20172332 2017-2018-2 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
第十一章 二叉查找树
- 1.二叉查找树:一种带有附加属性的二叉树。即每个结点其左孩子都要小于其父结点,而父结点又小于或等于其右孩子。(左孩子<父结点<=右孩子)
- 2.二叉查找树不仅具有二叉树的操作,还具有以下的特殊操作:
- 3.用链表实现二叉查找树:每个BinaryTreeNode对象要维护一个指向结点所存储元素的引用,另外还要维护指向结点的每个孩子的引用。
- 4.二叉查找树的构造函数代码(引用了父类的两个构造函数):
public LinkedBinarySearchTree()
{
super();
}
public LinkedBinarySearchTree(T element)
{
super(element);
if (!(element instanceof Comparable))
throw new NonComparableElementException("LinkedBinarySearchTree");
}
- 5.addElement操作:
①如果这个元素不是Comparable,则该方法会抛出NoComparableElementException异常;
②如果树为空,则这个新元素成为根结点;
③如果树非空,这个新元素会与树根元素进行比较,- (1)如果小于根结点中存储的元素且根的左孩子为null,则这个元素成为根的左孩子。
- (2)如果这个新元素小于根结点中存储的那个元素且根的左孩子不是null,则会遍历根的左孩子并再次进行比较操作。
- (3)如果这个新元素大于或等于树根存储的那个元素且根的右孩子为null,则这个新元素会成为根的右孩子。
- (4)如果这个新元素大于或等于树根处存储的那个元素且根的右孩子不是null,则会遍历根的右孩子,并再次进行比较操作。
- 代码实现:
public void addElement(T element)
{
if (!(element instanceof Comparable))
throw new NonComparableElementException("LinkedBinarySearchTree");
Comparable<T> comparableElement = (Comparable<T>)element;
if (isEmpty())
root = new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element);
else
{
if (comparableElement.compareTo(root.getElement()) < 0)
{
if (root.getLeft() == null)
this.getRootNode().setLeft(new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element));
else
addElement(element, root.getLeft());
}
else
{
if (root.getRight() == null)
this.getRootNode().setRight(new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element));
else
addElement(element, root.getRight());
}
}
modCount++;
}
private void addElement(T element, BinaryTreeNode<T> node)
{
Comparable<T> comparableElement = (Comparable<T>)element;
if (comparableElement.compareTo(node.getElement()) < 0)
{
if (node.getLeft() == null)
