Statement执行更新操作
Statement:Statement 是 Java 执行数据库操作的一个重要方法,用于在已经建立数据库连接的基础上,向数据库发送要执行的SQL语句。Statement对象,用于执行不带参数的简单SQL语句。
通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录,需要注意下面的几点:
* 1.Statement:用于执行SQL语句的对象
* 1).通过COnnection的createStatement()方法来获取
* 2).通过excuteUpdate(sql)可以执行SQL语句
* 3).传入的SQL可以是insert,update或者delete,但是不能是select
* 2.Connection、Statement都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接 资源,使用后一定要关闭
* 需要在finally中关闭Connection和Statement对象
* 异常可以不处理,但是连接一定要关闭
* 3.关闭的顺序:先关闭后获取的,即先关闭Statement,后关闭Connection
具体的代码实现:
public void testStatement() throws Exception{
//1.获取数据库连接
// Connection conn=getConnection();
Connection conn=null;
//4.执行插入
//1).获取操作SQL语句的Statement对象:调用Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
//注意Statement这里是java.sql包中的,而不是java.mysql.jdbc中的
// Statement statement=conn.createStatement();
Statement statement=null;
try {
//3.准备插入的SQL语句
conn=getConnection();
String sql=null;
//sql的插入操作
// sql="insert into customers(NAME,email,birth) values('xyz','xyz@atguigu.com','1988-7-1')";
//删除操作
// sql="delete from customers where id =1";
//修改操作
sql="update customers set name='Tom' where id =2";
statement = conn.createStatement();
//2).调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql),执行SQL语句进行插入
statement.execute(sql);
//5.关闭Statement对象
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 2.关闭连接
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}
}
}
【提示】:代码中的getConnction方法是在笔记一中定义的,可以看到我们可以对数据库中的记录进行插入(insert),更新(update),删除(delete)操作,使用Connection对象的createStatement( )方法创建一个statement对象,并且调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql),执行SQL语句进行插入;
我们的getConnection方法和关闭statement以及conn的操作稍显复杂,我们可以定义一个工具类,里面包含一些通用的方法,实现我们的插入、删除、更新数据的操作
具体代码:
public class JDBCTools {
// 关闭conn和statement的操作
public static void release(Statement statement, Connection conn) {
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 1。获取连接的方法 通过读取配置文件从数据库服务器获取一个连接
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
String driverClass = null;
String jdbcUrl = null;
String user = null;
String password = null;
// 读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
InputStream in = JDBCTools.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(
"jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 通过反射创建Driver对象
Driver driver = (Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
Properties info = new Properties();
info.put("user", user);
info.put("password", password);
Connection connection = driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
return connection;
}
}
我们更新数据的操作可以写成这样:这里update就是这个通用的方法;
public void update(String sql){
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement=null;
try {
//用到了我们写的一个工具类JDBCTools
conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
statement=conn.createStatement();
statement.execute(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(statement, conn);
}
}
传入不同的sql,执行相应的操作;
通过ResultSet执行查询操作
