[0. 需求]
最近在粗略学习《C++ Primer 4th》的容器内容,关联容器的章节末尾有个很不错的实例。
通过实现一个简单的文本查询程序,希望能够对C++的容器学习有更深的理解。
由于是浅略探讨研究,高手可无视,各位读者发现有什么不妥的地方,请指教。
程序将读取用户指定的任意文本文件,然后允许用户从该文件中查找单词。
查询的结果是该单词出现的次数,并列出每次出现所在的行。
如果某单词在同一行中多次出现,程序将只显示该行一次。
行号按升序显示,即第 1行应该在第 2 行之前输出,依此类推。
本人用到的文本文件“ inputfile.txt ”,内容如下(显示的行号并非文件原内容):
1 Our program will read a file specified by the user and then allow the user to 2 search the file for words that might occur in it. The result of a query will be 3 the number of times the word occurs and a list of lines on which 4 it appears. If a word occurs more than once on the same line, 5 our program should be smart enough to display that line only once. 6 Lines should be displayed in ascending orderthat is, 7 line 7 should be displayed before line 9, and so on.
[1. 程序的设计]
设计程序的一个良好习惯是首先将程序所涉及的操作列出来。
这样有助于建立需要的数据结构和实现这些行为。
本程序的需求如下:
它必须允许用户指明要处理的文件名字。
程序将存储该文件的内容,以便输出每个单词所在的原始行。
它必须将每一行分解为各个单词,并记录每个单词所在的所有行。
在输出行号时,应保证以升序输出,并且不重复。
对特定单词的查询将返回出现该单词的所有行的行号。
输出某单词所在的行文本时,程序必须能根据给定的行号从输入文件中获取相应的行。
1.1 数据结构
我们将用一个简单的类 TextQuery ,再配合几种容器的使用,实现这个程序的要求。
使用一个 vector<string> 类型的对象存储整个输入文件的副本。
输入文件的每一行是该 vector 对象的一个元素。
因而,在希望输出某一行时,只需以行号为下标获取该行所在的元素即可。
将每个单词所在的行号存储在一个 set 容器对象中。
使用 set 就可确保每行只有一个条目,而且行号将自动按升序排列。
使用一个 map 容器将每个单词与一个 set 容器对象关联起来,该 set 容器对象记录此单词所在的行号。
综上所述,我们定义的 TextQuery 类将有两个数据成员:
1. 储存输入文件的 vector 对象;
2. map 容器对象(其关联每个输入的单词和记录该单词所在行号的 set 容器对象)。
1.2 操作
对于类还要求有良好的接口。
查询函数需返回存储一组行号的 set 对象。这个返回类型应该如何设计呢?
事实上,查询的过程相当简单:使用下标访问 map 对象获取关联的 set 对象即可。
唯一的问题是如何返回所找到的 set 对象。安全的设计方案是返回该 set 对象的副本。
但如此一来,就意味着要复制 set 中的每个元素。
如果处理的是一个相当庞大的文件,则复制 set 对象的代价会非常昂贵。
其他可行的方法包括:
返回一个 pair 对象,存储一对指向 set 中元素的迭代器;或者返回 set 对象的 const 引用。
为简单起见,我们在这里采用返回副本的方法,
但注意:如果在实际应用中复制代价太大,需要新考虑其实现方法。
类的接口需提供下列三个 public 函数:
1. read_file 成员函数,其形参为一个 ifstream& 类型对象。
该函数每次从文件中读入一行,并将它保存在 vector 容器中。
输入完毕后,read_file 将创建关联每个单词及其所在行号的 map 容器。
2. run_query 成员函数,其形参为一个 string 类型对象,返回一个 set 对象,
该 set 对象包含出现该 string 对象的所有行的行号。
3. text_line 成员函数,其形参为一个行号,返回输入文本中该行号对应的文本行。
无论 run_query 还是 text_line 都不会修改调用此函数的对象,
因此,可将这两个操作定义为 const 成员函数。
为实现 read_file 功能,还需定义两个 private 函数来读取输入文本和创建 map 容器:
4. store_file 函数读入文件,并将文件内容存储在 vector 容器对象中。
5. build_map 函数将每一行分解为各个单词,创建 map 容器对象,同时记录每个单词出现的行号。
[2. TextQuery 类]
定义 TextQuery 类的头文件 “ TextQuery.h ” 内容如下:
