由此可见,若上述@Bean配置使用的是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,那必须手动的把属性文件设置location加载进去才行,否则是读取不到滴~
那么问题来了,为何使用PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer,只需要简单的new一个就成了勒(并不需要手动设置location)?
一样的,从源码处一看便知,非常非常简单:
// @since 3.1 直接实现了EnvironmentAware,说明此Bean可以拿到当前环境Environment
public class PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer extends PlaceholderConfigurerSupport implements EnvironmentAware {
...
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
...
// 把环境属性都放进来~
if (this.environment != null) {
this.propertySources.addLast(
new PropertySource<Environment>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) {
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String key) {
return this.source.getProperty(key);
}
}
);
}
// 把配置的属性放进来~~~
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource = new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
...
}
}
相信不用我做过多的解释,就知道为何不用自己设置location,直接使用注解@PropertySource("classpath:my.properties")就好使了吧。这个时候环境截图如下(注意:此处我截图是基于已经set了location的截图哦):
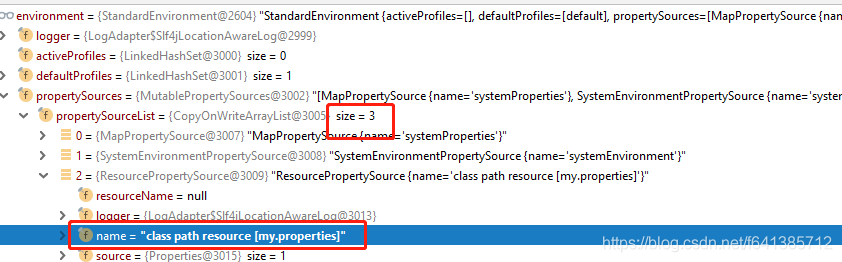
what?虽然配置时候set了location去加载属性文件,但是上面代码中add进去的属性源environmentProperties和localProperties
public static final String LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "localProperties";
public static final String ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "environmentProperties";
两个PropertySource都并没有出现?
关于此,我这里就不再解释了,哈哈。还是那句话,留给小伙伴们自己思考,若思考不明白的亦可扫码入群探讨哦~(当然参照上面文章也是可行的)
SpringBoot工程下使用
关于在SpringBoot中使用,简单到令人发指,毕竟SpringBoot的使命也是让你使用它能够简单到木有朋友。
so,在SpringBoot工程下使用@ImportResource和@PropertySource啥都不用配,它是能够天然的直接work的~
原因分析如下:
一切得益于SpringBoot强悍的自动化配置能力,它提供了这样一个配置类:
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) // 最高优先级
public class PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration {
// 注意此处使用的是PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
// 并且你可以在本容器内覆盖它的默认行为哟~~~~
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
}
PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration它被配置在了自动配置包下的spring.factories文件里:
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=
...
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration,
...
因此它会随着工程启动而自动生效。有了上面对Spring工程下的使用分析,此处就不用再花笔墨解释了~
另外附加说明一点:哪怕你的属性不使用@PropertySource导入,而是写在SB自带的application.properties文件里,依旧是没有问题的。
原因分析如下:
其实这个涉及到的是SpringBoot对application.properties的加载时机问题,因为本文对SB的介绍并不是重点,因此此处我直接简单的说出结论即止:
SpringBoot通过事件监听机制加载很多东西,加载此属性文件用的是ConfigFileApplicationListener这个监听器- 它监听到
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(环境准备好后)事件后开始加载application.properties等文件 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent的事件发出是发生在createApplicationContext()之前~~~ 部分代码如下:
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 此步骤 会发出ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 开始创建,初始化容器~
context = createApplicationContext();
...
}
...
}
so,在SB环境下已经早早把属性都放进环境内了,借助它默认配置好的PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer来处理的,那可不能正常work吗。一切都是这么自然,这或许就是SB的魅力所在吧~
关于小伙伴问题的解决
开头提出了问题,肯定得解决问题嘛~~~如下图
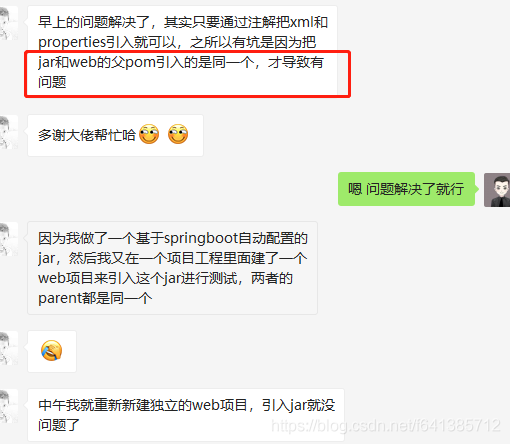
哈哈,虽然最终我并没有直接的帮助解决问题,但是此问题给了我写本文的动力,总体还是不错的~
总结
本文通过一个小伙伴咨询的小问题(真是小问题吗?)引申比较详细的说了Spring在处理占位符这块的内容(其实本并没打算写这么多的,尴尬~)
写本文的目的开头也说了,我认为在SpringBoot还并非100%渗透的当下,肯定有人会遇到从传统Spring项目向SpringBoot过度的一个阶段,而本文的描述或许能给你的迁移提供一种新的思路(特别是时间紧、任务重的时候),希望小伙伴们能有所收获,peace~
知识交流
若文章格式混乱,可点击:原文链接-原文链接-原文链接-原文链接-原文链接
The last:如果觉得本文对你有帮助,不妨点个赞呗。当然分享到你的朋友圈让更多小伙伴看到也是被作者本人许可的~
若对技术内容感兴趣可以加入wx群交流:Java高工、架构师3群。
若群二维码失效,请加wx号:fsx641385712(或者扫描下方wx二维码)。并且备注:"java入群" 字样,会手动邀请入群