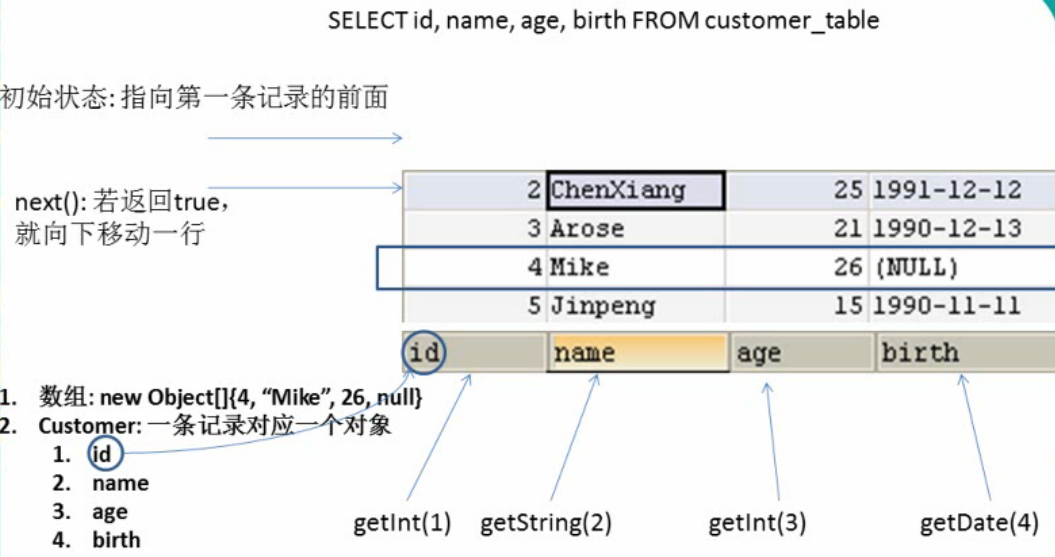
ResultSet:
/**
* ResultSet:结果集,封装了使用JDBC进行查询的结果
* 1.调用Statement对象的excuteQuery(sql)方法可以得到结果集
* 2.ResultSet返回的实际上就是一张数据表,有一个指针
* 指向数据表的第一样的前面,可以调用next()方法检测下一行是否有效,若有效则返回true
* ,并且指针下移,相当于迭代器对象的hasNext()和next()的结合体
* 3.当指针对位到确定的一行时,可以通过调用getXxx(index)或者getXxx(columnName)
* 获取每一列的值,例如:getInt(1),getString("name")
* 4.ResultSet当然也需要进行关闭
*/
ResultSet的返回结果:

具体的代码实现:
@Test
public void testResultSet(){
//获取id=2的customers数据表的记录,并打印
//面向接口的编程
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
//1.获取Connection
conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
//2.获取Statement
statement=conn.createStatement();
System.out.println(statement);
//3.准备SQL
String sql="select id,name,email,birth from customers";
//4.执行查询,得到ResultSet
rs=statement.executeQuery(sql);
System.out.println(rs);
//5.处理ResultSet
while(rs.next()){
int id=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString("name");
String email=rs.getString(3);
Date birth=rs.getDate(4);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(email);
System.out.println(birth);
System.out.println("--------------");
}
//6.关闭数据库资源
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(rs, statement, conn);
}
}
到目前为止的完整代码:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
//JDBC学习
public class JDBCTest {
/**
* ResultSet:结果集,封装了使用JDBC进行查询的结果
* 1.调用Statement对象的excuteQuery(sql)方法可以得到结果集
* 2.ResultSet返回的实际上就是一张数据表,有一个指针
* 指向数据表的第一样的前面,可以调用next()方法检测下一行是否有效,若有效则返回true
* ,并且指针下移,相当于迭代器对象的hasNext()和next()的结合体
* 3.当指针对位到确定的一行时,可以通过调用getXxx(index)或者getXxx(columnName)
* 获取每一列的值,例如:getInt(1),getString("name")
* 4.ResultSet当然也需要进行关闭
*/
@Test
public void testResultSet(){
//获取id=2的customers数据表的记录,并打印
//面向接口的编程
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
//1.获取Connection
conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
System.out.println(conn);
//2.获取Statement
statement=conn.createStatement();
System.out.println(statement);
//3.准备SQL
String sql="select id,name,email,birth from customers";
//4.执行查询,得到ResultSet
rs=statement.executeQuery(sql);
System.out.println(rs);
//5.处理ResultSet
while(rs.next()){
int id=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString("name");
String email=rs.getString(3);
Date birth=rs.getDate(4);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(email);
System.out.println(birth);
System.out.println("--------------");
}
//6.关闭数据库资源
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(rs, statement, conn);
}
}
/**
* 通用的更新的方法:包括insert,update,delete
* 版本1.
*/
/*public void update(String sql){
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement=null;
try {
//用到了我们写的一个工具类JDBCTools
conn=JDBCTools.getConnection();
statement=conn.createStatement();
statement.execute(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(statement, conn);
}
}*/
/*
* 通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录
* 我这里用的是图形化界面SQLyog
* SQLyog图形化界面连接mysql数据库,注册码:
* 这个可用【我用了还是可以】
Name:BAKA!