#ifndef __TEXTQUERY_H__ #define __TEXTQUERY_H__ #include <iostream> #include <istream> #include <fstream> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <set> #include <utility> #include <string> typedef std::vector<std::string>::size_type line_no; class TextQuery { public: // interface: void read_file(std::ifstream &is) { store_file(is); build_map(); } std::set<line_no> run_query(const std::string &) const; std::string text_line(line_no) const; private: // utility functions used by read_file void store_file(std::ifstream&); void build_map(); // associate each word with a set of line numbers // remember the whole input file std::vector<std::string> lines_of_text; // map word to set of the lines on which it occurs std::map< std::string, std::set<line_no> > word_map; }; #endif
注意:这个类的定义中,在引用标准库内容时都必须完整地使用 std:: 限定符。
read_file 函数在类的内部定义。该函数首先调用 store_file 读取并保存输入文件,
然后调用 build_map 创建关联单词与行号的 map 容器。
[3. TextQuery 类的使用]
下面的主程序 main 使用 TextQuery 对象实现简单的用户查询会话。
这段程序的主要工作是实现与用户的互动:
提示输入下一个要查询的单词,然后调用 print_results 函数输出结果。
3.1 引子
程序首先检查 argv[1] 是否合法,然后调用 open_file 函数打开以 main 函数实参形式给出的文件。
检查流以判断输入文件是否正确。
如果不正确,就给出适当的提示信息结束程序的运行,返回 EXIT_FAILURE 说明发生了错误。
一旦文件成功打开,建立支持查询的 map 容器就相当简单。
open_file 函数的实现如下:
// opens in binding it to the given file ifstream& open_file(ifstream &in, const string &file) { in.close(); // close in case it was already open in.clear(); // clear any existing errors // if the open fails, the stream will be in an invalid state in.open(file.c_str()); // open the file we were given return in; // condition state is good if open succeeded }
3.2 实现查询
为了使用户在每次会话时都能查询多个单词,我们将提示语句也置于 while 循环中:
#include "TextQuery.h" define EXIT_FAILURE -1 using namespace std; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { // open the file from which user will quer words ifstream infile; if(argc < 2 || !open_file(infile, argv[1])){ cerr << "No input file!" << endl; return EXIT_FAILURE; } TextQuery tq; tq.read_file(infile); // prompt for a word to file and print result while(true){ cout << "Enter word to look for(or Q/q to Quit): " ; string str; cin >> str; // stop if hit eof on input or a 'Q' is entered if(!cin || str == "Q" || str == "q") break; // get tje set of line numbers on which this word appears set<line_no> locs = tq.run_query(str); // print count an all occurrences, if any print_results(locs, str, tq); } return 0; }
while 循环条件为布尔字面值 true,这就意味着循环条件总是成立。
在检查 cin 和读入 s 值后,由紧跟的 break 语句跳出循环。
具体说来,当 cin 遇到错误或文件结束,或者用户输入 q 时,循环结束。
每次要查找一个单词时,访问 tq 获取记录该单词出现的行号的 set 对象。
将 set 对象、要查找的单词和 TextQuery 对象作为参数传递给 print_results 函数,该函数输出查询结果。
3.3 输出结果
输出时,首先给出查询到的匹配个数,即 set 对象的大小。
然后调用一个 make_plural 函数,根据 size 是否为 1 输出“time”或“times”。