node.setLeft(new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element));
else
addElement(element, node.getLeft());
}
else
{
if (node.getRight() == null)
node.setRight(new BinaryTreeNode<T>(element));
else
addElement(element, node.getRight());
}
}
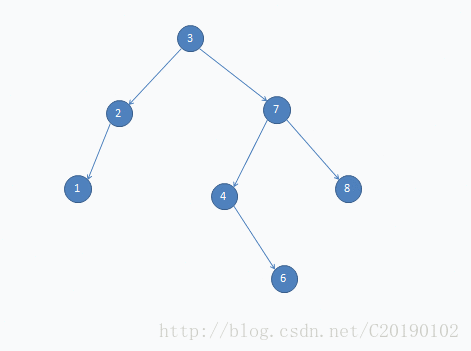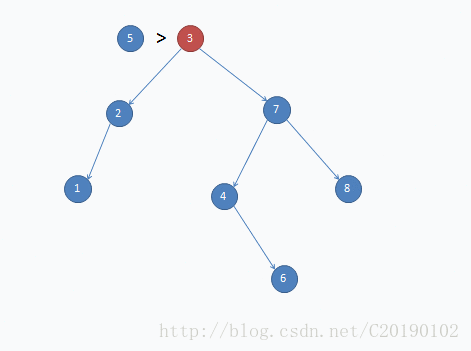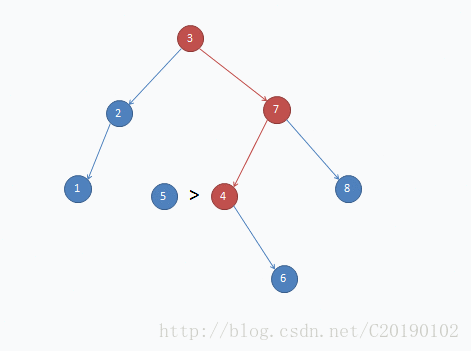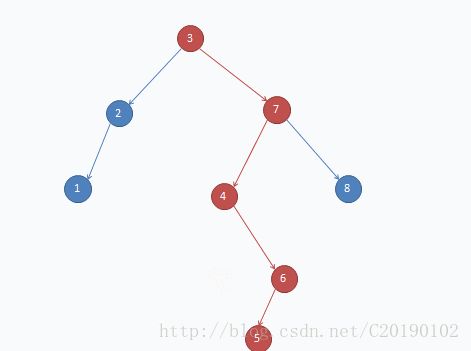
- 6.removeElement操作:(必须推选出另一个结点来代替要被删除的那个结点)
①找不到给定目标元素时,抛出ElementNotFoundException异常。
②如果被删除结点没有孩子,则replacement返回null。
③如果被删除结点只有一个孩子,则replacement返回这个孩子。
④如果被删除结点有两个孩子,则replacement会返回中序后继者(因为相等元素会放到右边) - 代码实现:
public T removeElement(T targetElement) throws ElementNotFoundException
{
T result = null;
if (isEmpty())
throw new ElementNotFoundException("LinkedBinarySearchTree");
else
{
BinaryTreeNode<T> parent = null;
if (((Comparable<T>)targetElement).equals(root.element))
{
result = root.element;
BinaryTreeNode<T> temp = replacement(root);
if (temp == null)
root = null;
else
{
root.element = temp.element;
root.setRight(temp.right);
root.setLeft(temp.left);
}
modCount--;
}
else
{
parent = root;
if (((Comparable)targetElement).compareTo(root.element) < 0)
result = removeElement(targetElement, root.getLeft(), parent);
else
result = removeElement(targetElement, root.getRight(), parent);
}
}
return result;
}
private T removeElement(T targetElement, BinaryTreeNode<T> node, BinaryTreeNode<T> parent) throws ElementNotFoundException
{
T result = null;
if (node == null)
throw new ElementNotFoundException("LinkedBinarySearchTree");
else
{
if (((Comparable<T>)targetElement).equals(node.element))
{
result = node.element;
BinaryTreeNode<T> temp = replacement(node);
if (parent.right == node)
parent.right = temp;
else