Code:560f17bf57745cf9
*/
/**
* 通过JDBC向指定的数据表中插入一条记录
* 1.Statement:用于执行SQL语句的对象
* 1).通过COnnection的createStatement()方法来获取
* 2).通过excuteUpdate(sql)可以执行SQL语句
* 3).传入的SQL可以是insert,update或者delete,但是不能是select
* 2.Connection、Statement都是应用程序和数据库服务器的连接资源,使用
* 后一定要关闭
* 需要在finally中关闭Connection和Statement对象
* 异常可以不处理,但是连接一定要关闭
* 3.关闭的顺序:先关闭后获取的,即先关闭Statement,后关闭Connection
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testStatement() throws Exception{
//1.获取数据库连接
// Connection conn=getConnection();
Connection conn=null;
//4.执行插入
//1).获取操作SQL语句的Statement对象:调用Connection的createStatement()方法来获取
//注意Statement这里是java.sql包中的,而不是java.mysql.jdbc中的
// Statement statement=conn.createStatement();
Statement statement=null;
try {
//3.准备插入的SQL语句
conn=getConnection();
String sql=null;
//sql的插入操作
// sql="insert into customers(NAME,email,birth) values('xyz','xyz@atguigu.com','1988-7-1')";
//删除操作
// sql="delete from customers where id =1";
//修改操作
sql="update customers set name='Tom' where id =2";
statement = conn.createStatement();
//2).调用Statement对象的excuteUpdate(sql),执行SQL语句进行插入
statement.execute(sql);
//5.关闭Statement对象
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 2.关闭连接
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}
}
}
public Connection testGetConnection2() throws Exception{
//1.准备连接数据库的四个字符串
//1).创建Properties对象
Properties properties=new Properties();
//2).获取jdbc.properties对应的输入流
InputStream in=this.getClass().
getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
//3).加载2)对应的输入流
properties.load(in);
//4).具体决定user,password等四个字符串
String user=properties.getProperty("user");
String jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
String password=properties.getProperty("password");
String driver=properties.getProperty("driver");
//2.加载数据库驱动程序(对应的Driver实现类中注册驱动的静态代码块)
Class.forName(driver);
//3.通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
return DriverManager.getConnection(jdbcUrl,user,password);
}
/**
* DriverManager是驱动的管理类
* 1).可以通过重载的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接,较为方便
* 2).可以同时管理多个驱动程序:若注册了多个数据库连接
* ,则调用getConnection()方法时传入的参数不同,即返回不同的数据库连接
* @throws Exception
*/
public void testDriverManager() throws Exception{
//1.准备连接数据库的四个字符串
//驱动的全类名
String driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
//url
String jdbcUrl="dbc:mysql://localhost:3306/atguigu";
//user
String user="root";
//password
String password="123456";
//读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
InputStream in=getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass=properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user=properties.getProperty("user");
//2.加载数据库驱动程序(对应的Driver实现类中注册驱动的静态代码块)
/*
*使用Drivermanager的好处:可以加载多个驱动
DriverManager
.registerDriver(Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance());
*
*/
Class.forName(driverClass);
password=properties.getProperty("password");
//3.通过DriverManager的getConnection()方法获取数据库连接
Connection connection=DriverManager
.getConnection(jdbcUrl, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
}
/**
* Driver是一个接口,数据库厂商必须提供实现的接口
* 能从其中获取数据库连接,可以通过Driver的实现类的对象获取连接
* 1.加入mysql驱动
* 1).解压mysql-connector-java-5.1.18.zip
* 2).在当前目录下新建lib目录
* 3).把mysql-connector-java-5.1.18-bin.jar复制到lib目录
* 4).右键->build-path->add build path加载到类路径下
* @throws SQLException
*
*/
/*
* MySQL附带了一个空密码有的root用户。成功后安装了数据库和客户端,需要进行如下设置root密码:
D:softwaremysql-5.6.25-winx64in> mysqladmin -u root password "123456";
注:
1. 关闭正在运行的MySQL服务。
2. 打开DOS窗口,转到 D:softwaremysql-5.6.25-winx64in 目录。
3. 输入mysqld --skip-grant-tables 回车。--skip-grant-tables 的意思是启动MySQL服务的时候跳过权限表认证。
4. 再开一个DOS窗口(因为刚才那个DOS窗口已经不能动了),转到mysqlin目录。