// return plural version of word if ctr isn't 1 string make_plural(size_t ctr, const string &word, const string &ending) { return (ctr == 1) ? word : word + ending; }
void print_results(const set<line_no>& locs, const string& sought, const TextQuery& file) { // if the word was found, then print count and all occurrences typedef set<line_no> line_nums; line_nums::size_type size = locs.size(); cout << " " << sought << " occurs " << size << " " << make_plural(size, "time", "s") << endl; // print each line in which the word appeared line_nums::const_iterator it = locs.begin(); for(; it != locs.end(); ++it){ // don't confound user with text lines starting at 0 cout << " (line" << (*it) +1 << ")" << file.text_line(*it) << endl; } }
以上几个函数定义和实现都放在 main.cpp 文件之中。
注意:为了与 C++ 的容器和数组下标编号匹配,在储存文本时,我们以行号 0 存储第一行。
但考虑到很多用户会默认第一行的行号为 1,所以输出行号时,
相应地所存储的行号上加 1 使之转换为更通用的形式。
[4. 成员方法的实现]
TextQuery 类的成员方法实现 “ TextQuery.cpp” 文件内容如下:
#include "TextQuery.h" #include <stdexcept> #include <sstream> using namespace std; set<line_no> TextQuery::run_query(const string &query_word) const { // must use find and not subscript he map directly // to avoid adding words to word_map map< string, set<line_no> >::const_iterator loc = word_map.find(query_word); if(loc == word_map.end()){ // not found, return empty set return set<line_no>(); } else{ // fectch and return set of line numbers for this word return loc->second; } } string TextQuery::text_line(line_no line) const { if(line < lines_of_text.size()) return lines_of_text[line]; throw std::out_of_range("line number out of range"); } // utility functions used by read_file void TextQuery::store_file(ifstream &is) { string textline; while (getline(is, textline)) lines_of_text.push_back(textline); } // associate each word with a set of line numbers void TextQuery::build_map() { // process each line from the input vector for (line_no line_num = 0; line_num != lines_of_text.size(); ++line_num) { // we'll use line to read the text a word at a time istringstream line(lines_of_text[line_num]); string word; while (line >> word){ // add this line number to the set; // subscript will add word to the map if it's not already there word_map[word].insert(line_num); } } }
[5. 编译运行]
之前一直是用 CFree5.0 做的《C++ Primer 4th》的练习,
但是由于没找到怎么手动添加参数运行程序,
>_<|||...有知道怎么搞的,还望不吝赐教。
没办法最后选了在 cygwin 下编译,命令如下:
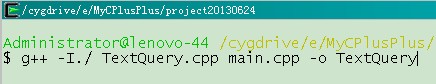
编译成功后,文件如下:
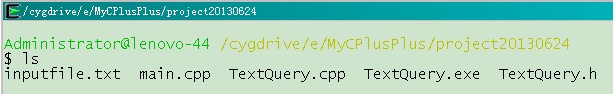
运行,命令如下:
结果显示如下:
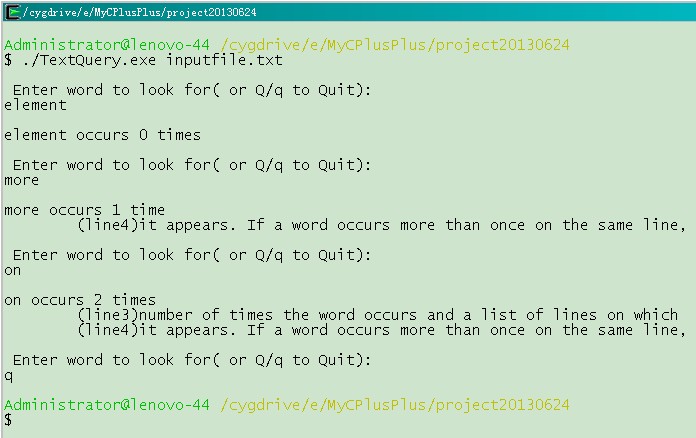
根据运行结果观察,应该是实现了预期的程序功能。O(∩_∩)O 哈哈~