parent.left = temp;
modCount--;
}
else
{
parent = node;
if (((Comparable)targetElement).compareTo(node.element) < 0)
result = removeElement(targetElement, node.getLeft(), parent);
else
result = removeElement(targetElement, node.getRight(), parent);
}
}
return result;
}
private BinaryTreeNode<T> replacement(BinaryTreeNode<T> node)
{
BinaryTreeNode<T> result = null;
if ((node.left == null) && (node.right == null))
result = null;
else if ((node.left != null) && (node.right == null))
result = node.left;
else if ((node.left == null) && (node.right != null))
result = node.right;
else
{
BinaryTreeNode<T> current = node.right;
BinaryTreeNode<T> parent = node;
while (current.left != null)
{
parent = current;
current = current.left;
}
current.left = node.left;
if (node.right != current)
{
parent.left = current.right;
current.right = node.right;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
- 7.removeAllOccurrences操作:(使用了contains方法,find方法被重载以便利用二叉查找树的有序属性。)
①当在树中找不到指定元素时,则抛出ElementNotFoundException异常
②如果指定的元素不是Comparable,则该方法也会抛出ClassCastException异常。
③只要树中还含有目标元素,就会再次调用removeElement方法。 - 代码实现:
public void removeAllOccurrences(T targetElement)
throws ElementNotFoundException
{
removeElement(targetElement);
try
{
while (contains((T)targetElement))
removeElement(targetElement);
}
catch (Exception ElementNotFoundException)
{
}
}
- 8.removeMin操作:
①如果树根没有左孩子,则树根就是最小元素,而树根的右孩子会变成新的根结点。
②如果树的最左侧结点是一片叶子,则这片叶子就是最小元素,这时只需设置其父结点的左孩子引用为null即可。
③如果树的最左侧结点是一个内部结点,则需要设置其父结点的左孩子引用指向这个将删除结点的右孩子。 - 代码实现:
public T removeMin() throws EmptyCollectionException
{
T result = null;
if (isEmpty())
throw new EmptyCollectionException("LinkedBinarySearchTree");
else
{
if (root.left == null)
{
result = root.element;
root = root.right;
}
else
{