5. 输入mysql回车,如果成功,将出现MySQL提示符 >。
6. 连接权限数据库: use mysql; 。
6. 改密码:update user set password=password("123456") where user="root";(别忘了最后加分号) 。
7. 刷新权限(必须步骤):flush privileges;
8. 退出 quit。
9. 注销系统,再进入,使用用户名root和刚才设置的新密码 123456 登录。
现在使MySQL服务器的连接,那么使用下面的命令:
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1.创建一个Driver实现类的对象
Driver driver=new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
/*
* JDBC URL的标准由三部分组成
* jdbc:<子协议>:<子名称>
* 1).协议:JDBC URL中的协议总是JDBC
* 2).子协议:子协议用于标识一个数据库驱动程序
* 3).紫明成:一种标识数据库的方法。子名称可以一句不同的
* 子协议而变化,用子名称的目的是为了定位数据库提供足够的信息
* 例如:jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/test【这是我的主机上的,你的不一定】
* 查看端口号:在mysql后面输入show global variables like 'port';别写错了,切记别忘记写英文状态下的分号
*/
//2.准备连接数据库的基本信息,url,user,password
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
Properties info=new Properties();
info.put("user", "root");
info.put("password", "123456");
//3.调用Driver接口实现类对象的connect(url,info)方法获取数据库的连接
//此处Connection是一个接口,java.sql包下的接口
Connection connection=driver.connect(url, info);
System.out.println(connection);
}
/**
* 编写一个通用的方法,在不修改源程序的情况下,可以获取任何数据库的连接
* 解决方案:把数据库驱动Driver实现类的全类名、url、user、password
* 放入一个配置文件中,通过修改配置文件的方法实现和具体的数据库解耦
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @throws IllegalAccessException
* @throws InstantiationException
*/
public Connection getConnection() throws Exception{
String driverClass=null;
String jdbcUrl=null;
String user=null;
String password=null;
//读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
InputStream in=getClass().getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties=new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass=properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl=properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user=properties.getProperty("user");
password=properties.getProperty("password");
//通过反射创建Driver对象
Driver driver=(Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
Properties info=new Properties();
info.put("user", user);
info.put("password", password);
Connection connection=driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
return connection;
}
@Test
public void testGetConnection() throws Exception{
System.out.println(getConnection());
}
}
JDBCTools:
package com.atguigu.jdbc;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Properties;
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver;
/**
* 操作JDBC的工具类,其中封装了一些工具方法
* Version 1
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class JDBCTools {
// 关闭conn和statement的操作
public static void release(ResultSet rs,Statement statement, Connection conn) {
if(rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 1。获取连接的方法 通过读取配置文件从数据库服务器获取一个连接
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
String driverClass = null;
String jdbcUrl = null;
String user = null;
String password = null;
// 读取类路径下的jdbc.properties文件
InputStream in = JDBCTools.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(
"jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driver");
jdbcUrl = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
user = properties.getProperty("user");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
// 通过反射创建Driver对象
Driver driver = (Driver) Class.forName(driverClass).newInstance();
Properties info = new Properties();
info.put("user", user);
info.put("password", password);
Connection connection = driver.connect(jdbcUrl, info);
return connection;
}
}
本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/
1、本博客的原创原创文章,都是本人平时学习所做的笔记,如有错误,欢迎指正。
2、如有侵犯您的知识产权和版权问题,请通知本人,本人会即时做出处理文章。
3、本博客的目的是知识交流所用,转载自其它博客或网站,作为自己的参考资料的,感谢这些文章的原创人员