Something happened in Uzhlyandia again... There are riots on the streets... Famous Uzhlyandian superheroes Shean the Sheep and Stas the Giraffe were called in order to save the situation. Upon the arriving, they found that citizens are worried about maximum values of the Main Uzhlyandian Function f, which is defined as follows:
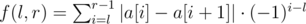
In the above formula, 1 ≤ l < r ≤ n must hold, where n is the size of the Main Uzhlyandian Array a, and |x| means absolute value of x. But the heroes skipped their math lessons in school, so they asked you for help. Help them calculate the maximum value of f among all possible values of l and r for the given array a.
The first line contains single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the size of the array a.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (-109 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the array elements.
Print the only integer — the maximum value of f.
5
1 4 2 3 1
3
4
1 5 4 7
6
In the first sample case, the optimal value of f is reached on intervals [1, 2] and [2, 5].
In the second case maximal value of f is reachable only on the whole array.
#include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std; typedef long long LL; const LL N = 1e5 + 10; LL num[N], dp1[N], dp2[N]; int main() { LL n, m, i; cin >> n; for(i = 1; i <= n; i++) { scanf("%lld", &num[i]); if(i > 1) dp2[i - 1] = dp1[i - 1] = abs(num[i] - num[i - 1]); } for(i = 1; i < n; i++) { if(i % 2 == 0) dp1[i] *= -1; else dp2[i] *= -1; } LL sum = 0, ans = dp1[1]; for(i = 1; i < n; i++) { sum += dp1[i]; if(sum < 0) sum = 0; else if(sum > ans) ans = sum; } sum = 0; for(i = 1; i < n; i++) { sum += dp2[i]; if(sum < 0) sum = 0; else if(sum > ans) ans = sum; } printf("%lld ", ans); return 0; }