BinaryTreeNode<T> parent = root;
BinaryTreeNode<T> current = root.left;
while (current.left != null)
{
parent = current;
current = current.left;
}
result = current.element;
parent.left = current.right;
}
modCount--;
}
return result;
}
- 9.用有序列表实现二叉查找树:实现ListADT接口和OrderedListADT接口。
- 10.BinarySearchTreeList实现的分析:add操作与remove操作都要求重新平衡化树。
- 11.树实现中的有些操作更为有效,有些操作更为低效。
- 12.蜕化树:无分支的树(效率比链表还低)
- 13.平衡树的方法:
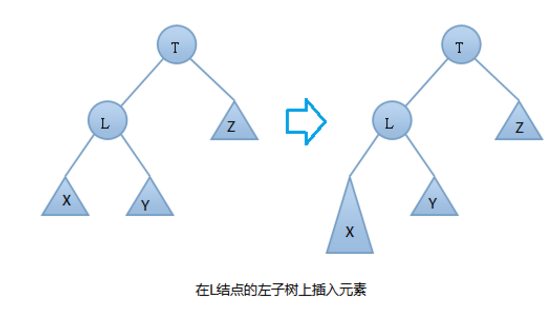
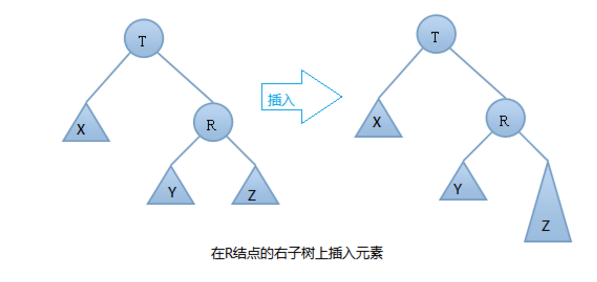
- (1)右旋(左子树长):①使树根的左孩子元素成为新的根元素。②使原根元素成为这个新树根的右孩子元素。③使原树根的左孩子的右孩子,成为原树根的新的左孩子。
- (2)左旋(右子树长):①使树根的右孩子元素成为新的根元素。②使原根元素成为这个新树根的左孩子元素。③使原树根右孩子结点的左孩子,成为原树根的新的右孩子。
- (3)右左旋(树根右孩子的左子树长):①让树根右孩子的左孩子,绕着树根的右孩子进行一次右旋。②让所得的树根右孩子绕着树根进行一次左旋。
- (4)左右旋(树根左孩子的右子树长):①让树根左孩子的右孩子绕着树根的左孩子进行一次左旋。②让所得的树根左孩子绕着树根进行一次右旋。
- 14.实现二叉查找树:①AVL树。②红黑树。(自树根而下的路径最大长度必须不超过log2 n,而且自树根而下的路径最小长度必须不小于log2 n -1)
- 15.平衡因子:右子树的高度减去左子树的高度
- 16.使树变得不平衡有两种方法:①插入结点。②删除结点。
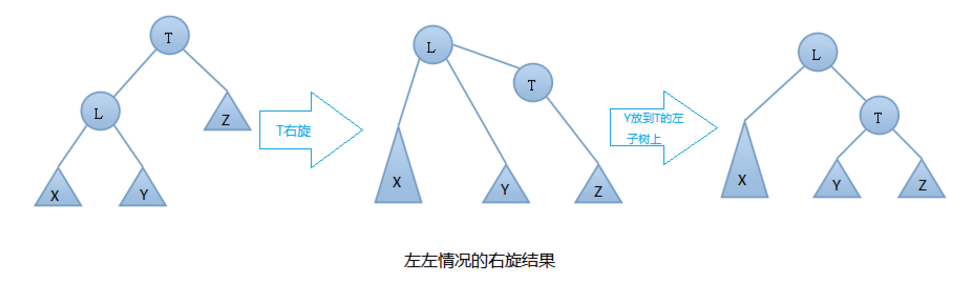
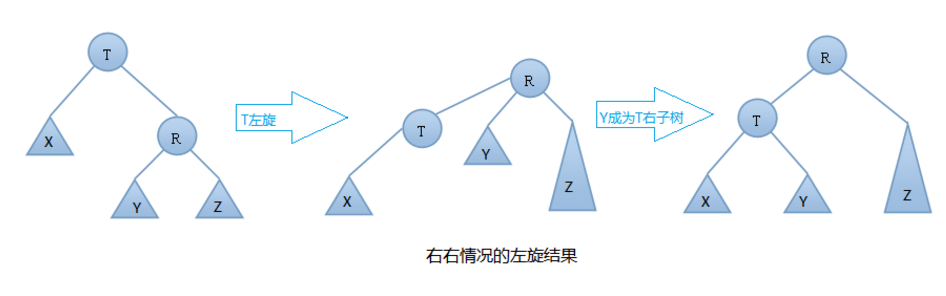
- 17.AVL树的右旋:由下图可知我们是在结点T的左结点的左子树上做了插入元素的操作,我们称这种情况为左左情况,我们应该进行右旋转(只需旋转一次,故是单旋转)【步骤与右旋步骤一样】
- 过程:
- 18.AVL树的左旋:由下图可知我们是在结点T的右结点的右子树上做了插入元素的操作,我们称这种情况为右右情况,我们应该进行左旋转(只需旋转一次,故是单旋转)【步骤与左旋步骤一样】
- 过程:
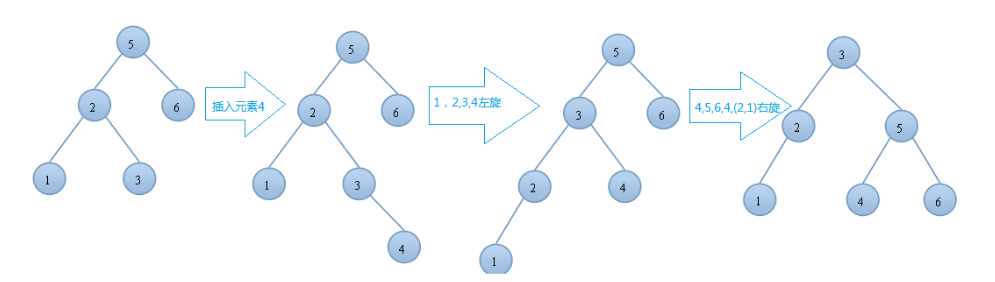
- 19.AVL树的左右(先左后右)旋:如下图,只是单纯的进行一次旋转,得到的树仍然是不平衡的。所以应该进行二次旋转。
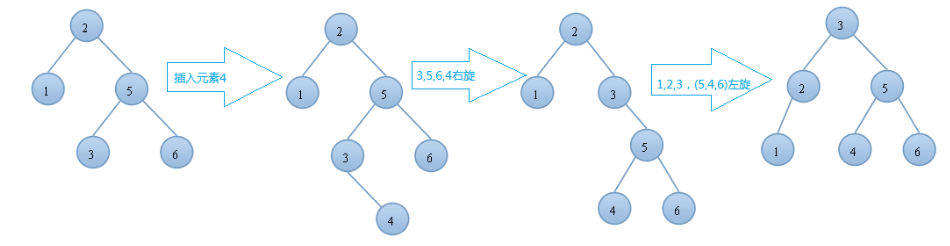
- 20.AVL树的右左(先右后左)旋:如下图,只是单纯的进行一次旋转,得到的树仍然是不平衡的。所以应该进行二次旋转。
-
21.红黑树:每个结点存出一种颜色(红色或黑色,通常用一个布尔值来实现,false等价于红色)
- 红黑树的特性:
- (1) 每个节点或者是黑色,或者是红色。
- (2) 根节点是黑色。
- (3) 每个叶子节点是黑色。 [注意:这里叶子节点,是指为空的叶子节点!]
- (4) 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的。
- (5) 从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点。
-
22.红黑树的元素添加及删除。
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:replacement会返回中序后继者的中序后继者是什么东西?
- 问题1解决方案:从被删除的结点出发经过它的右结点,然后右结点最左边的叶子结点就是中序后继结点。
public Node getSuccessor(Node delNode){ //参数为被删除的节点
//定义一个当前节点的引用,直接让往下走一步,走到被删除节点的右节点
Node curr=delNode.right;
Node successor=curr; //用来指向中级后续节点
Node sucParent=null; //用来指向中级后续节点的父节点
while(curr!=null){
sucParent=successor;
successor=curr;
curr=curr.left;
}
//循环停止,中级后续节点被找出
if(successor!=delNode.right){
//将后继节点的子节点(只可能有右节点)替补到后继节点的位置上
sucParent.left=successor.right;
//将被删除的右孩子连接到后继节点的右节点上
successor.right=delNode.right;
//将被删除的左孩子连接到后继节点的右节点上(就是用后继节点替换掉被删除的节点)
}
return successor;
}
-
问题引申:为什么要找中序后继者作为代替删除结点的位置。
-
问题引申解决方案:如果直接删结点,整个树的大小顺序就乱了,所以需要考虑,在树中找到一个合适的节点来把这个结点给替换掉,用这种方法来保持整个树的稳定。需要在树中找出所有比被删除节点的值大的所有数,并在这些数中找出一个最小的数来。
-
问题2:AVL树的作用。
-
问题2解决方案:删除时树的平衡性受到破坏,提高它的操作的时间复杂度。而AVL树就不会出现这种情况,树的高度始终是O(lgN).高度越小,对树的一些基本操作的时间复杂度就会越小。
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
- 问题1:红黑树的元素添加。
- 问题1解决方案:
- 步骤1:将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点插入。
- 步骤2:将插入的节点着色为"红色"。
- 步骤3:通过一系列的旋转或着色等操作,使之重新成为一颗红黑树。
private void insert(RBTNode<T> node) {
int cmp;
RBTNode<T> y = null;
RBTNode<T> x = this.mRoot;
// 1. 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中。
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
node.parent = y;
if (y!=null) {
cmp = node.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = node;
else
y.right = node;
} else {
this.mRoot = node;
}
// 2. 设置节点的颜色为红色
node.color = RED;
// 3. 将它重新修正为一颗二叉查找树
insertFixUp(node);
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
public void insert(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node=new RBTNode<T>(key,BLACK,null,null,null);
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if (node != null)
insert(node);
}
- 问题2:红黑树的元素删除。
- 问题2解决方案:
- 步骤1:将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点删除。
- 步骤2:通过"旋转和重新着色"等一系列来修正该树,使之重新成为一棵红黑树。
/*
* 删除结点(node),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* node 删除的结点
*/
private void remove(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> child, parent;
boolean color;
// 被删除节点的"左右孩子都不为空"的情况。
if ( (node.left!=null) && (node.right!=null) ) {
// 被删节点的后继节点。(称为"取代节点")
// 用它来取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将"被删节点"去掉。
RBTNode<T> replace = node;
// 获取后继节点
replace = replace.right;
while (replace.left != null)
replace = replace.left;
// "node节点"不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父节点)
if (parentOf(node)!=null) {
if (parentOf(node).left == node)
parentOf(node).left = replace;
else
parentOf(node).right = replace;
} else {
// "node节点"是根节点,更新根节点。
this.mRoot = replace;
}
// child是"取代节点"的右孩子,也是需要"调整的节点"。
// "取代节点"肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点。
child = replace.right;
parent = parentOf(replace);
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = colorOf(replace);
// "被删除节点"是"它的后继节点的父节点"
if (parent == node) {
parent = replace;
} else {
// child不为空
if (child!=null)
setParent(child, parent);
parent.left = child;
replace.right = node.right;
setParent(node.right, replace);
}
replace.parent = node.parent;
replace.color = node.color;
replace.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
return ;
}
if (node.left !=null) {
child = node.left;
} else {
child = node.right;
}
parent = node.parent;
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = node.color;
if (child!=null)
child.parent = parent;
// "node节点"不是根节点
if (parent!=null) {
if (parent.left == node)
parent.left = child;
else
parent.right = child;
} else {
this.mRoot = child;
}
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 红黑树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
public void remove(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node;
if ((node = search(mRoot, key)) != null)
remove(node);
}
- 问题3:按着书上讲的左旋右旋步骤来做,会出现错误
- 问题3解决方案:
- 问题代码的过程为下图,很显然出现了覆盖结点,导致丢失结点的问题。
- 改正:
- 过程:
代码托管
上周考试错题总结
- 无。
点评过的同学博客和代码
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
- 查找二叉树是二叉树的引申学习,难度真的很大!
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 0/0 | 1/1 | 2/2 | |
| 第二周 | 1010/1010 | 1/2 | 10/12 | |
| 第三周 | 651/1661 | 1/3 | 13/25 | |
| 第四周 | 2205/3866 | 1/4 | 15/40 | |
| 第五周 | 967/4833 | 2/6 | 22/62 | |
| 第六周 | 1680/6513 | 1/7 | 34/96 | |
| 第七周 | 2196/8709 | 1/8 | 35/131 |
-
计划学习时间:30小时
-
实际学习时间:35小时
-
改进情况:AVL树和红黑树真的耗费了大量的时间!